Moral Hazard
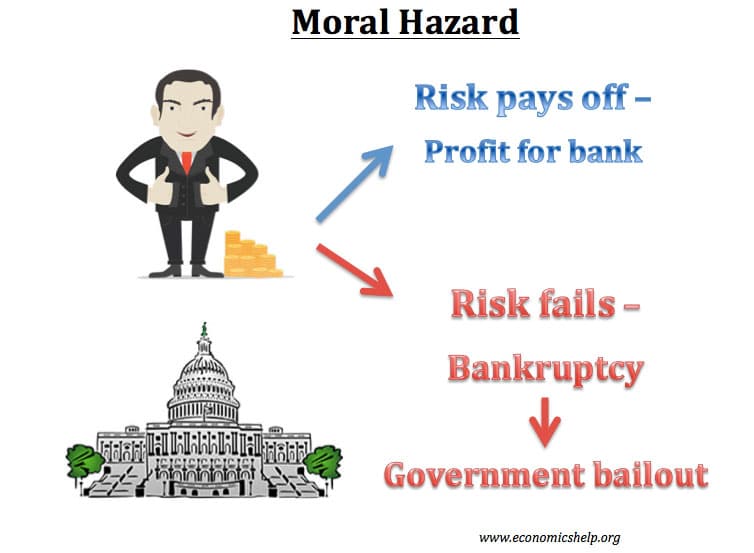
Moral Hazard is the concept that individuals have incentives to alter their behaviour when their risk or bad-decision making is borne by others. Examples of moral hazard include: Comprehensive insurance policies decrease the incentive to take care of your possessions Governments promising to bail out loss-making banks can encourage banks to take greater risks. Conditions …