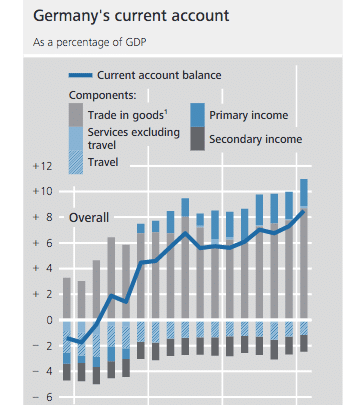
In 2015, the German current account surplus surged to 8.5% of GDP. A record level and a surplus which has implications for the Eurozone and global economy.
Source: Bundesbank
The surplus is primarily due to the surplus on trade in goods. Though in recent years, there has also been a surplus in primary income. This is mostly net income from foreign investment oversees.
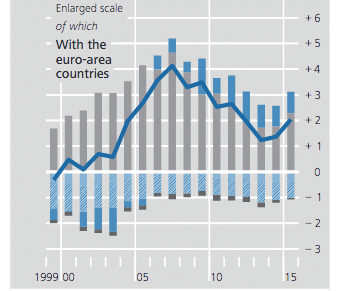
In the past few years, the German current account surplus with Eurozone countries has declined. This is mostly because of the weak growth and limited demand. The Eurozone recovery in the past 18 months, has seen the current account surplus rise back to 2% of GDP.
What does Germany produce?
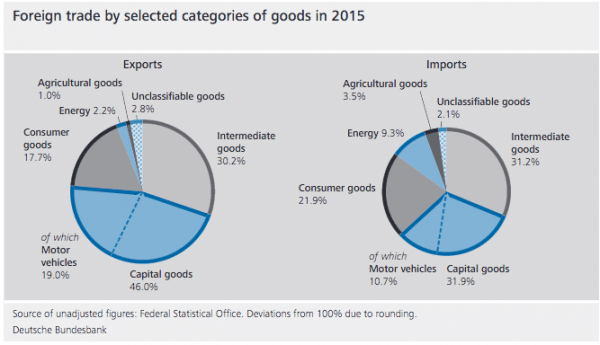
Germany is a net exporter of cars, capital goods, such as machines.
Top 10 Exports
- Vehicles: US$249 billion (18.7% of total exports)
- Machines, engines, pumps: $226.1 billion (17%)
- Electronic equipment: $131.1 billion (9.9%)
- Pharmaceuticals: $76.1 billion (5.7%)
- Medical, technical equipment: $61.5 billion (4.6%)
- Plastics: $60.7 billion (4.6%)
- Aircraft, spacecraft: $46 billion (3.5%)
- Oil: $33 billion (2.5%)
- Iron or steel products: $29.1 billion (2.2%)
- Organic chemicals: $26.9 billion (2%)
Source top 10 exports
It is a net importer of oil, energy and food.
In 2015, exports accounted for 35% of total German economic output
Causes of German current account surplus
1. Undervaluation of Euro. Since 2000, German unit labour costs have risen by about 20%-30% less than its main Eurozone competitors. This means German exports have become roughly 20% more competitive, but there has been no change in the exchange rate – The Euro permanently fixes the exchange rates. If Germany had its own currency, we would expect the D-Mark to appreciate by 15-20%
If Germany still had the D-Mark, it is almost certain that the increased competitiveness of German exports would have caused an appreciation in the German currency. This appreciation would have rebalanced demand – lowed export demand, and encouraged more German imports. A flexible exchange rate would have moderated the rise in the German current account surplus. The current account surplus would have much much less than 7% of GDP. But, in the Euro, there is no currency revaluation.
2. Strong export sector. German manufacturing has done relatively well in recent years. There have been improvements in productivity, and high-tech German exports have weathered the global downturn, better than many other countries. For example, Germany is less affected by the financial services decline like the UK; Germany is less affected by increased competition on low tech manufacturing industries like Italy.
3. Weak consumer demand. German economic growth has been increasingly dominated by exports. Domestic saving is high and consumer spending weak. Therefore, German growth is coming from exports rather than consumer spending.
4. Saving greater than investment. In 2015, saving was 25% of GDP (driven by ageing population), whearas investment was 16% (indicating weak economic growth). This indicates a large savings surplus. This contributes towards a current account surplus because spending (on imports) is low
5. Fall in oil prices. Part of the recent rise in the German current account surplus is a decline in oil and gas prices. As Germany is a net importer, the fall in price of oil has reduced the value of imports, causing a bigger surplus.
Does the German current account surplus matter?
Some economists argue that a large current account surplus limits growth in other countries. German exports to other countries but is not important. The large current account surplus and undervaluation of currency was good for Germany, but it was holding back exports in other countries. If Germany boosted domestic demand and allowed slightly higher domestic inflation, they would provide a much needed boost to global demand and help to overcome unemployment in other countries.
The real problem of the German current account surplus is not for the US (they can still devalue against the Euro and have their own monetary policy). The real problem is faced by countries in the south of Europe who are experiencing severely depressed domestic demand.
Given the imbalances in the Eurozone, southern European economies face a long period of deflation as they slowly seek to restore competitiveness against their northern competitors. However, given European wide austerity, this period of deflation is proving very costly in terms of lost GDP and high unemployment.
If Germany was willing to boost domestic consumption, and temporarily target higher inflation, this would provide greater export demand within Europe. A lower German current account surplus would help increase economic growth in southern Europe. Given the debt crisis and lack of growth, export led growth would be very welcome for easing the depth of the recession.
However, Germany is currently unwilling to pursue any policy which risks a slight deviation from the inflation target. (The ECB increased interest rates in 2011 over concerns about inflation). Therefore, with domestic demand constrained, the German current account surplus is likely to remain. This will be a factor in keeping demand elsewhere in Europe depressed.
