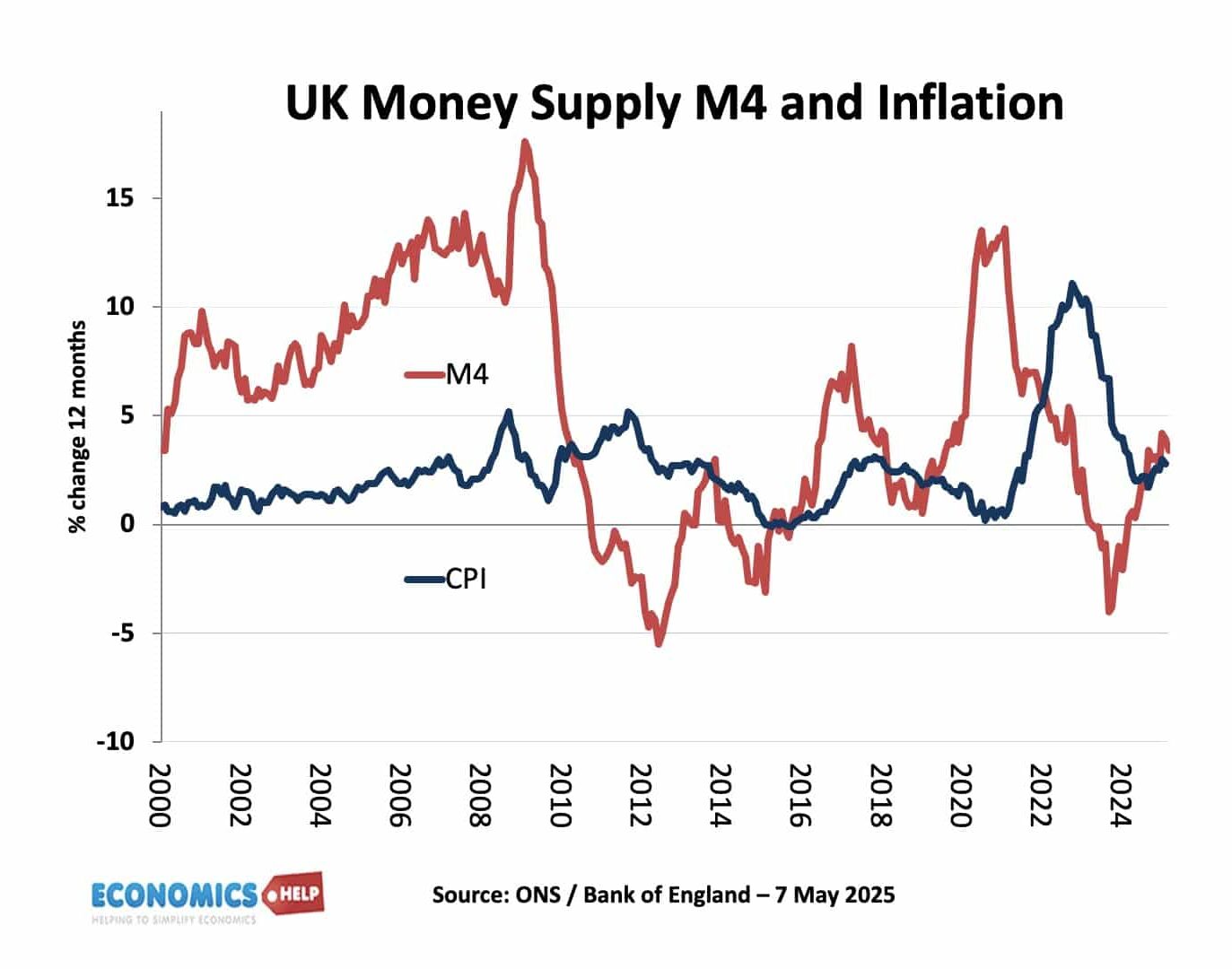
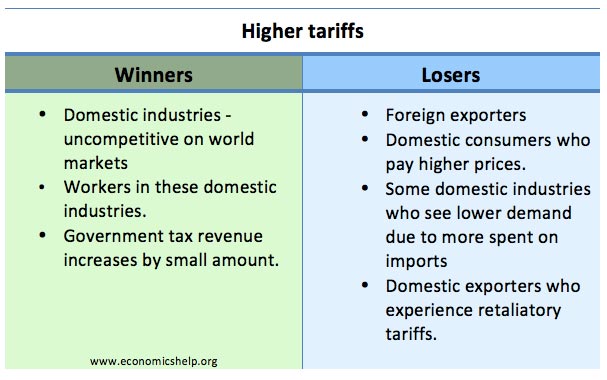
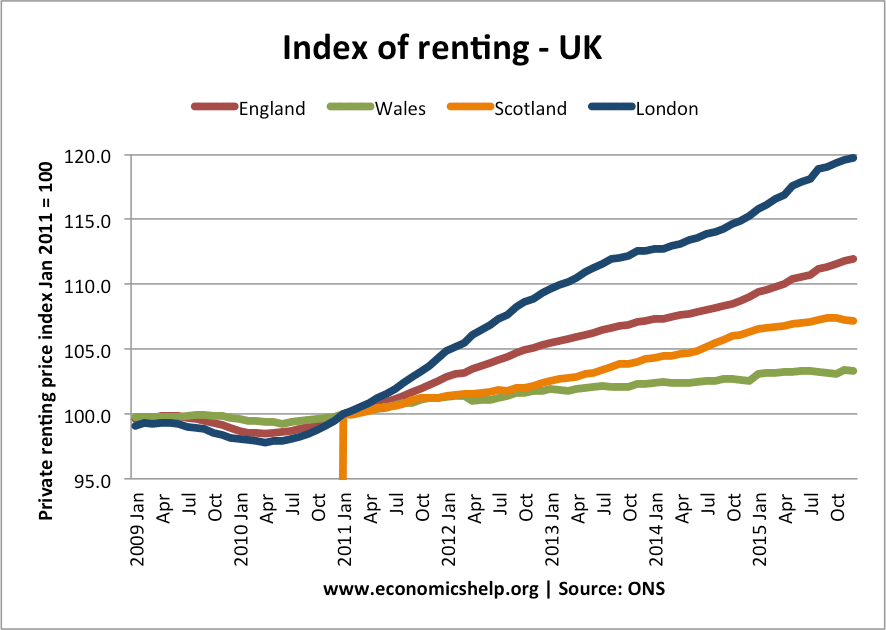
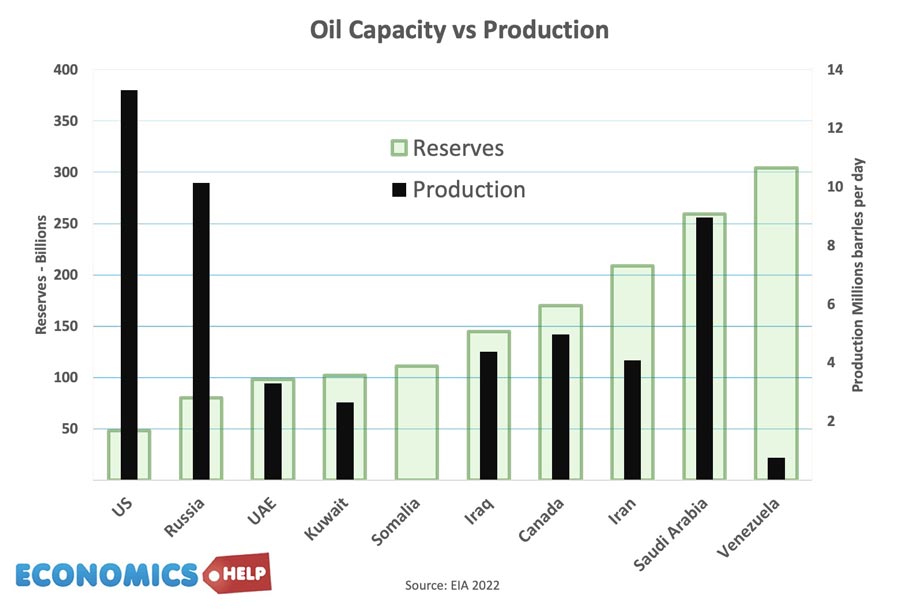
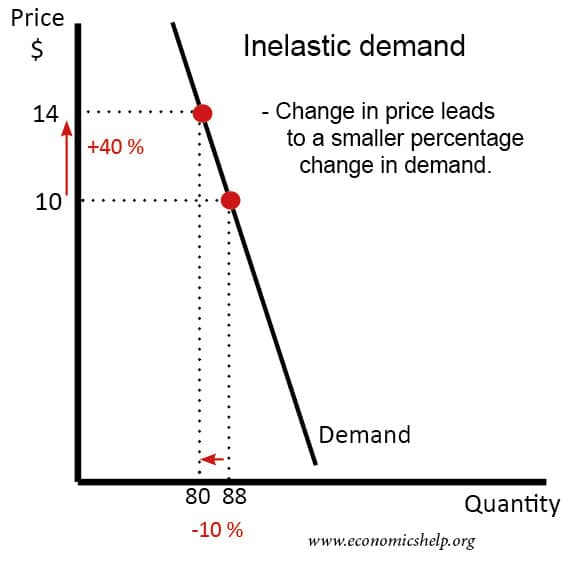
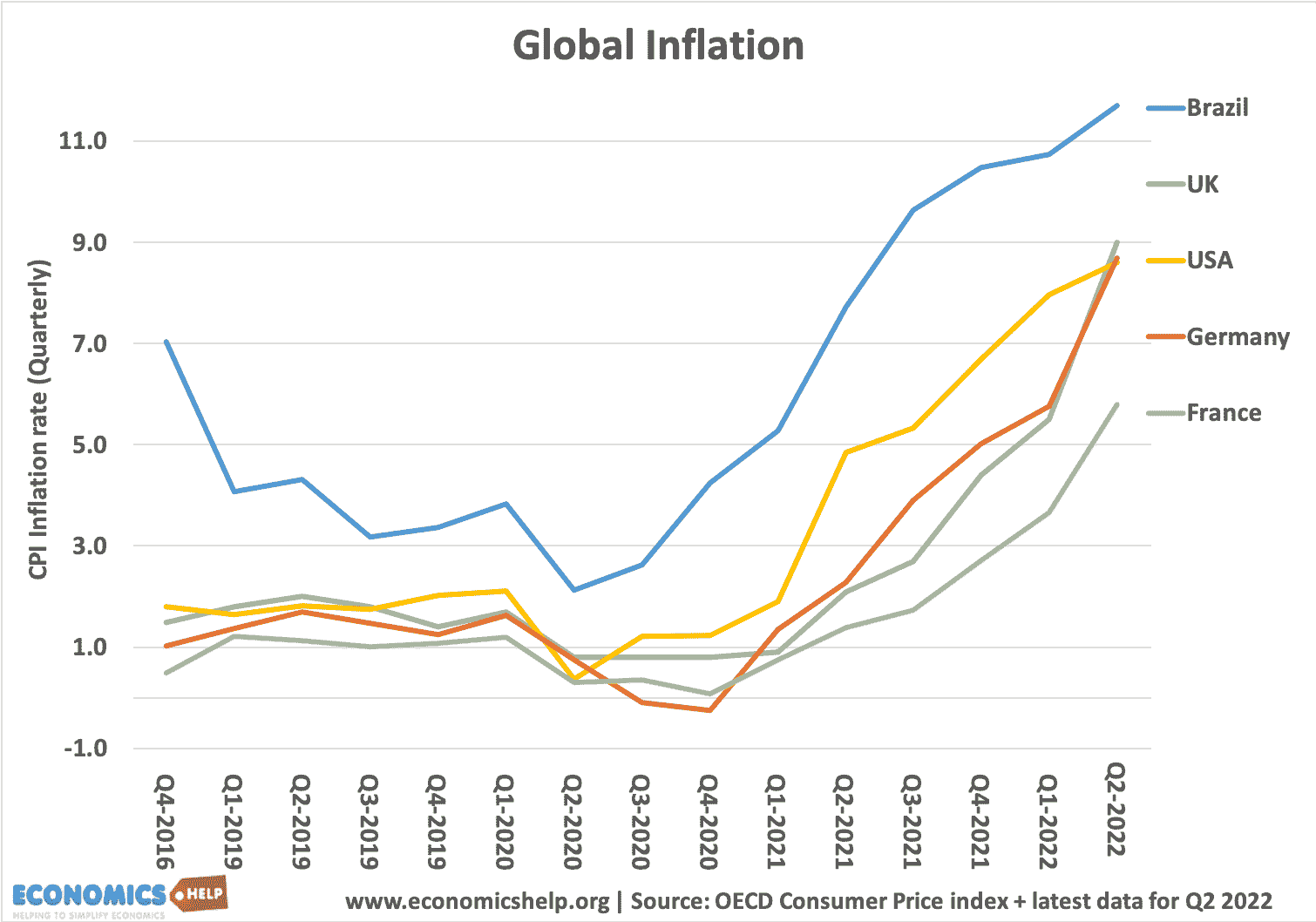
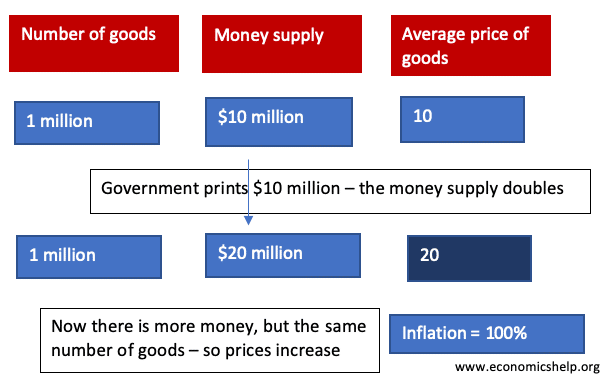
Does Printing Money and QE Directly Lead to Inflation
Will Printing Money and QE cause Runaway Inflation?Watch this video on YouTube After the First World War, the German government were left with huge debts and reparation payments to the Allies. Faced with striking workers the government began printing money to pay workers higher salaries. It gave the government a temporary breathing space, …