- Definition of Household savings ratio: The percentage of disposable income that is saved. (1)
- Total savings = Disposable income – Household consumption
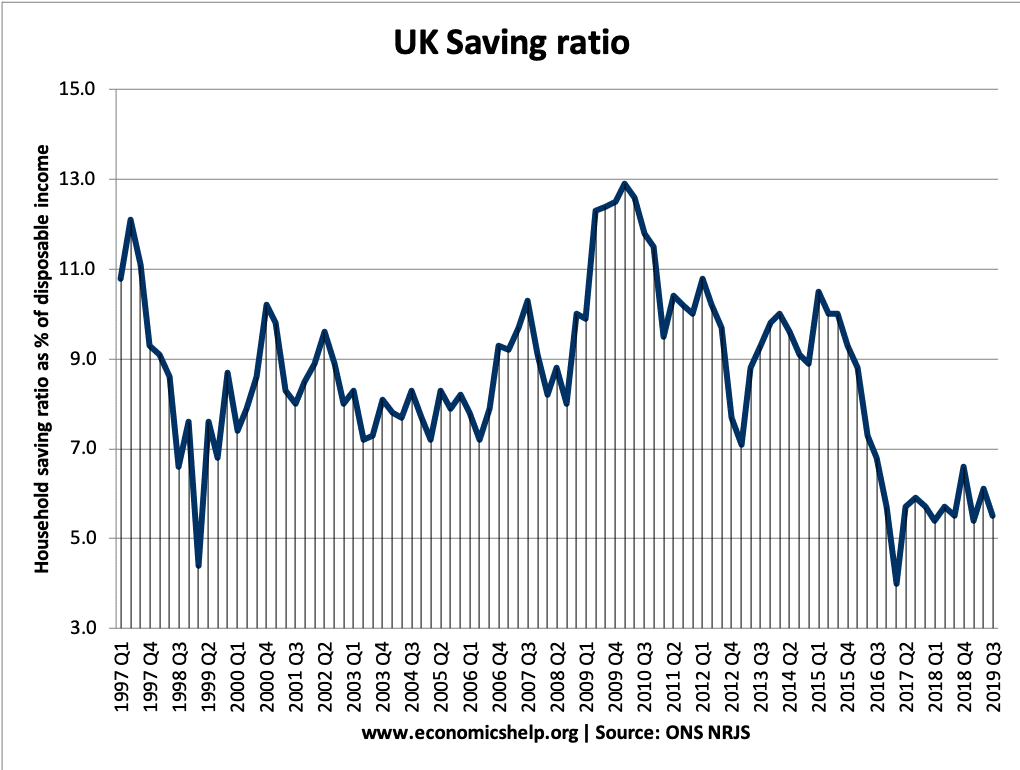
UK Saving Ratio
- Latest UK household savings ratio: 2021 = 10% But, by 2021 Q4 the saving ratio had fallen to 6.2%
- By contrast, the average savings ratio in the past 54 years is 9.2% of disposable income.
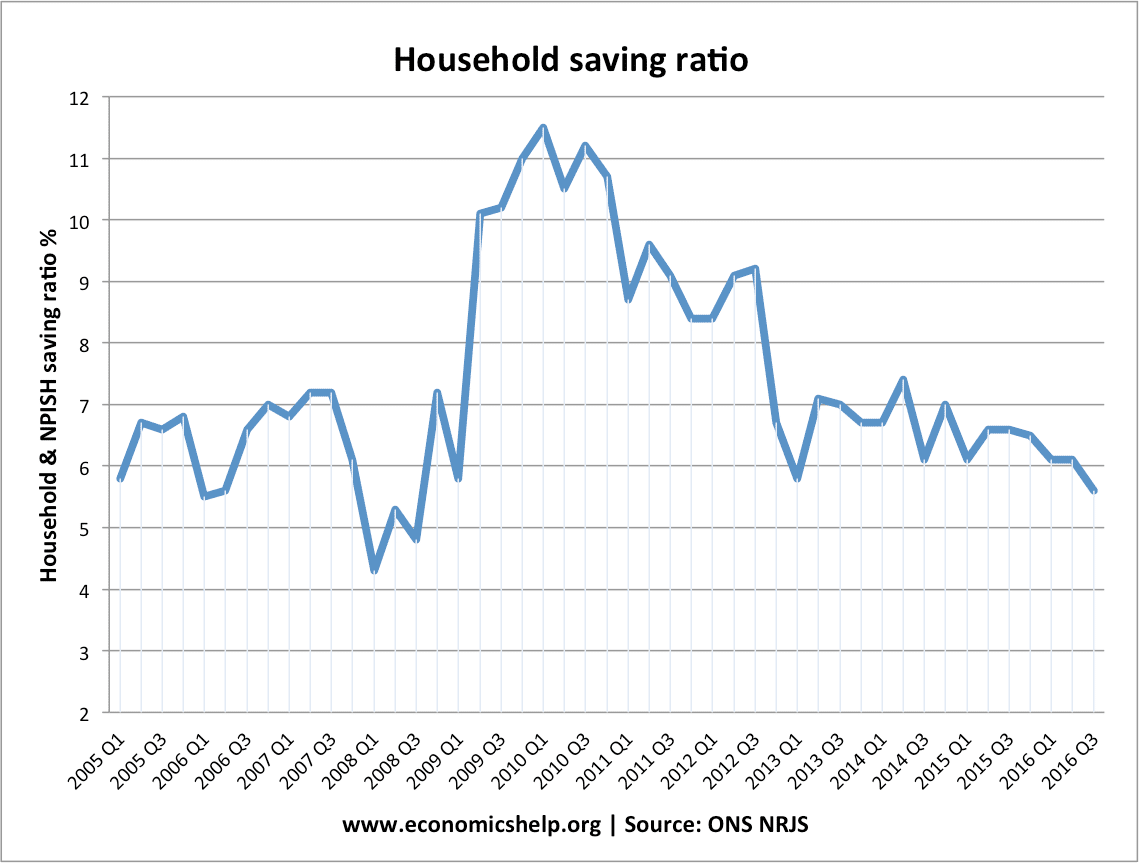
Rise in savings during Covid Pandemic
2020/21 saw a spike in the savings ratio due to the unusual circumstances of the Covid Pandemic. With normal economic activity curtailed many households were unable to spend on usual items like