Status Quo Bias
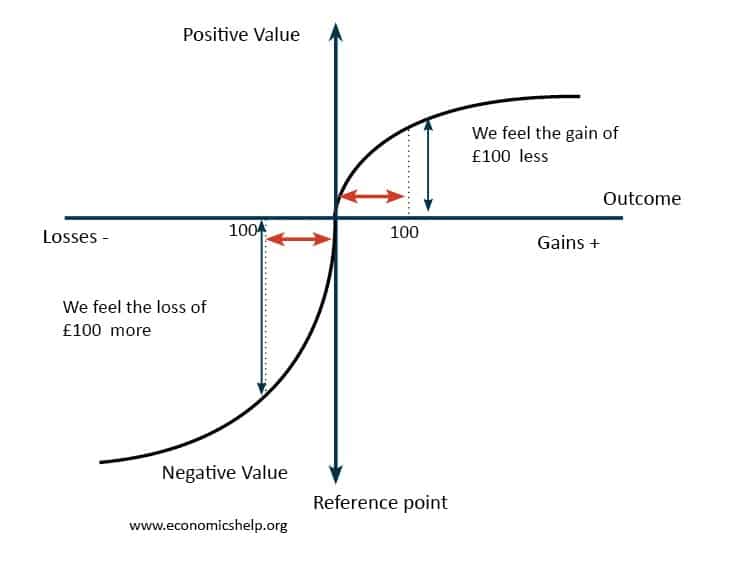
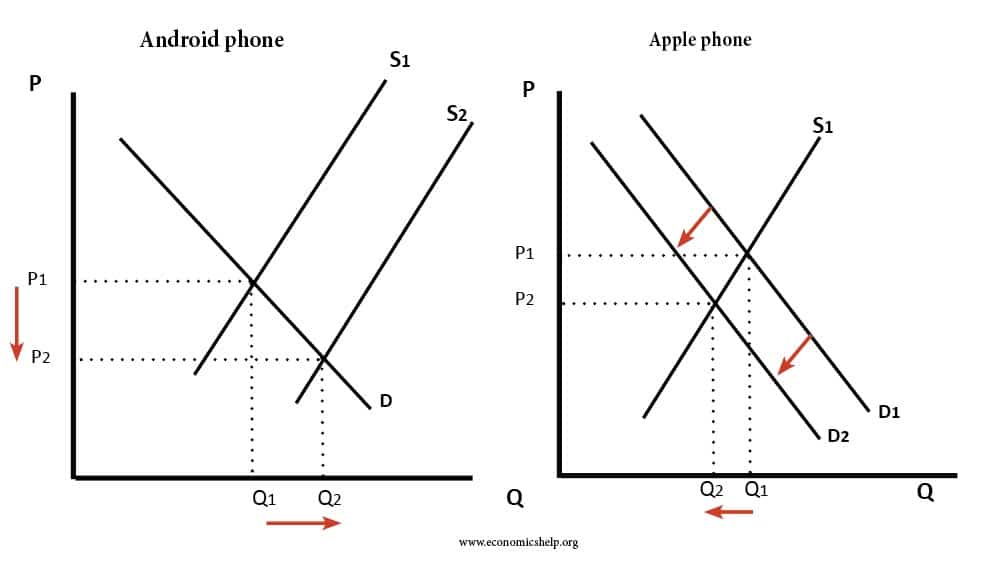
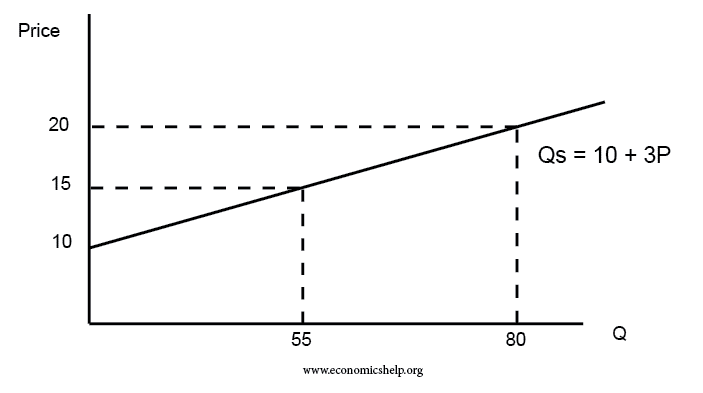
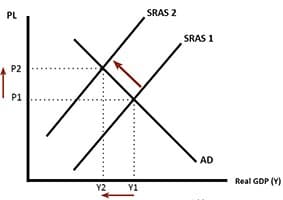
Status Quo bias is an emotional preference for the current situation. In economics, status quo bias can cause individuals to make seemingly non-rational decisions to stay with a sub-optimal situation. For example, over a lifetime, it is rational to save for a pension. However, some individuals may have a reluctance to change their current situation …