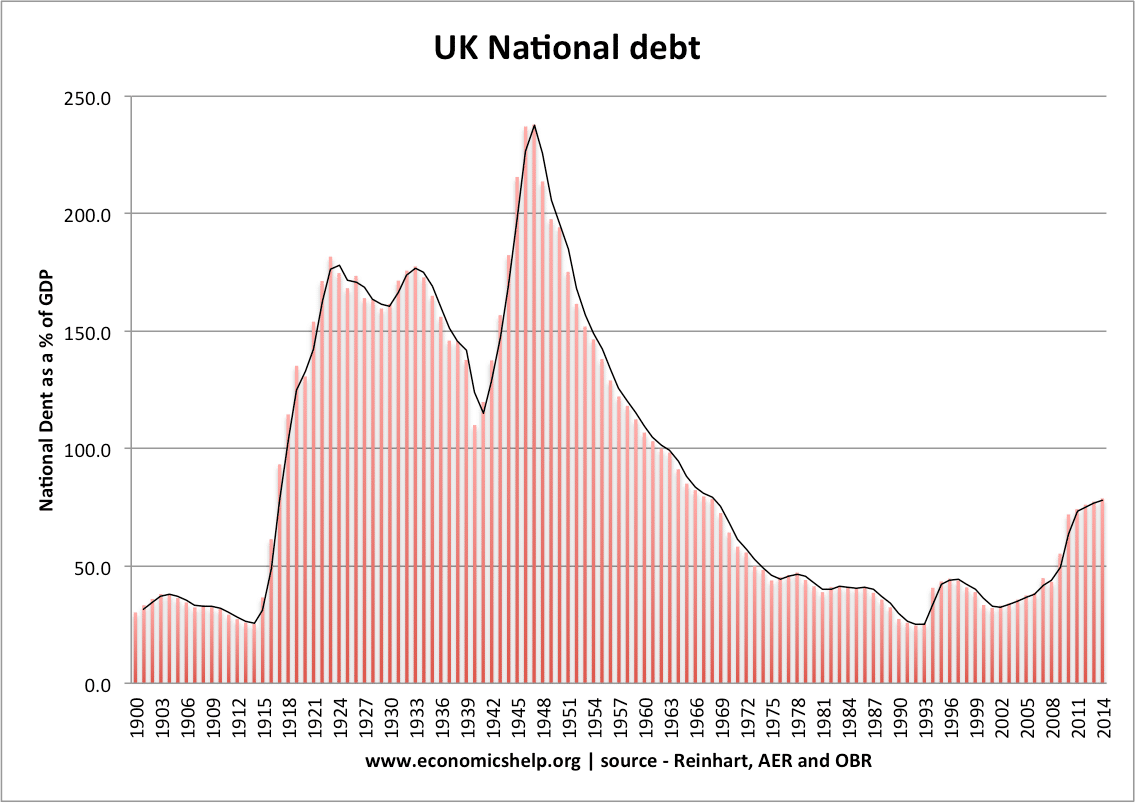
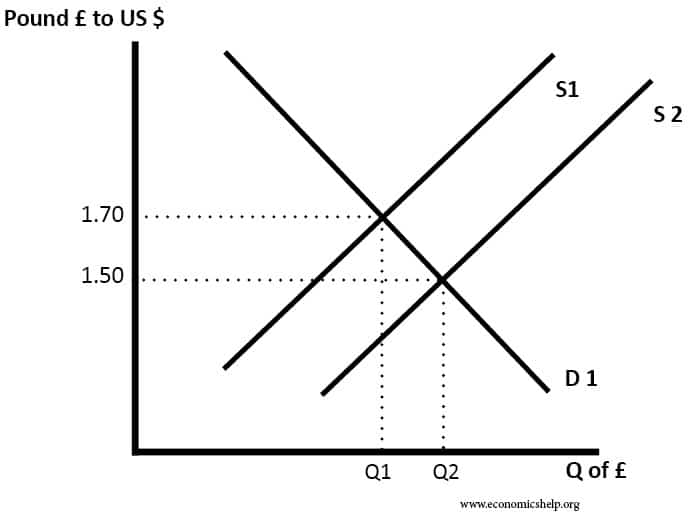
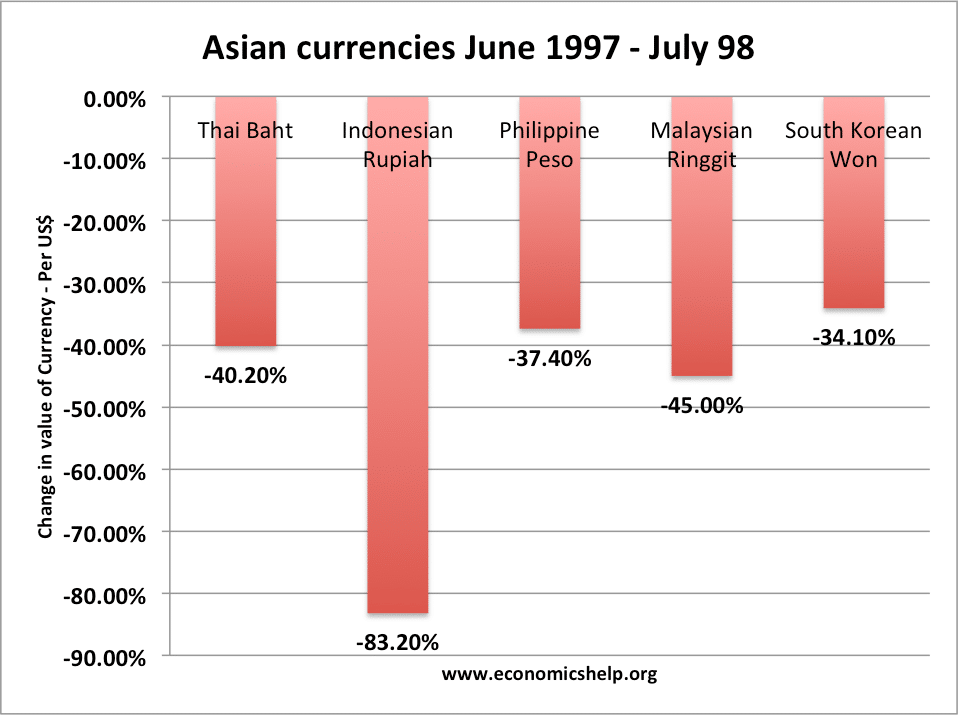
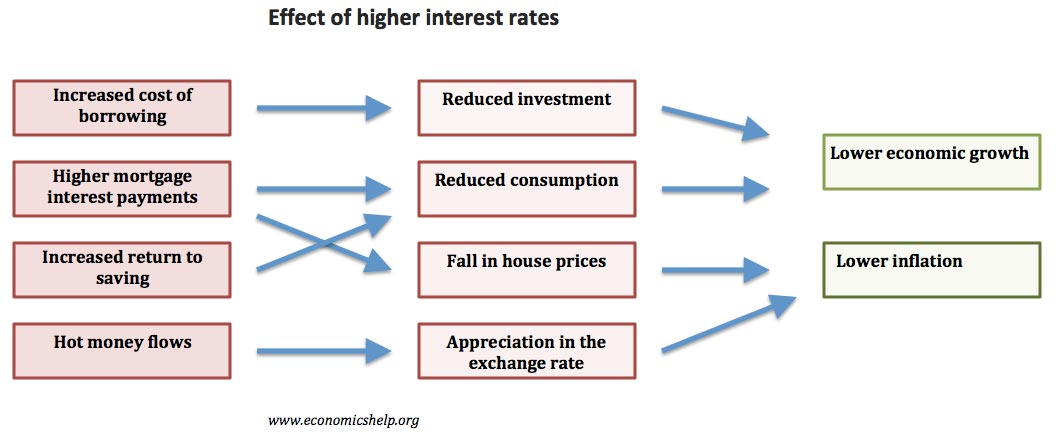
Imports and Inflation
Readers Question: How does an increase in imports cause inflation in the economy? If the quantity of imports increases, this should reduce domestic demand-pull inflation (AD = C+I+G+X-M). Therefore if consumers spend more on imports it will, ceteris paribus, reduce domestic demand. Therefore, we get lower growth of AD and lower inflation. Suppose there is an …