How The Bank of England set interest rates
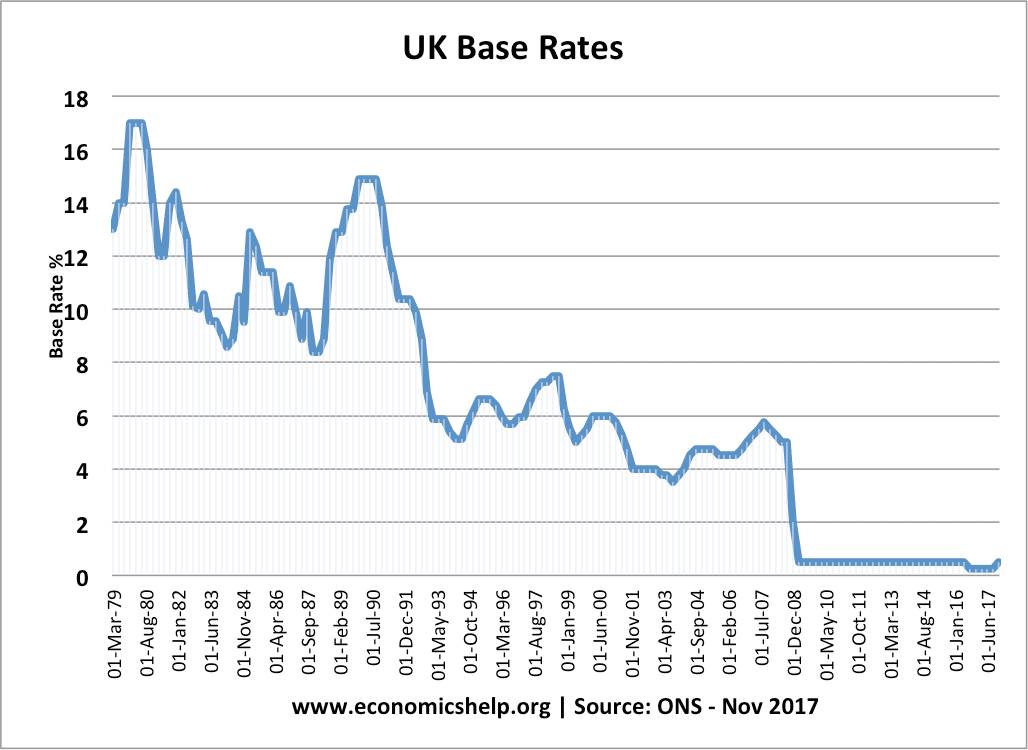
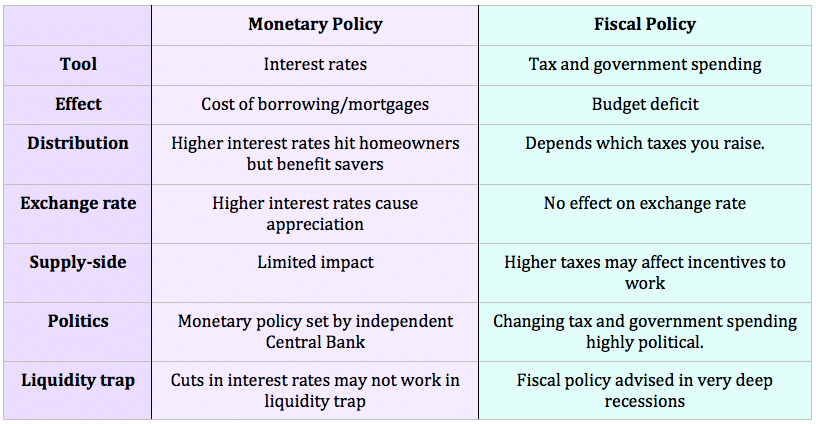
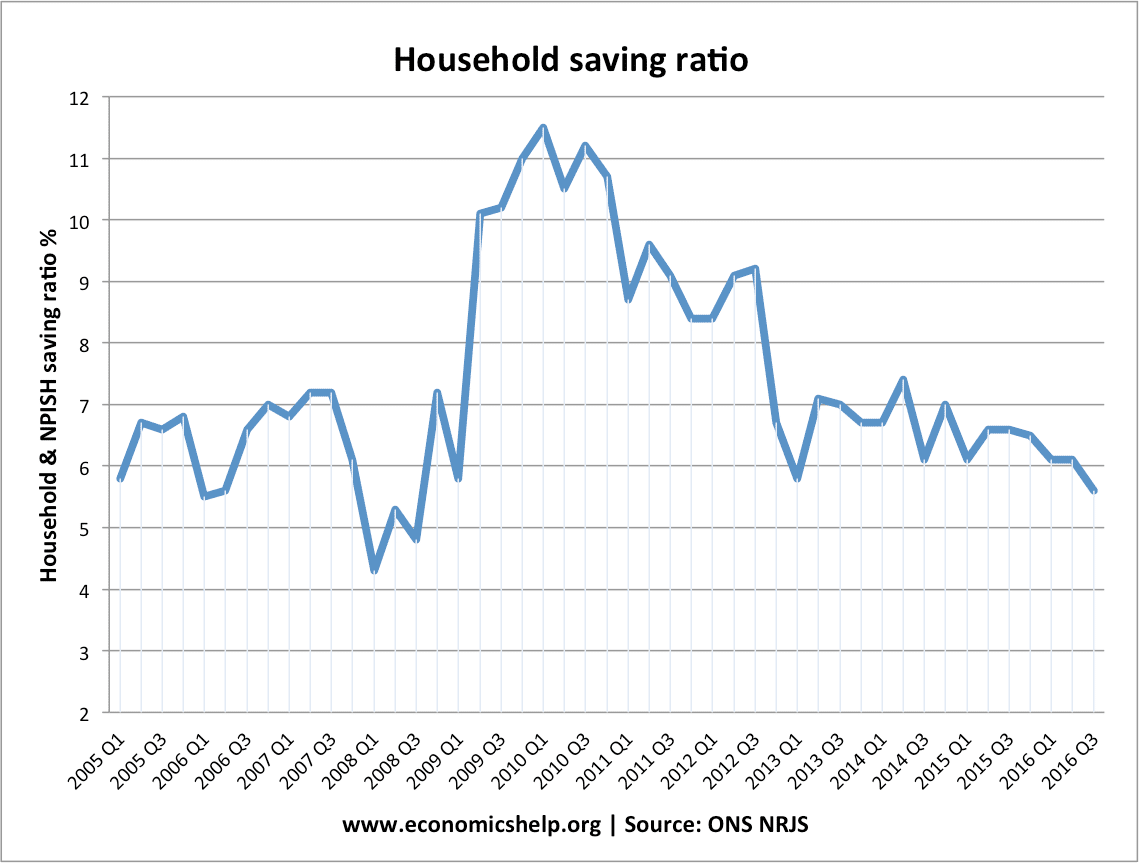
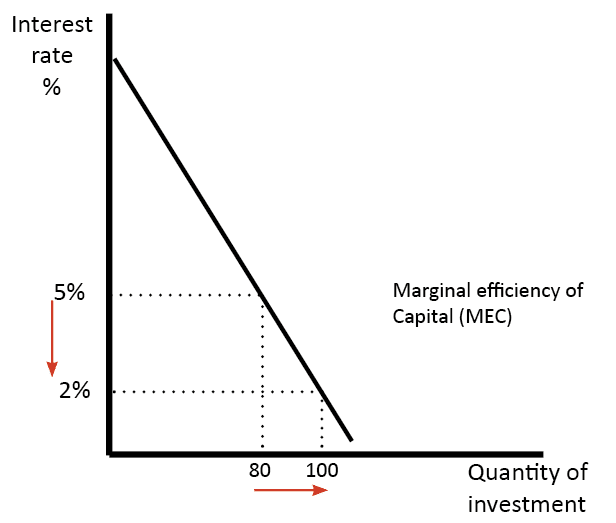
Q. How does the Bank of England decide and set interest rates? The Bank of England set the repo rate. This is sometimes known as the ‘base rate’. It is the interest rate at which commercial banks (like Lloyds and Natwest) borrow from the Bank of England. The Bank of England can control liquidity and …