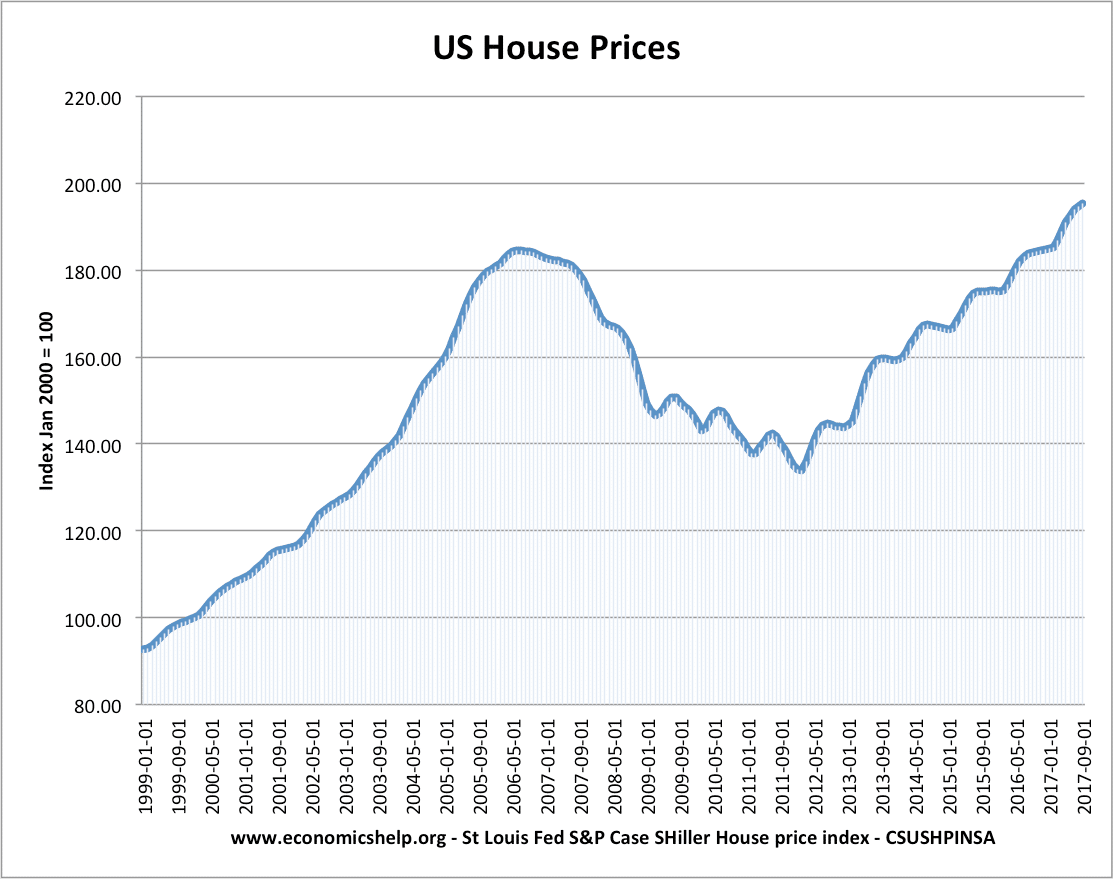
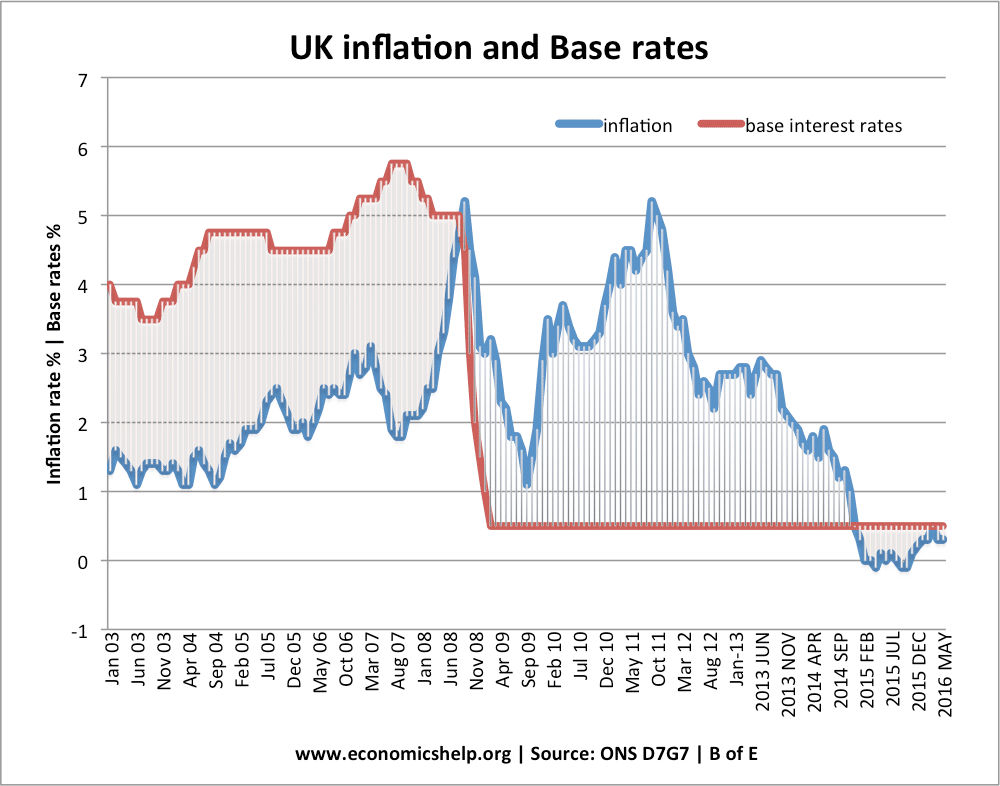
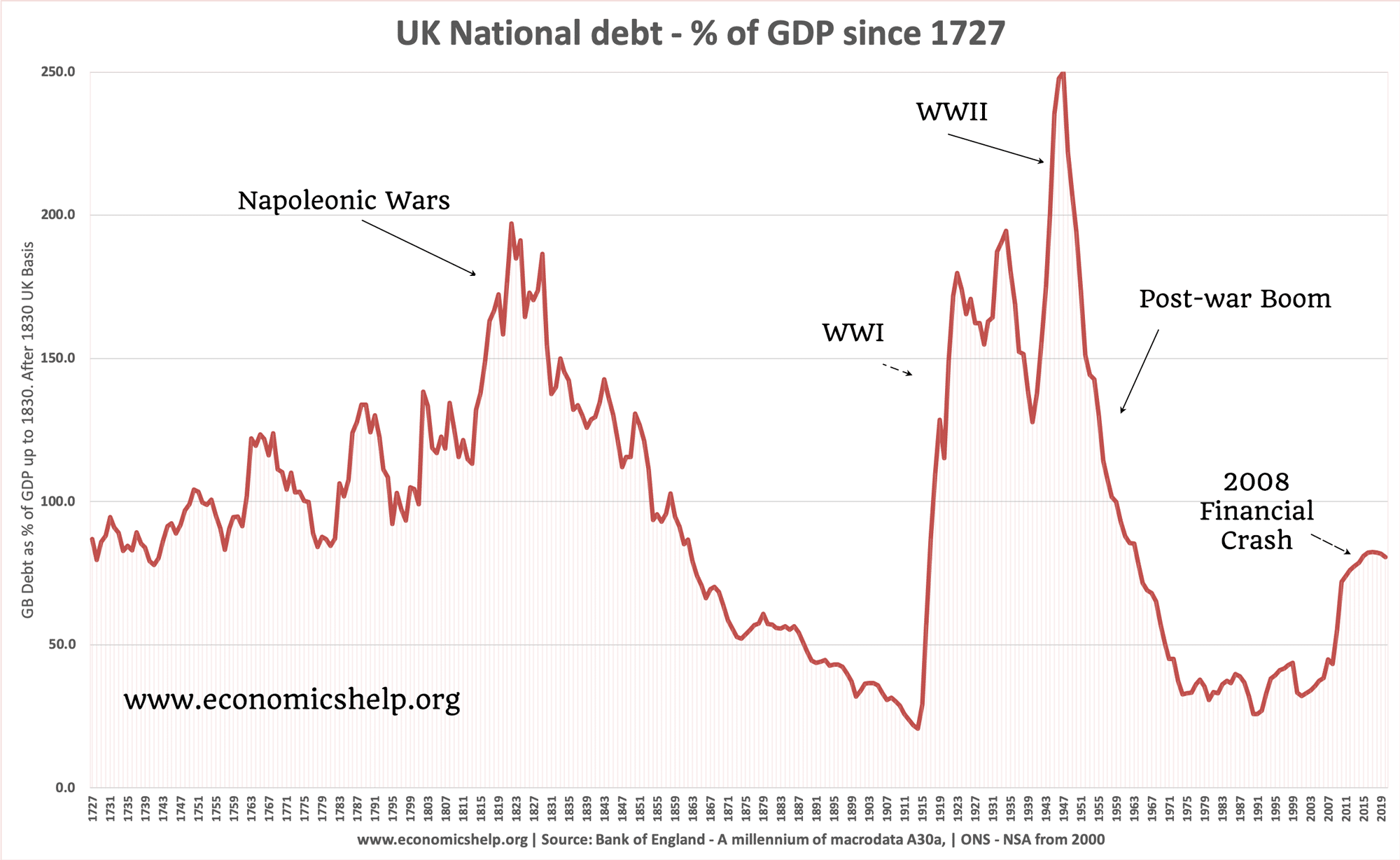
