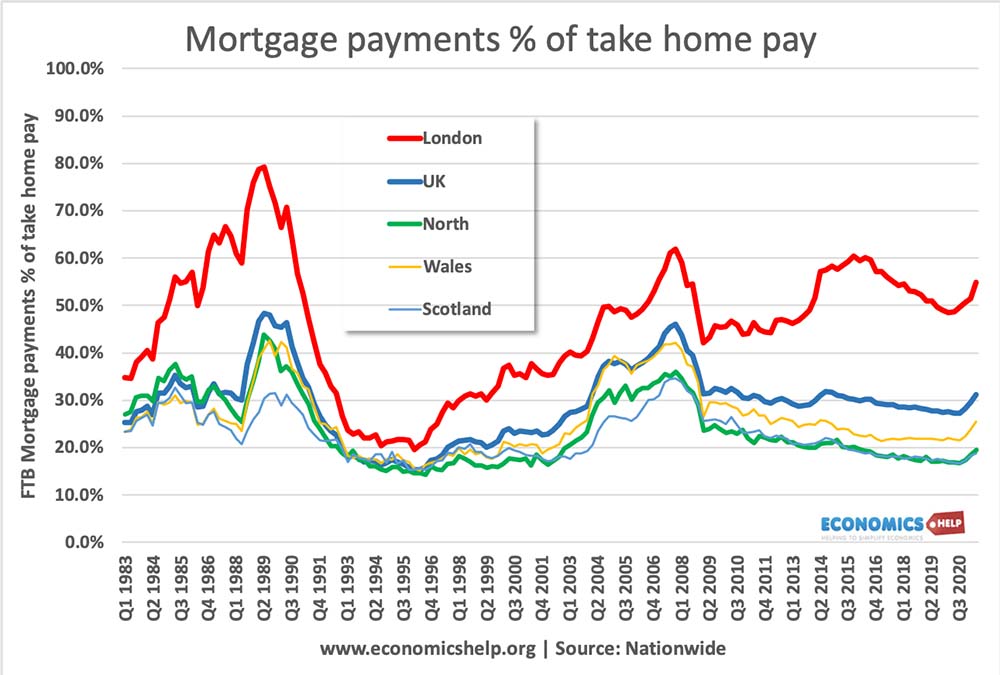
The throw-away economy refers to the prevalence of consumer goods which only last for a short period of time. When they stop working / no longer relevant, we throw them away and replace them with new goods.
This is in contrast to an economy where resources are more scare – and if a good is purchased, we expect to make it last a considerable time – repairing if necessary.
For example, in the past, if our socks had a hole, we would sew them up (‘darning’ your socks). But, these days, if socks get a hole, it is more convenient to throw them away and buy some cheap socks instead.
If average wages are £10 an hour. Why spend 30 minutes sewing your socks, when you can buy a new pair for £3? In the past, wages were much lower compared to prices. If you only earnt £1 an hour, then it is worth sewing your socks to save buying a new pair for £3.
Therefore, rising real wages make a throw-away economy more likely.
Repair shops

In the past, there were many TV repair shops – if your tv or electronic goods broke down, you would try to have them fixed. In today’s world, if a TV broke down, we would be liable to throw away the TV and buy a new one. It is not so expensive and electronic goods are always offering new features. After a couple of years, your electronic goods can feel ‘outdated’ pretty quick. I have a stack of CDs I don’t play in CD players any more.
The problem of the tin openers

The inspiration for this post has been the number of tin-openers we have got through in the past 12 months. We have bought four tin openers, all of which have ceased working after a short period of use. In each case, we have thrown it away and bought a new one. The first two were from Sainsburys and Asda. They cost about £4 and looked fairly robust. But, after a few weeks, they stopped working properly, and then failed completely. My lodger uses the tin-opener most, so I told him since I paid £5 for a tin-opener and it stopped working, he might as well go get one from a Pound shop. The first tin opener did open one can of Heinz soup then it snapped. 99p to open one tin! That is called a false economy!
He took it back to the 99p shop and the workers laughed. They obviously got returned tin openers all the time. He got a replacement, but that broke straight-away, even before opening a tin.