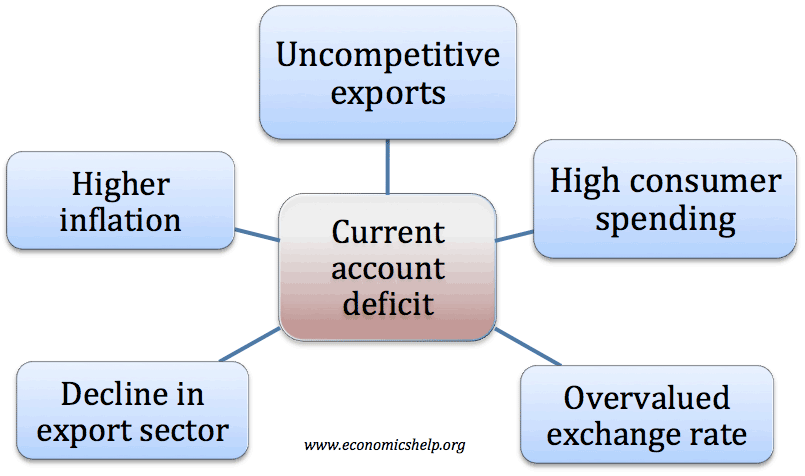
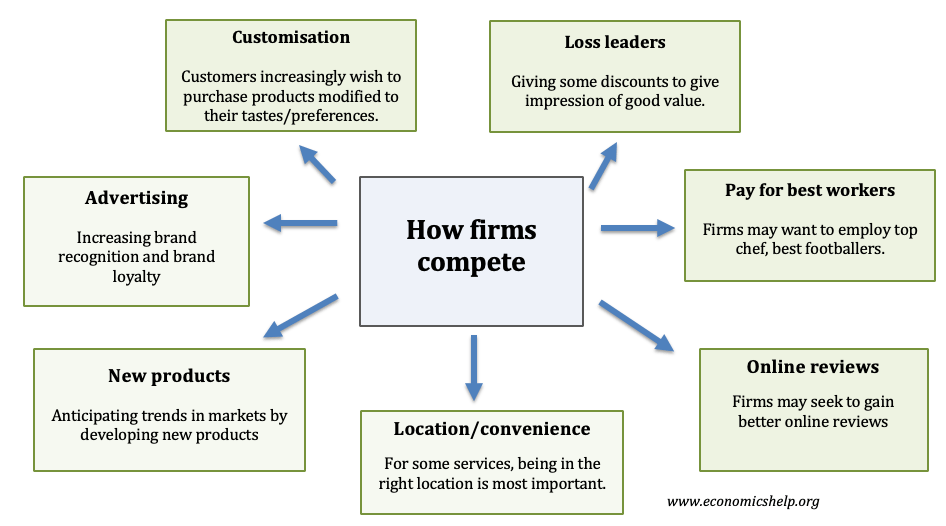
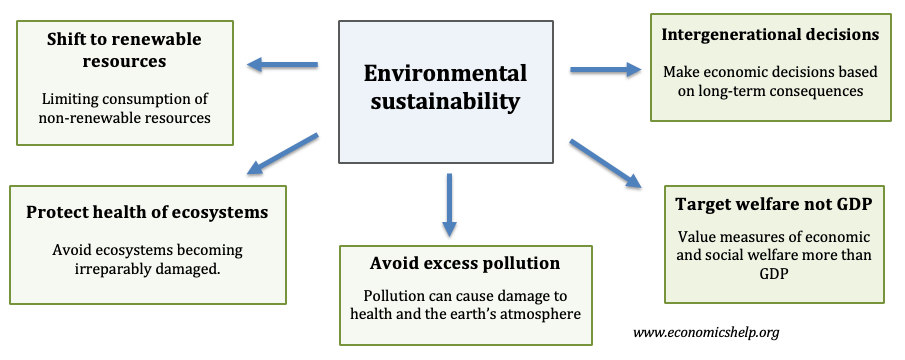
Challenges facing Chinese economy
For the past 40 years, China has been one of the strongest performing economies – transforming itself from a developing economy to an unprecedented level of prosperity. However, in recent years, there have been concerns the rapid rate of growth in China is beginning to slow down and over the next few years, economic challenges …