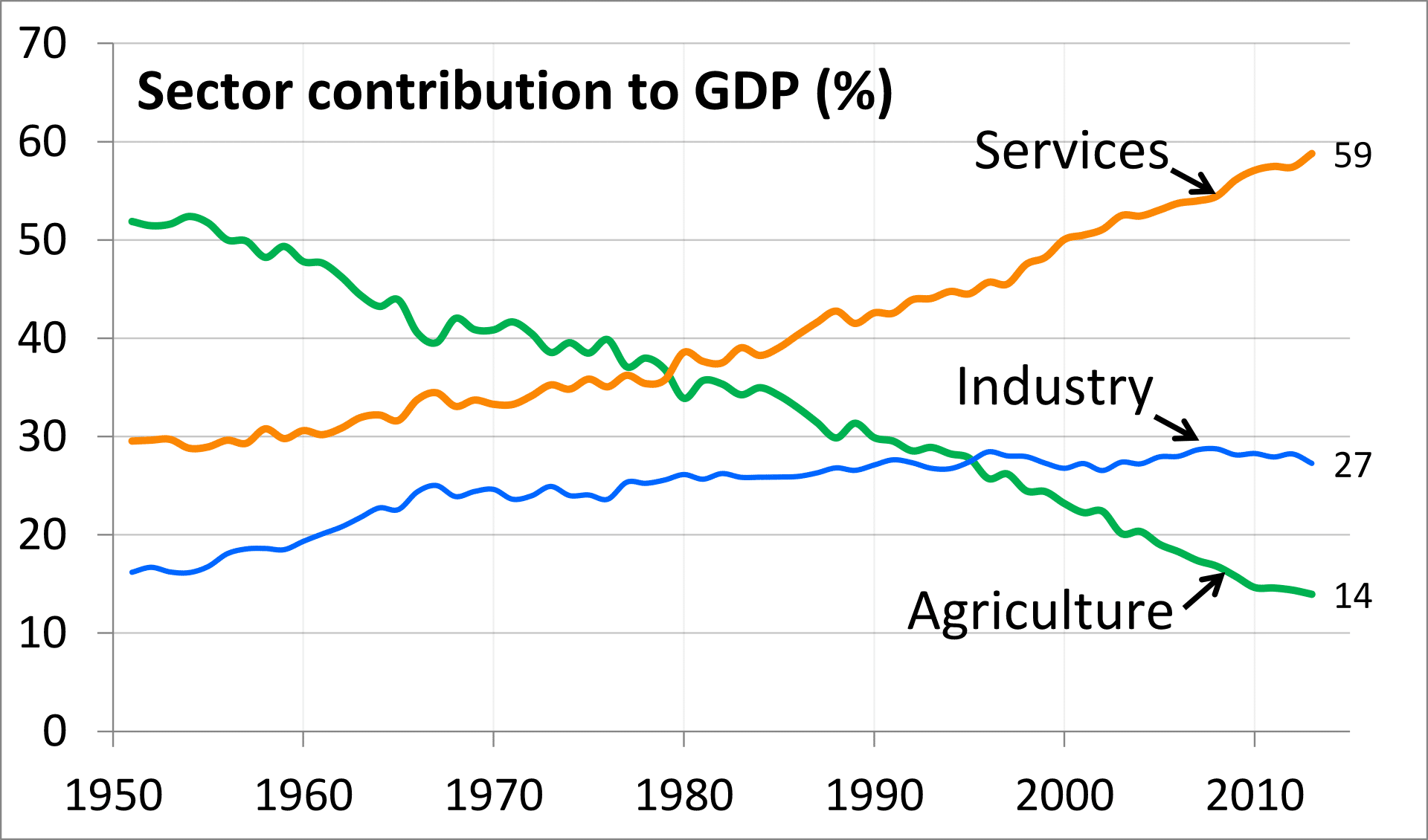
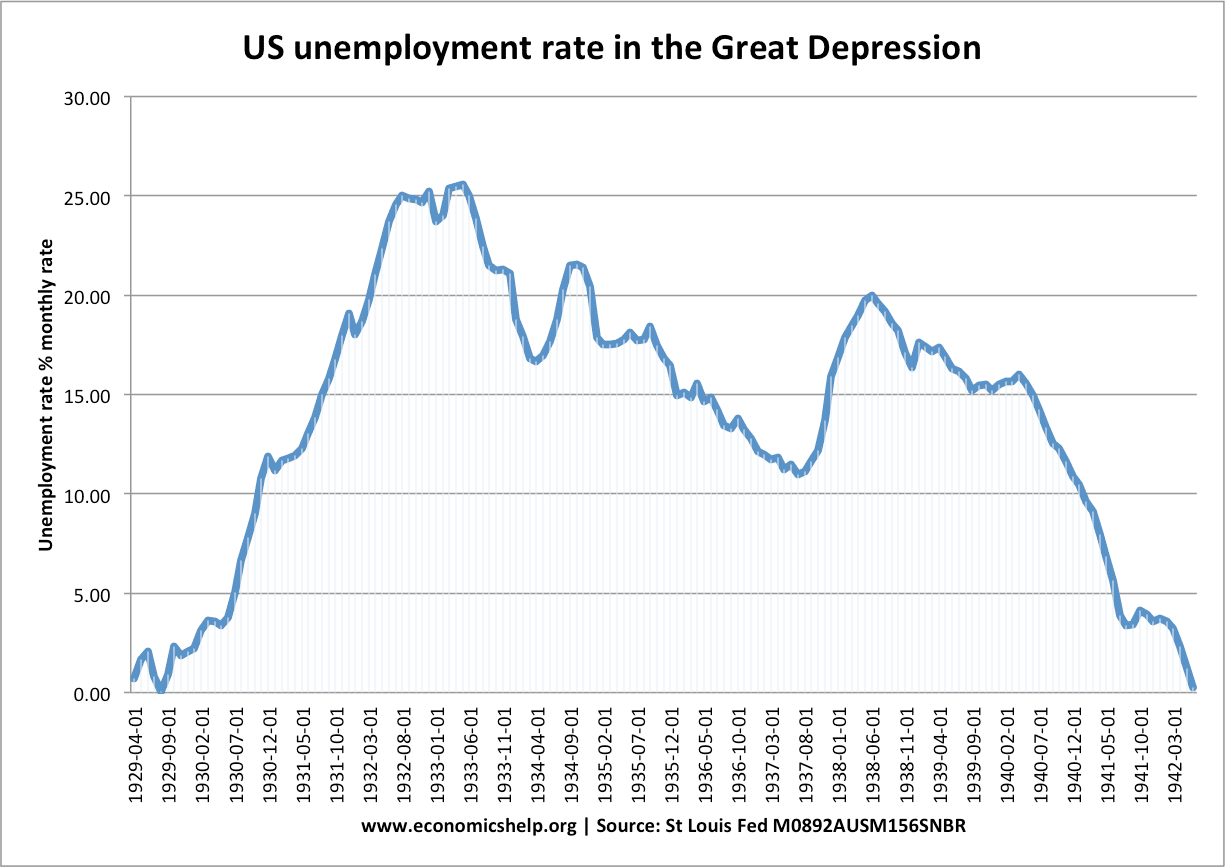
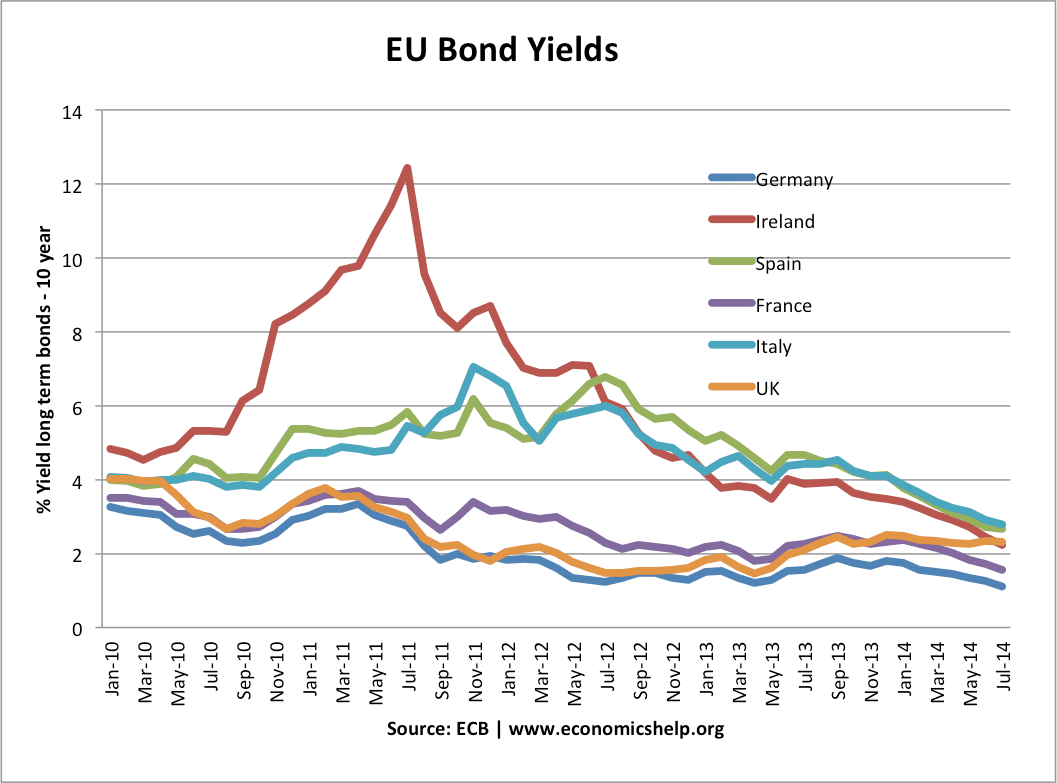
