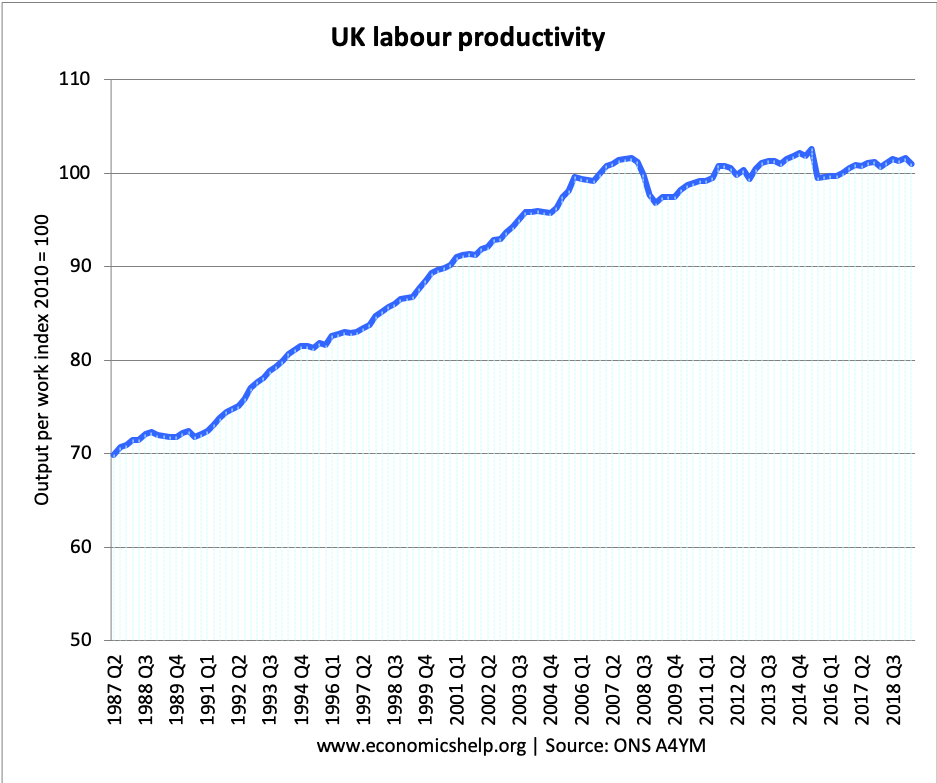
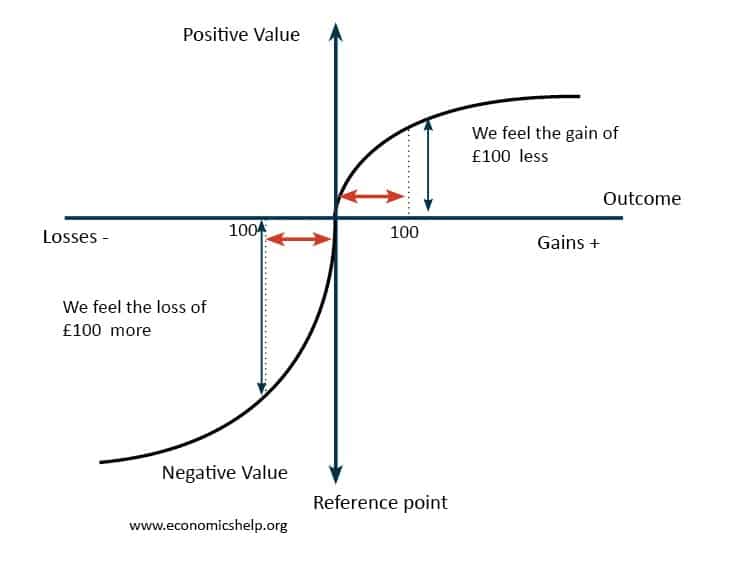
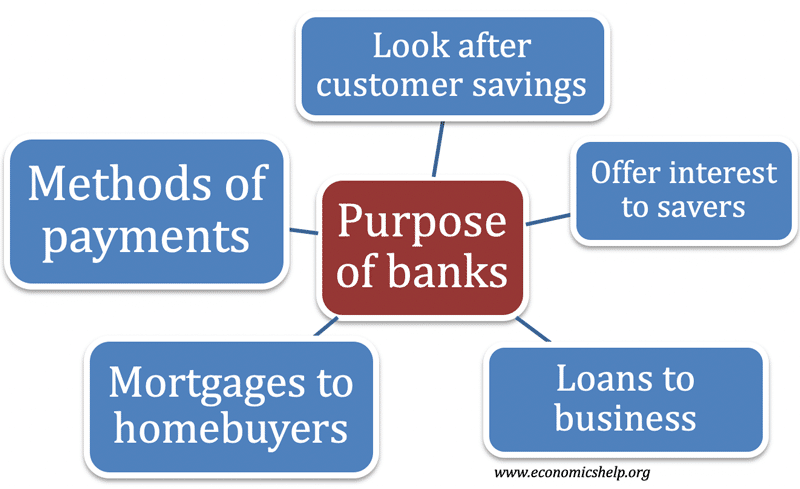
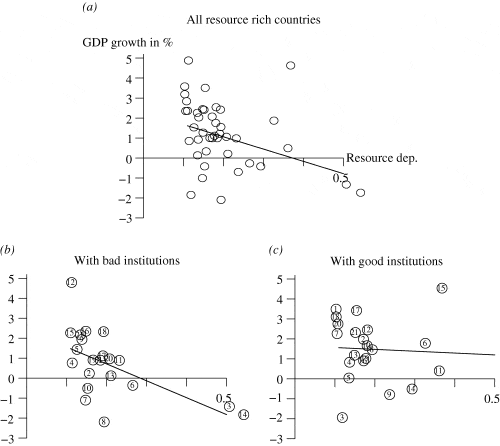
Product and Factor Markets
A product market refers to a place where goods and services are bought and sold A factor market refers to the employment of factors of production, such as labour, capital and land. Product market Demand for product markets comes primarily from households The main sellers of goods are different kinds of firms. Demand for goods …