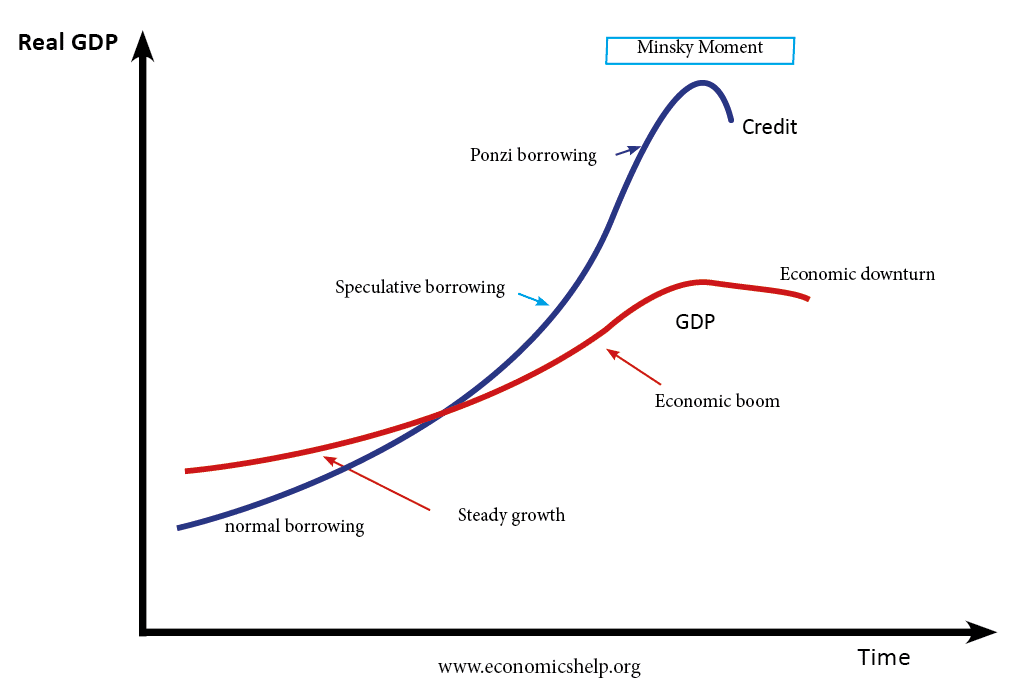
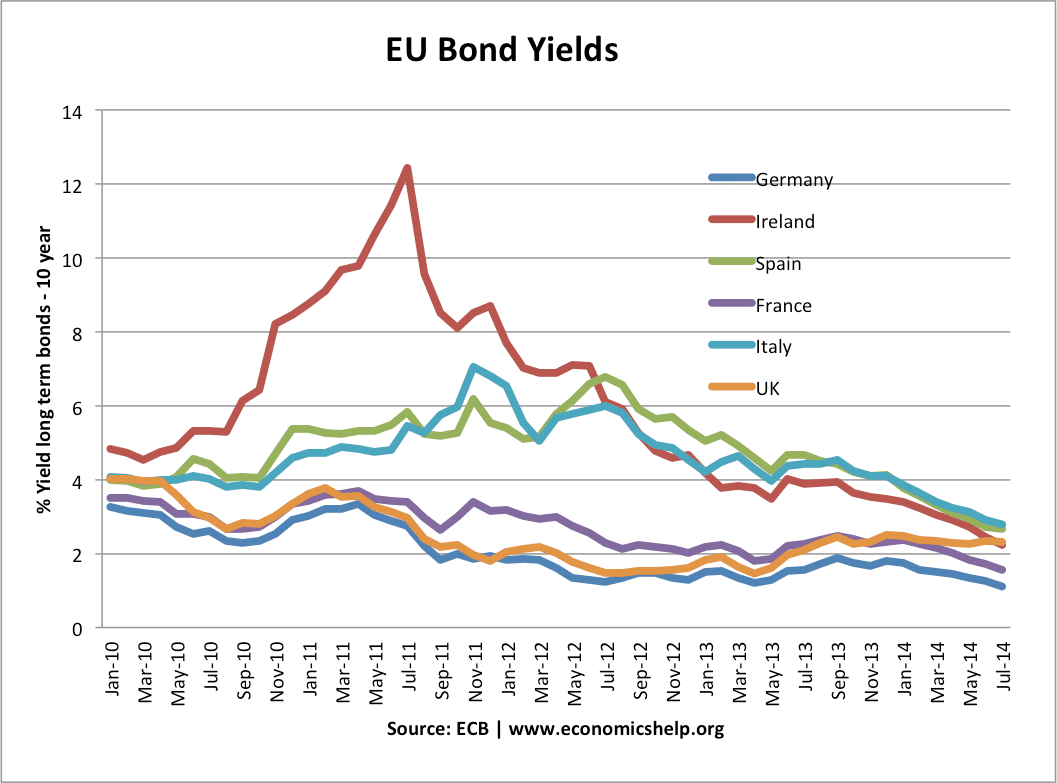
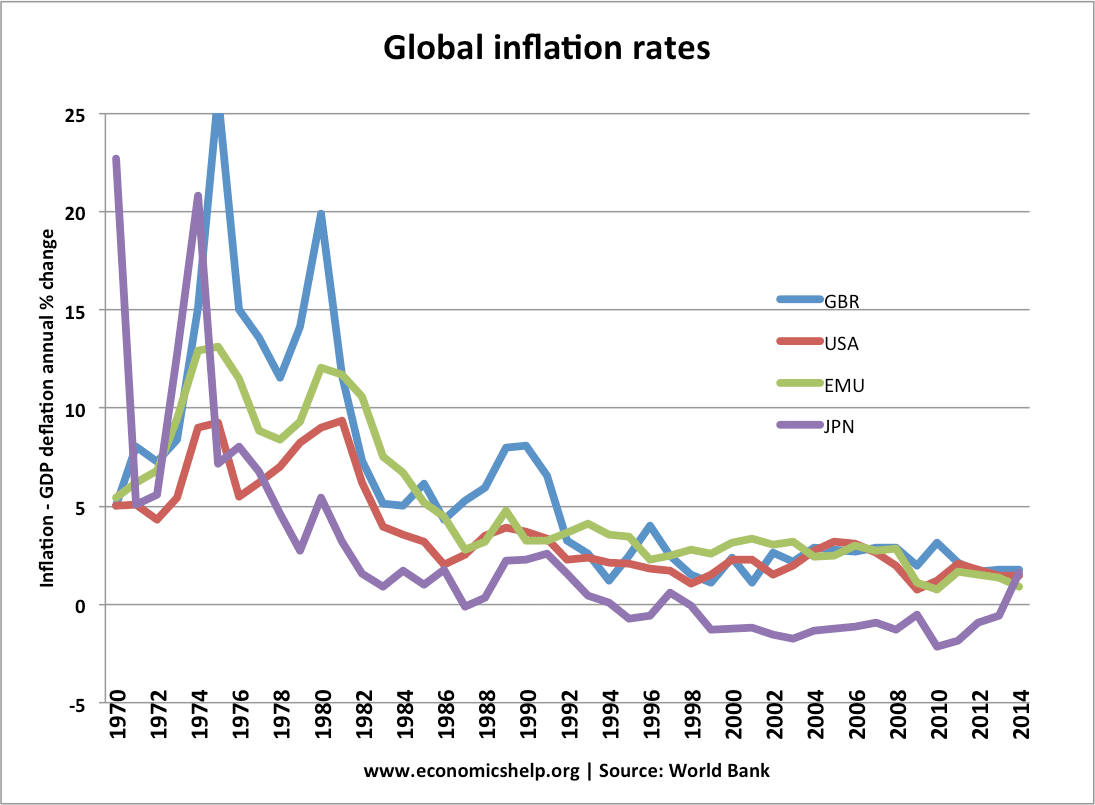
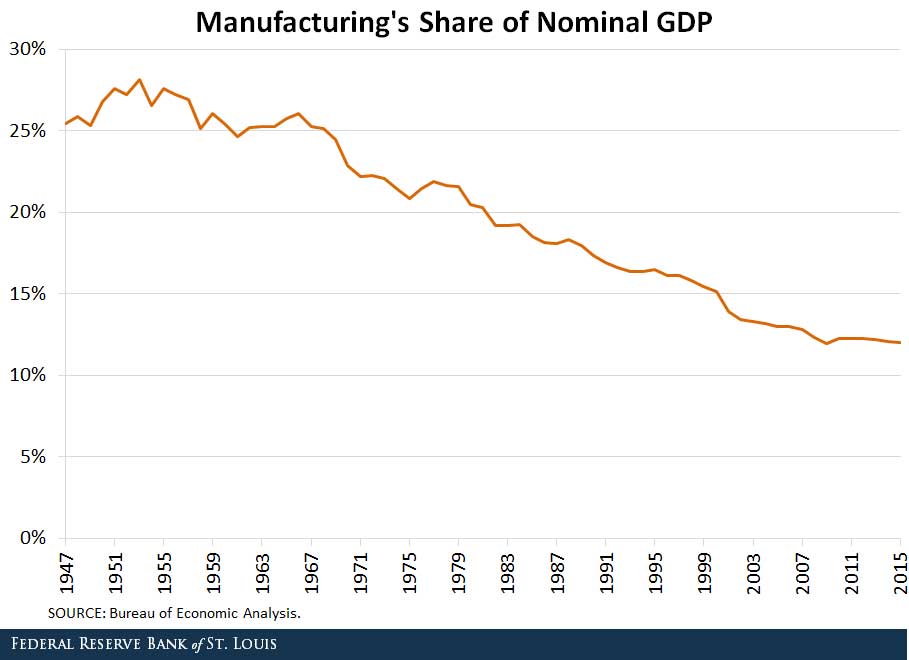
Balanced and unbalanced economic growth
What do we mean by balanced economic growth? Also, is it important for an economy to promote a balanced approach to growth? A balanced economy suggests that economic growth is sustainable in the long-term, and the economy is also growing across different sectors – and not focused on one particular industry or area. A balanced …