Savings ratio UK
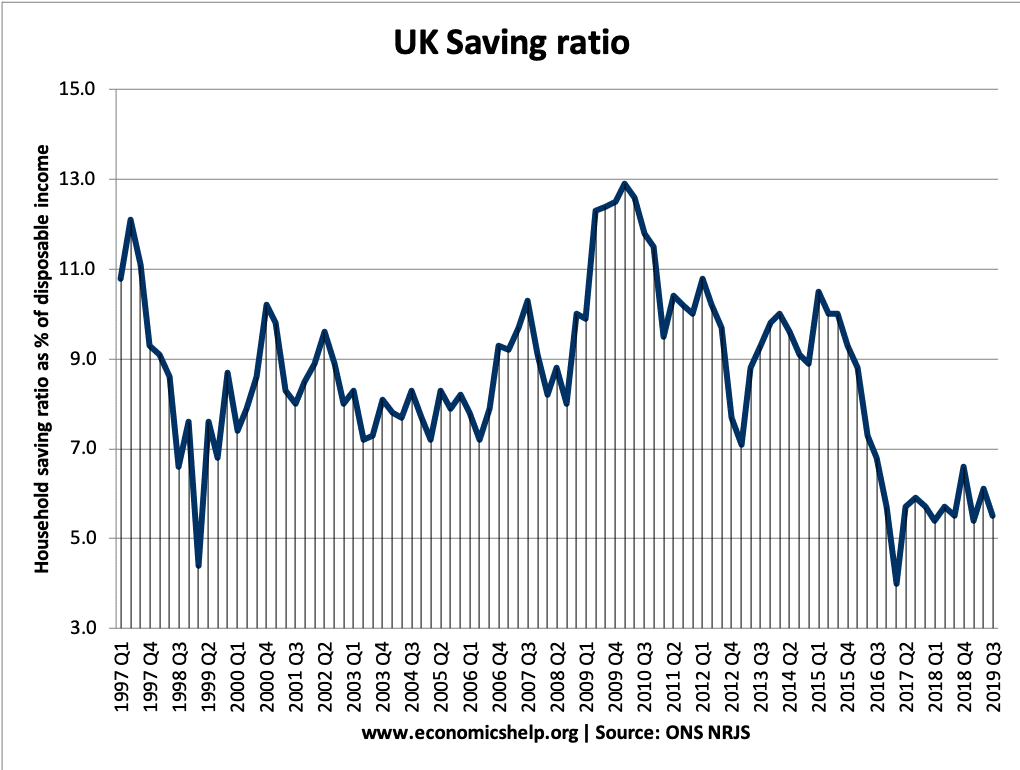
Definition of Household savings ratio: The percentage of disposable income that is saved. (1) Total savings = Disposable income – Household consumption UK Saving Ratio Latest UK household savings ratio: 2021 = 10% But, by 2021 Q4 the saving ratio had fallen to 6.2% By contrast, the average savings ratio in the past 54 years …