holidays, leisure and going out. Therefore, household savings rose sharply. With the end of covid lockdowns, the savings ratio fell. The forecast for savings in 2022 and 2023 is for savings to fall sharply due to the cost of living crisis, with many households seeing a fall in real income. This will cause households to run down savings to meet the rising cost of fuel and energy.
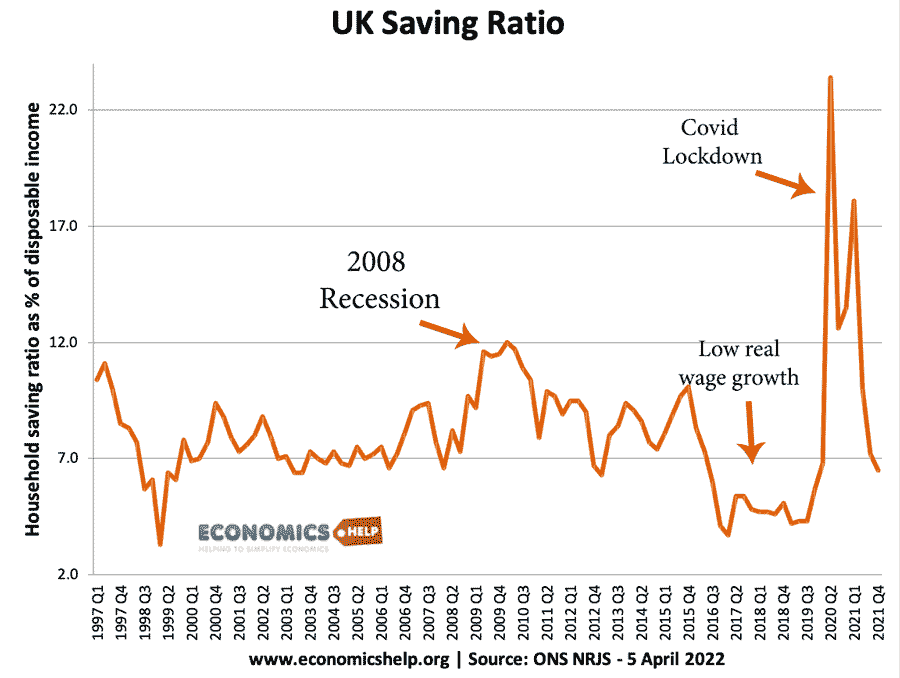
UK Saving ratio. Source: National income accounts NRJS dataset
NRJS = Households + NPISH (Non-Profit Institutions Serving Households)
Low saving ratio 2017-2019
This period saw a significant fall in the UK savings ratio to a record low. This fall in the savings ratio has been caused by
