An ad valorem tax imposes a tax on a good or asset, depending on its value. The tax is usually expressed as a percentage. For example, in the UK, VAT is charged at 20% on most goods offered for sale.
Ad valorem means – according to value. Thus it is a tax which is flexible and depends on the value of the asset or the price of the good. In this regard, it is likely to be more progressive than a specific tax. If your house is worth more, you will pay a higher amount of stamp duty. Therefore, the wealthy tend to pay more stamp duty than those on a low income.
Diagram of ad valorem tax
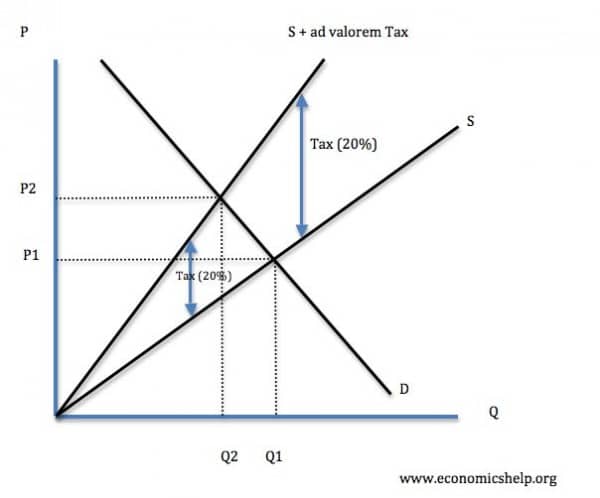
A tax shifts the supply curve to the left. The amount of tax depends on the price. For example, if we take VAT at 20%. The amount of tax will be as follows:
| Price | Tax (20% | Final Price inc. VAT |
| 5 | 1 | 6 |
| 10 | 2 | 12 |
| 15 | 3 | 18 |
| 20 | 4 | 24 |
| 30 | 6 | 36 |
| 100 | 20 | 120 |
Examples of Ad Valorem tax
1. Stamp duty
This is an ad valorem tax on buying a new house.
The marginal tax rates on new houses in the UK is:
- 2% tax on purchases between £125,000 and £250,000
- 5% tax on purchases from £250,000 up to £925,000
- 10% tax on purchases from £925,000 to £1.5m
- 12% tax on purchases over £1.5m
- Stamp duty UK
2. Property tax
A property tax could charge an annual tax on the value of a person’s property and real estate.
3. Consumption tax – VAT (20%)
Most modern economies charge VAT – a form of a consumption tax on the purchase price of the final good. It is an indirect tax because the retailer is responsible for paying the tax, though the consumer will pay higher prices.
VAT is different from a sales tax in that VAT is only due to the value added by the retailer. e.g. if the cost is £10, and the selling price is £25, the retailer is only responsible for paying VAT on the extra £15. The manufacturer is also due to pay VAT on the value added by their stage of production.
Related concepts
Specific tax. This is a tax which is a certain amount – e.g. cigarette tax is £5 per packet, regardless of the price charged.
Related pages
- Tax on negative externalities
- Tobin tax – ad valorem tax on share transactions.
- Tax revenue sources

what is income tax?
It is a tax imposed on any amount given to people in exchange of their service within the geographical boundaries of the country.
Is a tax levied on income of individuals
I wanna know how ad volurum tax affect to the supply equation. In other words how ad volurum effect can be worked out through formula.
*Ad Valorem
Suppose an ad-valorem sales tax is levied on the producers. What is the effect of the ad-valorem tax on the equilibrium price?
is,capital gain tax is a type of indirect tax?
In an case of introduction of 100% ad valorem tax, what will be the relationship with interest rates?
negative relationship between 100 percent advalorem tax and interest rates