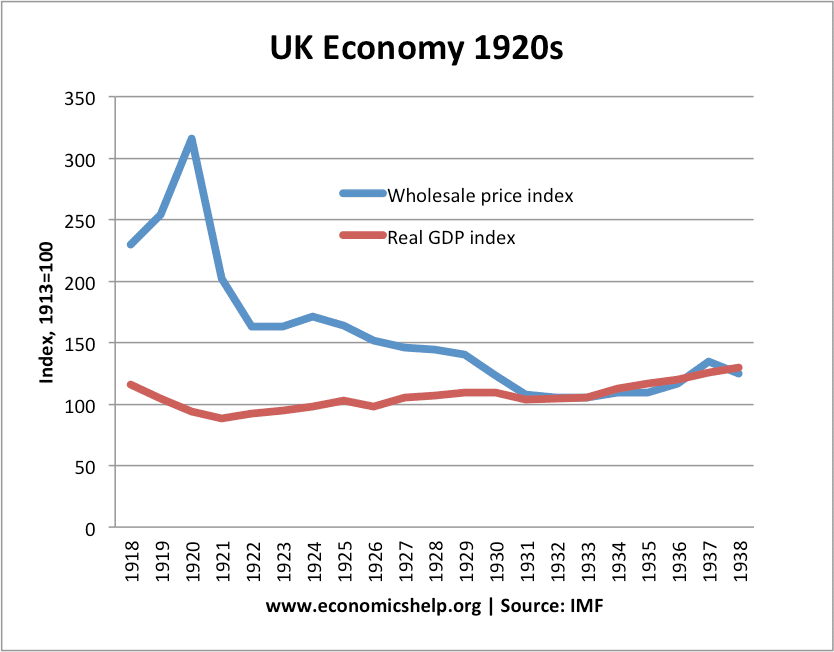
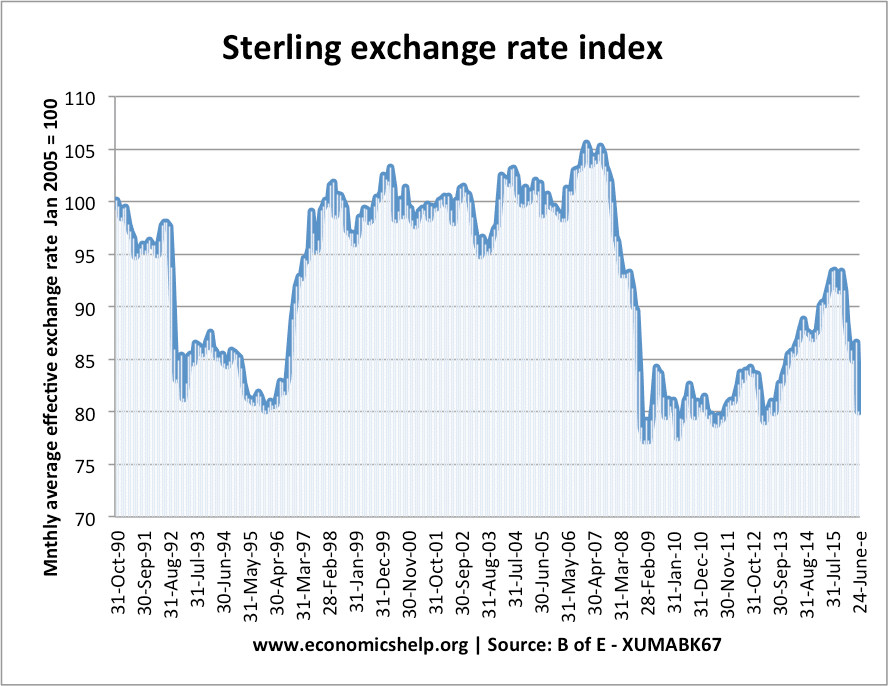
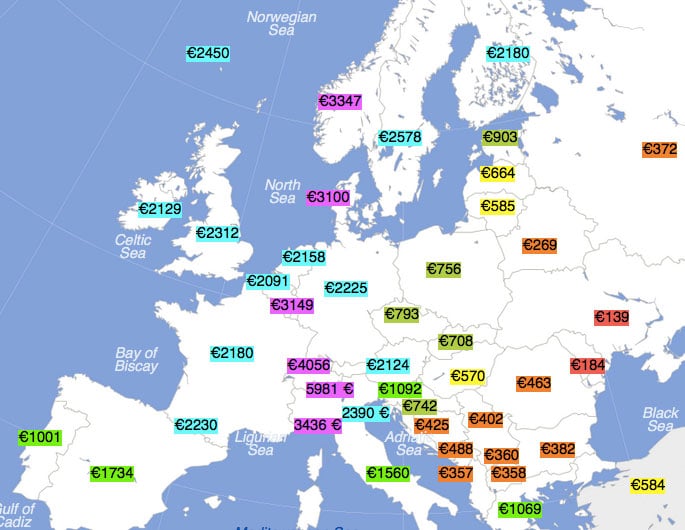
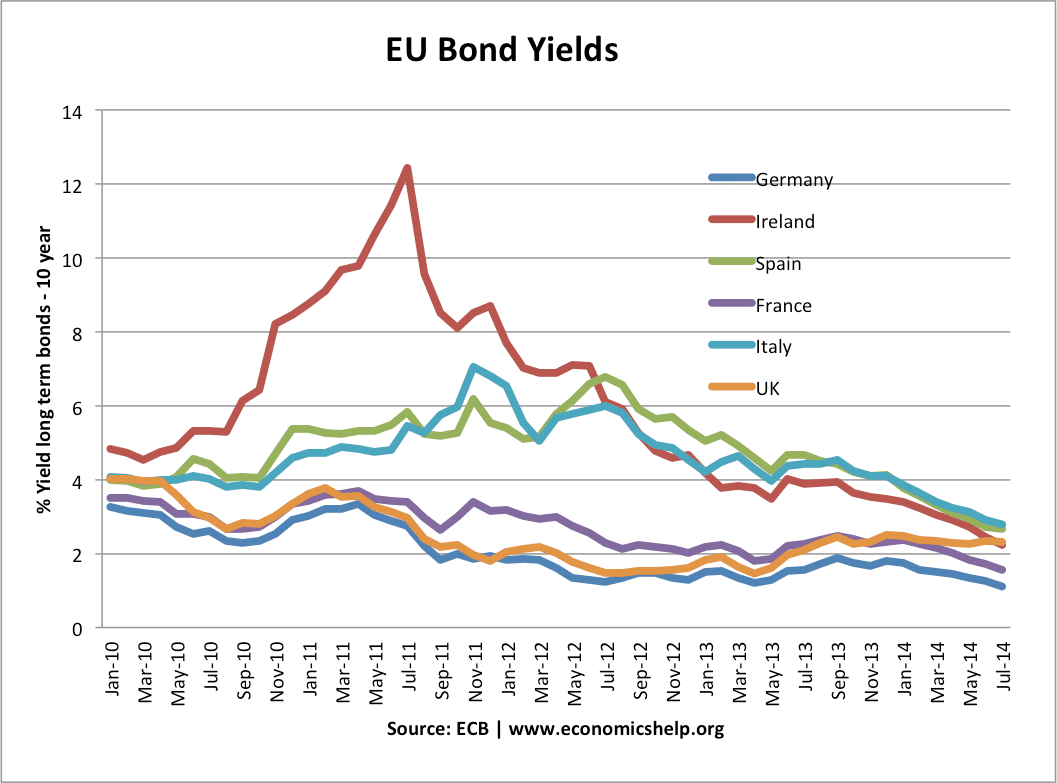
Consumer confidence
Consumer confidence is the outlook that consumers have towards the economy and their own personal financial situation. This outlook can be optimistic (high consumer confidence) or pessimistic (low consumer confidence) The level of consumer confidence will be an important factor that determines the willingness of consumers to spend, borrow and save. A high level of …