A look at the changing profile of energy production in the UK.
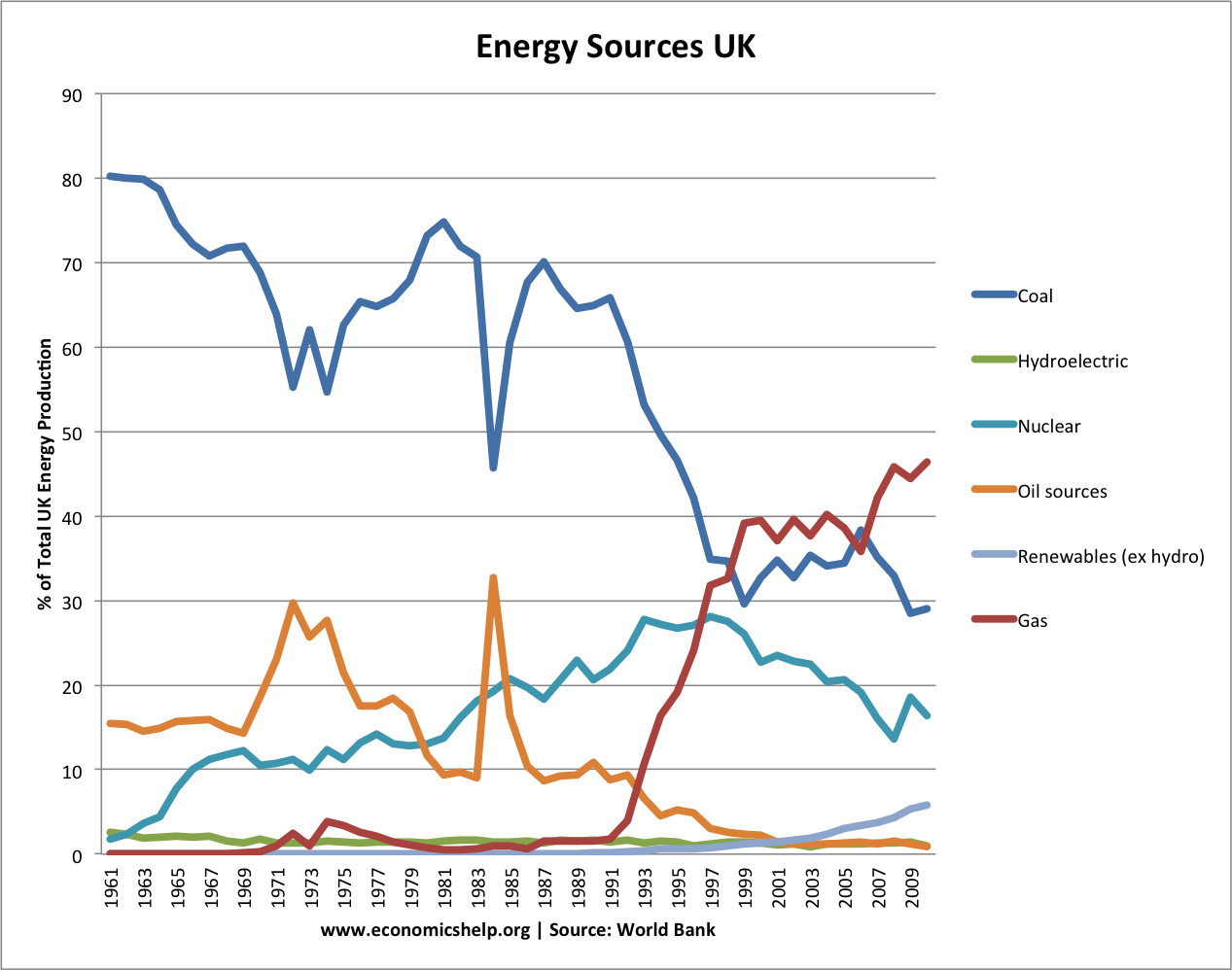
In the early 1960s, coal provided 81% of UK energy needs By 2010, this had fallen to 30%. At peak times in cold winters, coal use can increase to 40% of the UK’s electricity production. Despite a revival in coal production in the last year. A third of our current coal power stations are expected to close by 2016 so that they meet EU air quality legislation.
