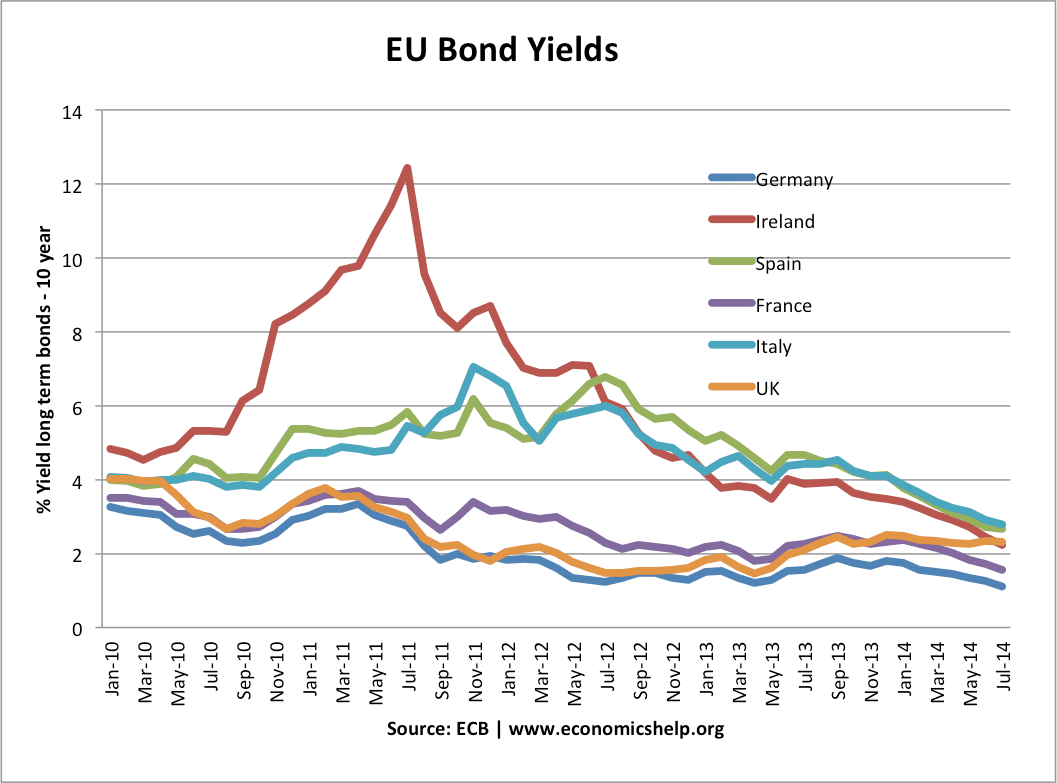
Economic inactivity – definition and causes
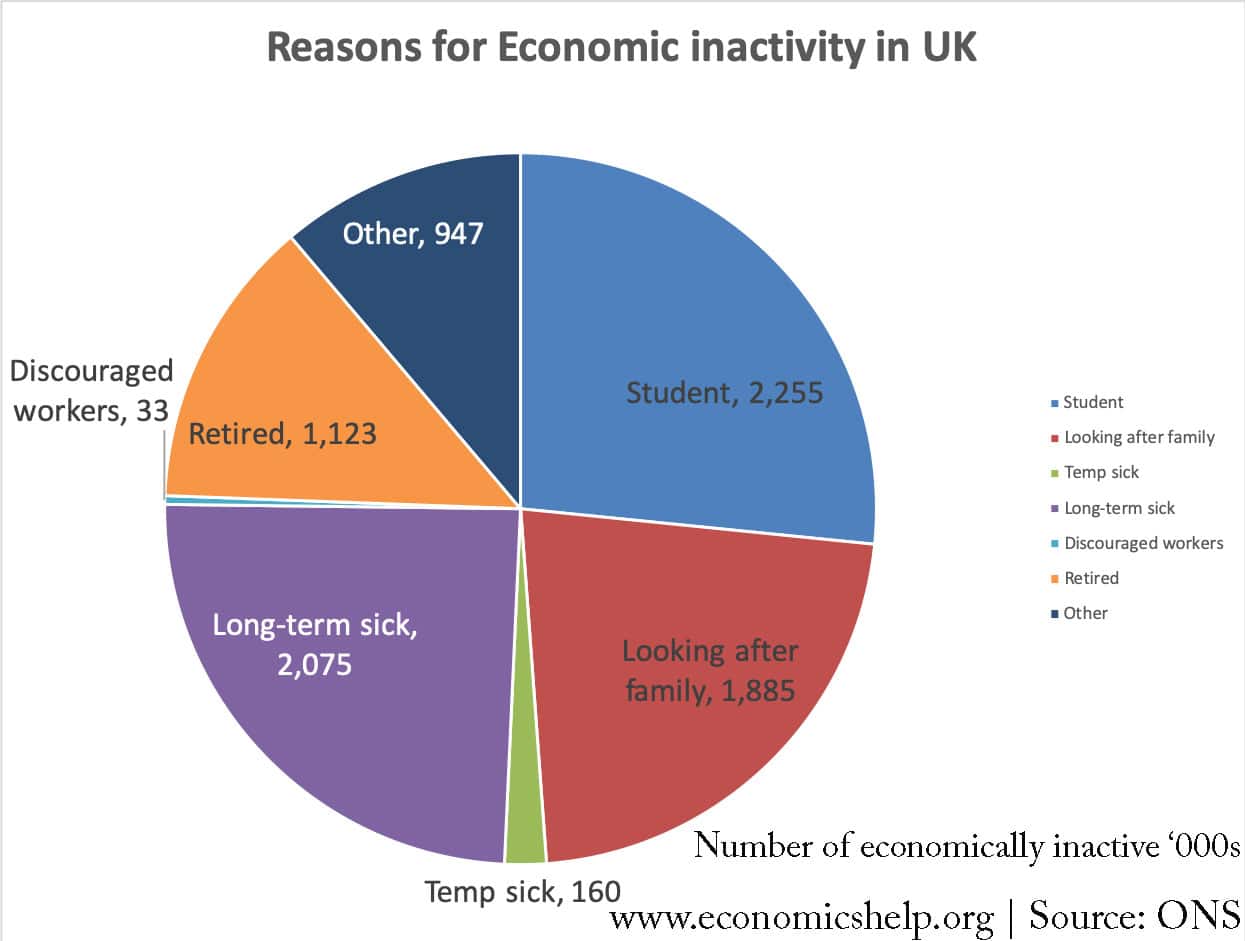
Definition: Economic inactivity means that people (aged 16-64) are not involved in the labour market – they are neither working or actively seeking employment. Economic inactivity includes students, early retirees and the long-term sick. There are 8.5 million counted as economically inactive in the UK. The unemployed who are seeking working and willing and able …