- Fall in real wages
- Depreciation in Sterling post-Brexit – pushing up the cost of living and contributing to falling in real wages
- To maintain spending, consumers have borrowed and dipped into savings
- Temporary factors (high tax payments on dividends)
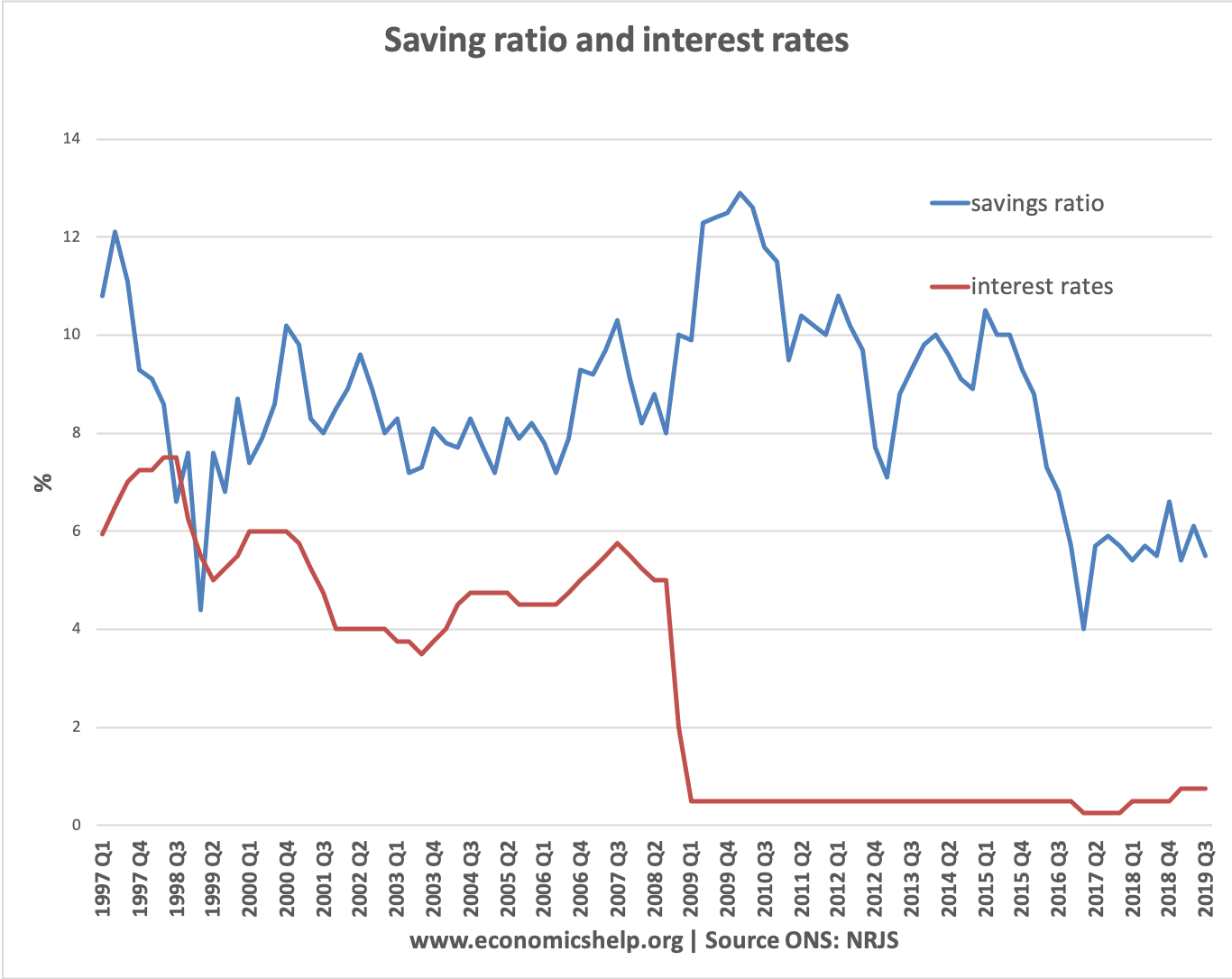
Saving ratio and base interest rates
In theory, lower interest rates reduce the incentive to save. But, the interest rate is only one of many factors influencing decisions to save. The most important factor is the state of the economy. In 2009, we saw a rapid rise in the saving rate because of the recession – despite interest rates cut to zero.