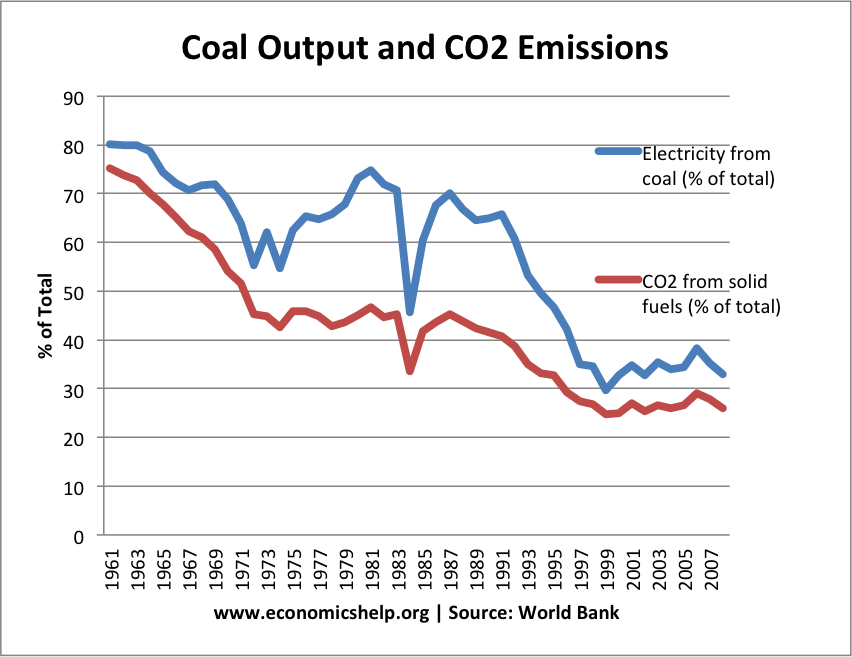
The % of electricity from coal has continued to fall. (The big drop in 1984 was the coal miners strike.)
Renewable Energy
Despite government commitments to using more renewable energy sources, the % of energy produced from renewable sources such as wind, solar and wave energy is still a fraction of the overall energy budget. On a practical level, wind power has proved controversial because it has a big impact on the landscape for the relatively small amount of energy created. (pros and cons of wind farms)
The government has a target of Britain producing 15% of its energy from renewable sources by 2020. However, green campaigners argue there is little prospect of that occurring.
Poverty v Green Energy
Rising energy bills have been a growing issue, with energy prices rising above the rate of inflation. This has created ‘fuel poverty‘ for those who spend a large proportion of their income on energy.
Currently, renewable energy receives government subsidies.
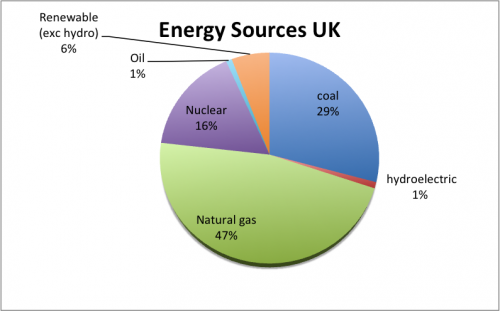
Energy sources UK 2010 – Source: World Bank.
CO2 Emissions Target
A big factor behind the decision to reduce reliance on coal power is the government’s commitment to target a cut in greenhouse emissions of at least 80% by 2050 compared with 1990.
Falling Coal Output and CO2 Emissions from Solid Fuels

3 thoughts on “Top Energy Sources in the UK”
Comments are closed.