Most firms seek to become bigger – increasing sales and market share. Firms can grow through internal expansion, external growth (merger) or diversification into related industries. The motives for increasing in size can include:
- Greater sales lead to greater profit, making the firm more attractive to shareholders
- Successful, growing firms are likely to increase salaries/pay bonuses to managers.
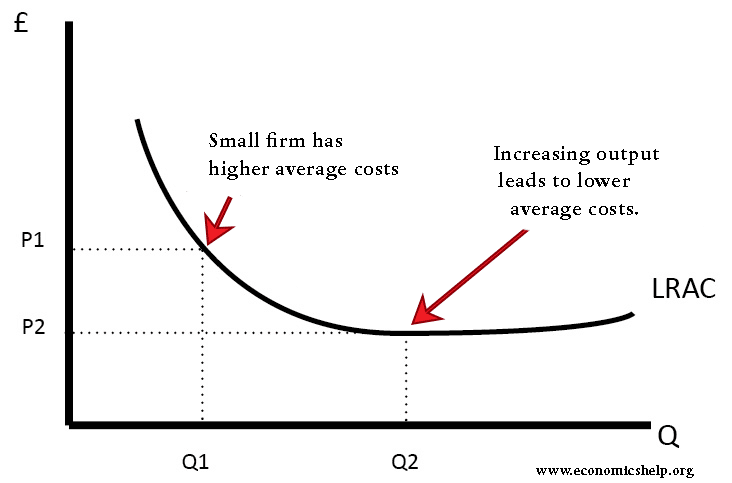
- Increasing output enables economies of scale, greater efficiency and lower average costs.
- Increased prestige for managers seeing the firm become more influential and powerful.
- Greater risk diversification, e.g. when growth comes from product diversification.
- Growing in size enables growth in market share and monopoly power, enabling even greater profitability.
- Owners having a passion for their product and wanting to see it do well.
- Globalisation has enabled firms to sell product in global market.
Reasons for firms growing
Profit motive
The profit motive is probably the biggest motive why firms try to grow in size. It is the incentive of profit which encourages owners to take risks to set up the business in the first place. When a firm has shareholders, there is a greater incentive to try and make profit to be able to pay shareholders a dividend. However, when a firm seeks to grow, there is no guarantee that it will be more profitable. To increase market share may require lower prices, which reduce profitability. If a firm seeks to grow in size by diversifying into related industries, it may lack the expertise to do well in these different industries, e.g if an old media firm like Time Warner buys a new internet firm like AOL, there is no guarantee that Time Warner can prosper in the internet industry.
Motivations of managers and workers
Managers and workers may prefer to work for a bigger firm. This is maybe in the hope of getting a better salary or it may just be the personal satisfaction of working for a successful firm. However, it depends on worker morale; it may be that many workers and managers have little desire to see the firm grow – growth may just increase their stress and responsibility. Therefore, rather than growing, firms may end up pursuing a type of ‘satisficing‘ where they do enough to keep their owners happy, but then pursue other objectives.
Economies of scale
Economies of scale are a justification for many mergers, which lead to a big increase in the size of firms. For industries with high fixed costs, growing in size may be necessary to stay competitive in a global market. For example, the building of airlines has become highly concentrated due to the very large economies of scale in that industry. Other industries like the car industry have also become increasingly concentrated with a smaller number of large firms dominating the market. Globalisation has definitely increased the speed at which large multinational companies have grown due to their global presence.