Pricing strategies
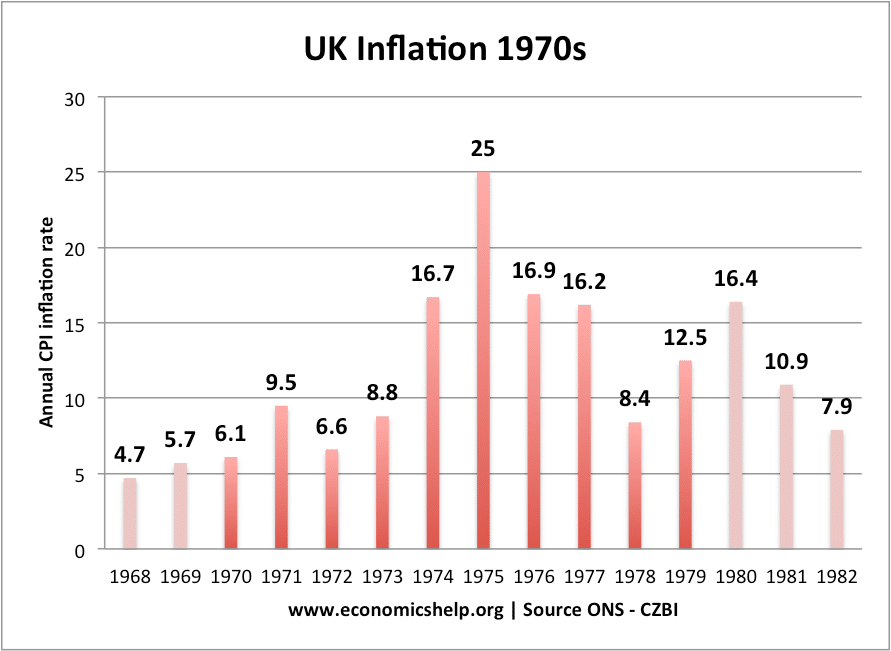
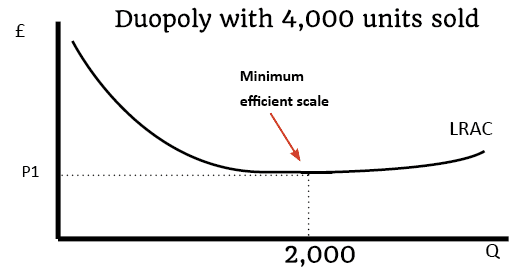
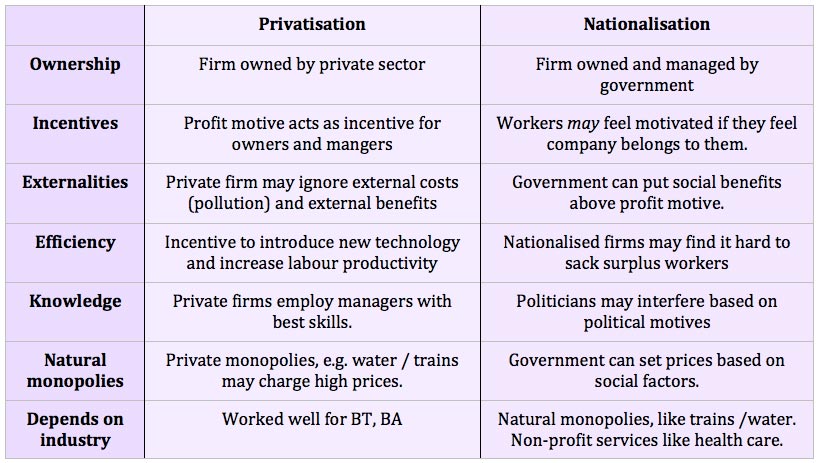
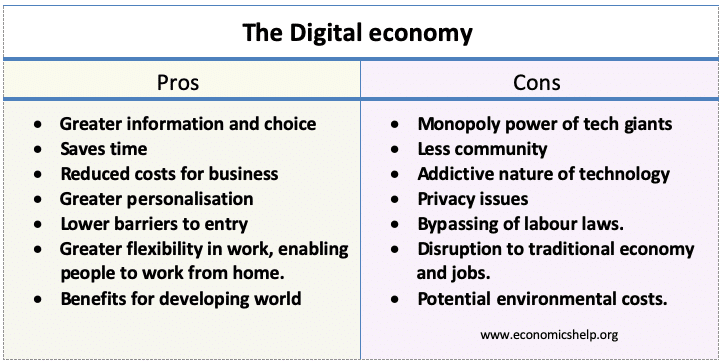
A look at different pricing strategies a firm may use to try and increase profitability, market share and gain greater brand loyalty. Types of pricing strategies General strategies Profit maximisation. One strategy is to ignore market share and try to work out the price for profit maximisation. In theory, this occurs at a price where …