Definition
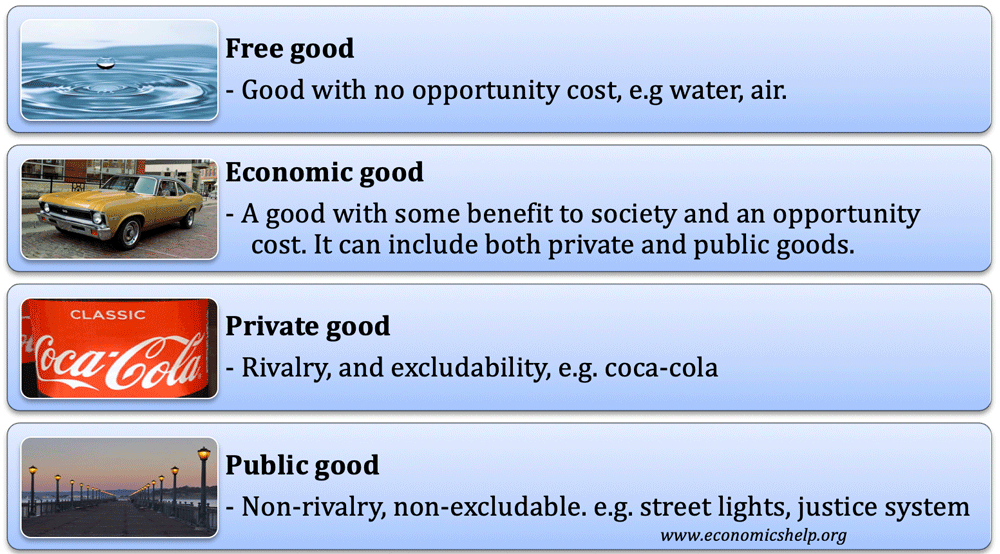
An economic good is a good or service that has a benefit (utility) to society. Also, economic goods have a degree of scarcity and therefore an opportunity cost.
This is in contrast to a free good (like air, sea, water) where there is no opportunity cost – but abundance. Free goods cannot be traded because nobody living by the sea would buy seawater – there is no point.
However, with economic goods where there is some scarcity and value, people will be willing to pay for them (in some form).
Another feature of an economic good is that if it can have a value placed on the good, it can be traded in the marketplace and valued using a form of money.
An economic good will have some degree of scarcity in relation to demand. It is the scarcity that creates a value people become willing to pay for. It is the scarcity which creates opportunity cost. – For example, if we pick apples from a tree, it means that other people will not be able to enjoy them. If we devote resources to mining gold, the opportunity cost is that we can’t devote this time and effort to growing corn.
Readers Question: Can endangered plant/animal species be economic goods? If so then why?

Firstly, do endangered plants/animal species have a value to man?
- Many endangered plants and species do have a benefit to humanity, even if we are not aware of them. For example, rare plants may hold the key to creating a vaccine for a disease. If we allow the plant to become extinct, then we lose this bio-diversity and future potential to treat human diseases. This is a clear example of how endangered plants could have a very high economic value.
- It may be harder to make the case for endangered species. You could argue that some reptile on the verge of extinction has little or no value to humans, therefore some might not class it as an economic good.
- However, others may disagree, they argue that when considering economic value, we shouldn’t just consider narrow human interest. We could argue that we should look at the issue from a less human-specific perspective. We should see all life as having an intrinsic value.
- Furthermore, ecologists may argue that protecting the biodiversity of the planet should give joy to humans – we should get utility and satisfaction from being guardians of the planet rather than destroyers of life. Therefore protecting so called ‘useless’ species can actually give utility to humans because we can feel ‘good’ about being responsible citizens of the planet.
- The difficulty is that a strict definition of an economic good says that the value of the good should have some market value and be traded. It is hard to put a value on the benefit of saving a rare species from extinction. But at least, some people would spend money to save a species from extinction because they feel it is a worthwhile act. Therefore, the rare species do have an economic value.