Why can’t everyone be like Germany?
Some argue that the Eurozone crisis shows that southern European economies need to be more like Germany / Netherlands. Rather than relying on devaluation – this crisis should be the spur to cut unit labour costs, increase productivity, remove inflexibilities in the economy and boost exports. But, as many have pointed out, you can’t have every country having a current account surplus of 8% of GDP! – Not every country can benefit from have an undervalued exchange rate. Secondly, the structural reforms to restore competitiveness take a long time and are creating great economic pain. In theory, it sounds fine – restore competitiveness. But, in practise in requires several years of deflation, mass unemployment and wasted resources – which creates a negative multiplier effect. The kind of price readjustment we are seeing in southern Europe could lead to painful social disorder.
Evaluation –
Some may disagree with the extent to which current account imbalances are the source of the Eurozone crisis. They may argue that current account deficits in the south are rapidly falling – but there is limited signs economic growth. It is true that competitiveness is not the only issue and cause of the Eurozone crisis.
However, The current account deficits are falling primarily because of weake domestic consumption. If you have a deep recession because of austerity, imports will fall – improving the current account. However, there still needs to be a more positive rebalancing of European demand. Germany could learn to love a little bit of inflation and investment. It might prove less painful than the continued request to bailout countries in the throes of debt deflation.
Past trade imbalances
A few years ago, global trade imbalances were dominated by China and the US. At its peak, China’s current account surplus reached over 10% of GDP. By contrast, the US current account deficit reached over 6% of GDP. The classic image was of China manufacturing goods, selling them to the US consumer.
Then with this export revenue, China bought US Treasuries to keep the Chinese Yuan permanently undervalued. Many in the US criticised China for this ‘currency manipulation‘ – In fact, Mitt Romney, the 2012 Republican Presidential candidate, promised to label China a currency manipulator from day one. However, Romney was really a couple of years behind reality.
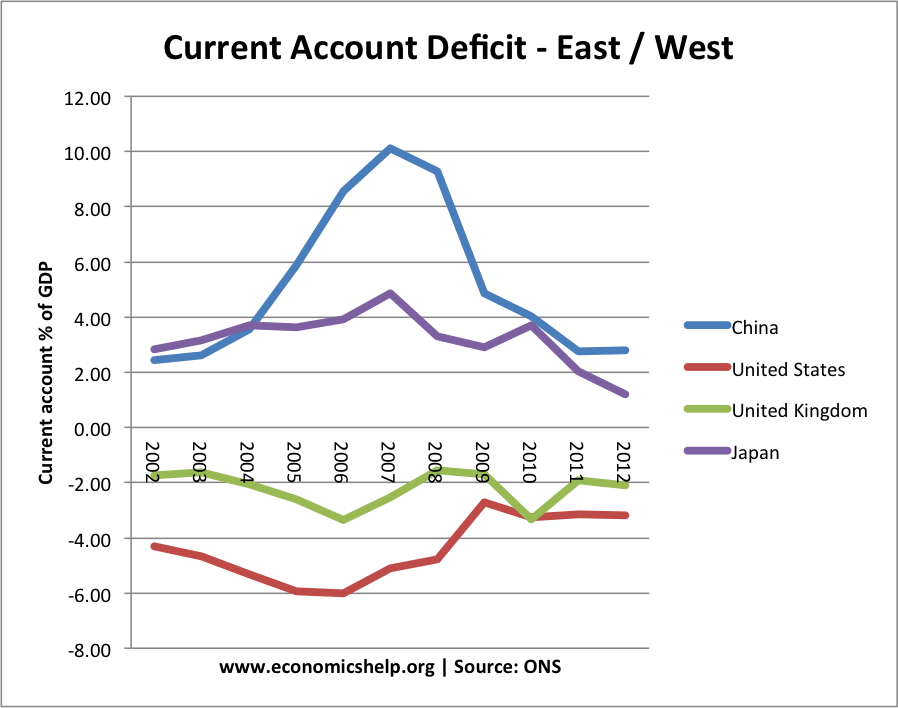
China still has a current account surplus, but it has fallen from 10% of GDP to 2.6% of GDP in 2012. China’s currency is no longer chronically undervalued, and the Yuan has appreciated 40% in real terms against the Dollar since 2005. Although China’s economy is still reliant on exports and investment, it has begun a process of rebalancing the economy. It is not the same source of global imbalances that it was five years ago,
The biggest global imbalances, in absolute terms, now come from Germany, who have seen their current account surplus to continue to increase. In Q3 2012, their current account surplus widened to $58 211 million (equivalent to an annualised surplus of $ 232,844 million – (7.0% of GDP) OECD)
Current account deficits
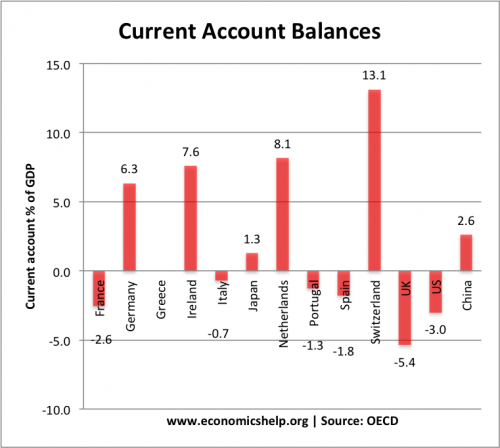
The largest current account surplus is in Switzerland (13.1% of GDP) though this reflects the unique challenges Switzerland faces as a safe haven resort (investors trying to save money in a safe currency are pushing up the Swiss Franc causing an appreciation.)