One of the main issues in economics is the extent to which the government should intervene in the economy. Free market economists argue that government intervention should be strictly limited as government intervention tends to cause an inefficient allocation of resources. However, others argue there is a strong case for government intervention in different fields, such as externalities, public goods and monopoly power.

This is a summary of whether should the government intervene in the economy.
Arguments for government intervention
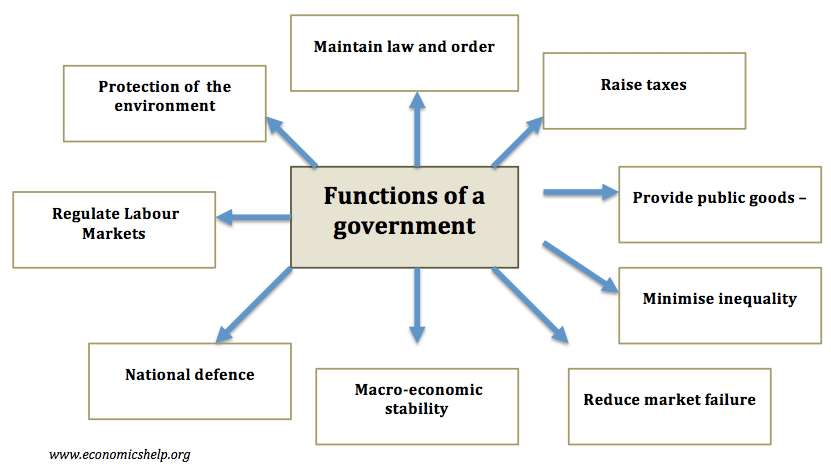
- Greater equality – redistribute income and wealth to improve equality of opportunity and equality of outcome.
- Overcome market failure – Markets fail to take into account externalities and are likely to under-produce public/merit goods. For example, governments can subsidise or provide goods with positive externalities.
- Macroeconomic intervention. – intervention to overcome prolonged recessions and reduce unemployment.
- Disaster relief – only government can solve major health crisis such as pandemics.
Arguments against government intervention
- Governments liable to make the wrong decisions – influenced by political pressure groups, they spend on inefficient projects which lead to an inefficient outcome.
- Personal freedom. Government intervention is taking away individuals decision on how to spend and act. Economic intervention takes some personal freedom away.
- The market is most efficient at deciding how and when to produce.