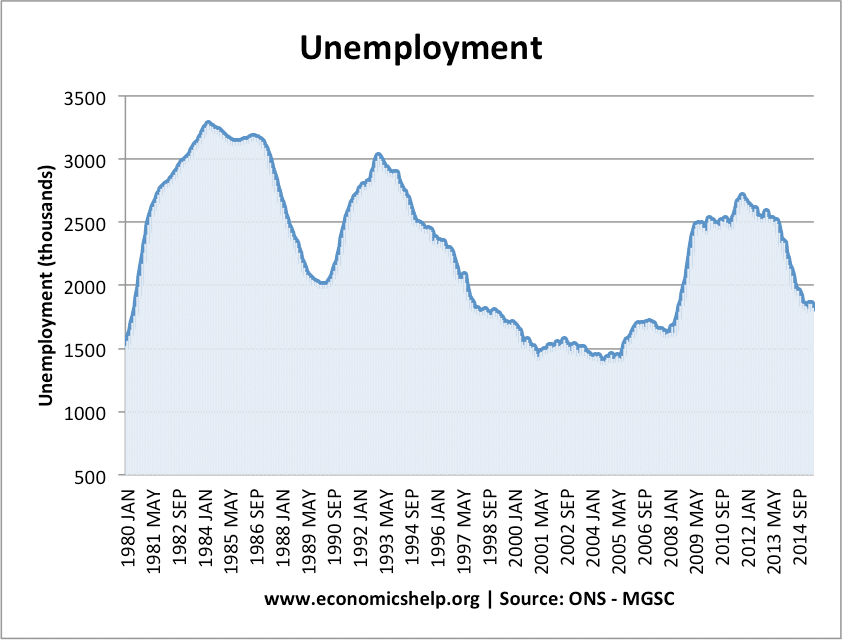
Definition of the housing market
The Housing Market refers to the supply and demand for houses, usually in a particular country or region. A key element of the housing market is the average house prices and trend in house prices. Definitions related to housing market UK nominal house prices – actually monetary value – not adjusted for inflation Real house …