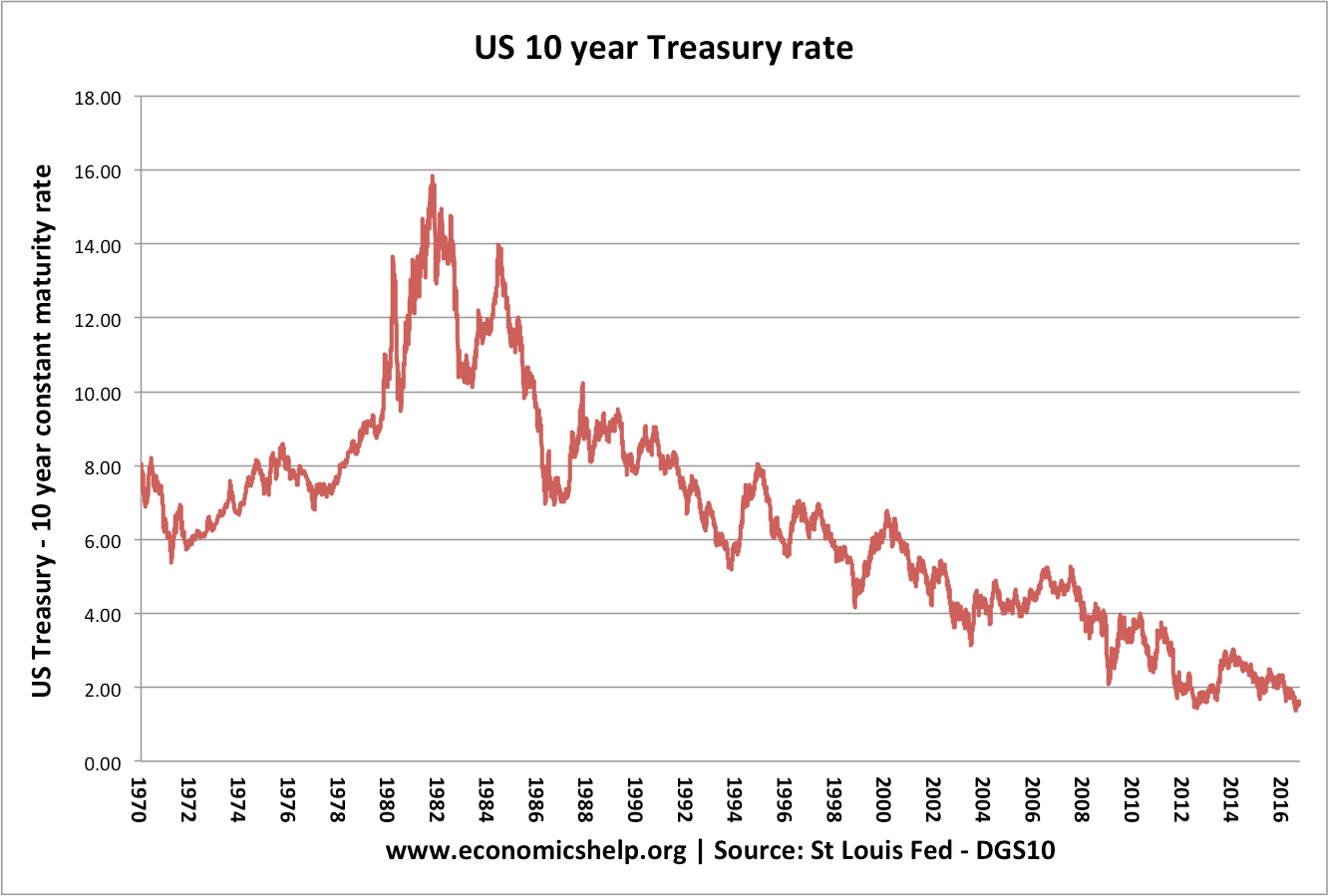
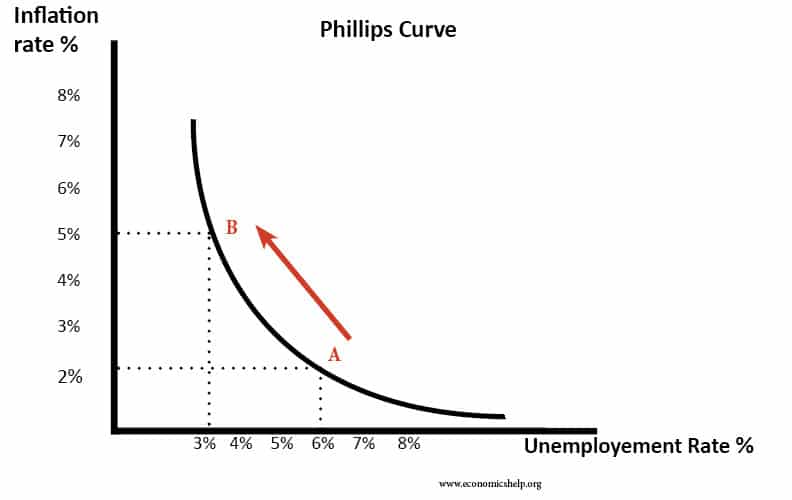
How Much Bargaining Power Do Workers Have?
Readers Question: How much bargaining power do workers have? Bargaining Power is the ability for firms or workers to get what they want. An example of bargaining power is related to the power of trades unions. If a part-time worker works for a firm with monopsony power, they will have very low bargaining power. However, …