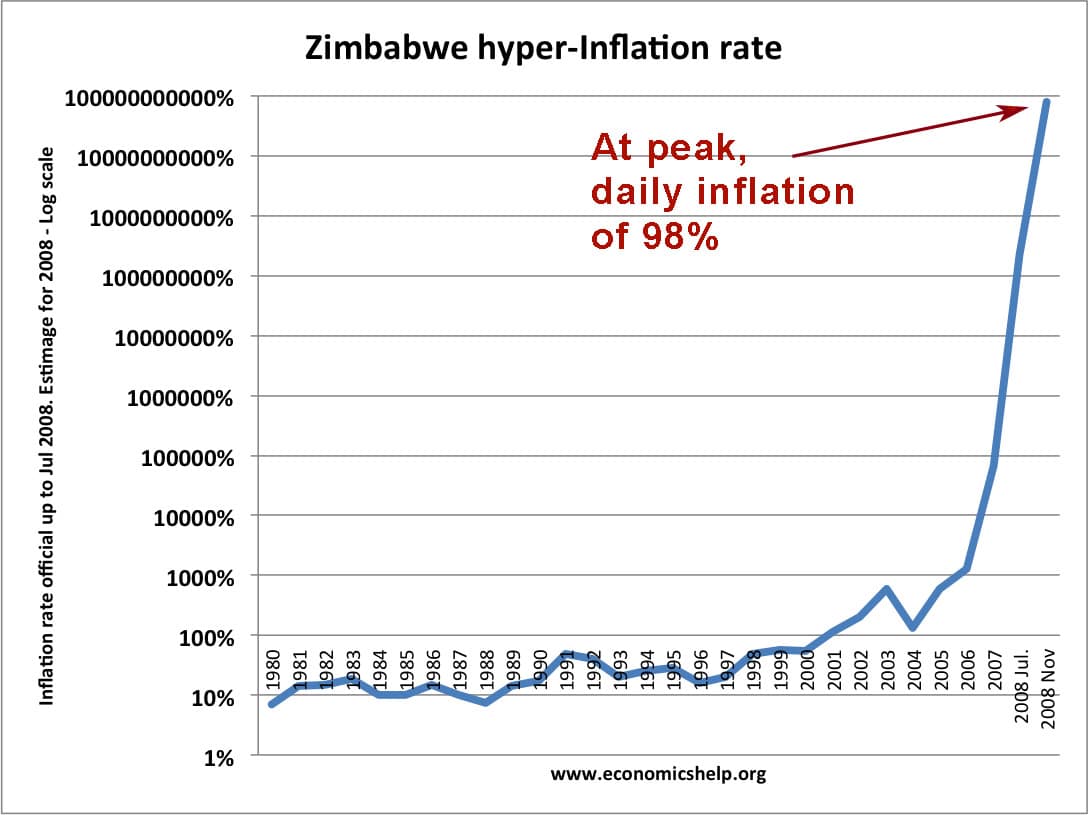
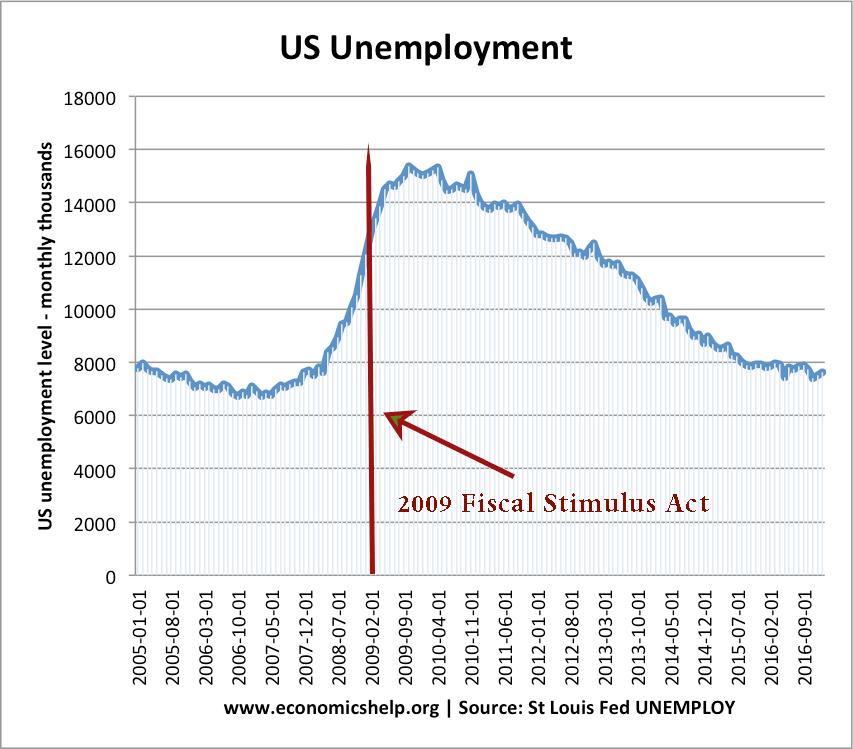
In 2008, Zimbabwe had the second highest incidence of hyperinflation on record. The estimated inflation rate for Nov 2008 was 79,600,000,000%
That is effectively a daily inflation rate of 98.0. Roughly every day, prices would double. It was also a time of real hardship and poverty, with an unemployment rate of close to 80% and a virtual breakdown in normal economic activity. The hyper-inflation was caused by printing money in response to a series of economic shocks.
(The highest hyperinflation rate was Hungary 1946 with a daily inflation of 195%)
Causes of hyper-inflation in Zimbabwe
- Government printing money in response to:
- High national debt
- Decline in economic output.
- Decline in export earnings.
- Price controls which exacerbate shortages.
- Lack of confidence in government, economy and political life.
- Expectations of hyperinflation
- In the late 1990s, the Zimbabwe government introduced a series of land reforms. This involved redistributing land from the existing white farmers to black farmers. But, with little experience, the new farmers struggled to produce food, and there was a large fall in food production.
- The economy experienced a sharp fall in output (both agricultural and manufacturing), and this caused a collapse in bank lending.
- The government began increasing the rate at which they were printing money and increasing the money supply. This started with printing money to finance a war in the Congo and also to increase the salaries of officials and soldiers. But, as the economic crises worsened, printing money became a very short-term solution to try and placate people relying on government pay.
- With the economy in decline, government debt increased. To finance the higher debt, the government responded by printing more money, which caused more inflation. Inflation meant bondholders saw a fall in the value of their bonds and so it was hard to sell future debt.
- The economy also experienced many shortages of goods.
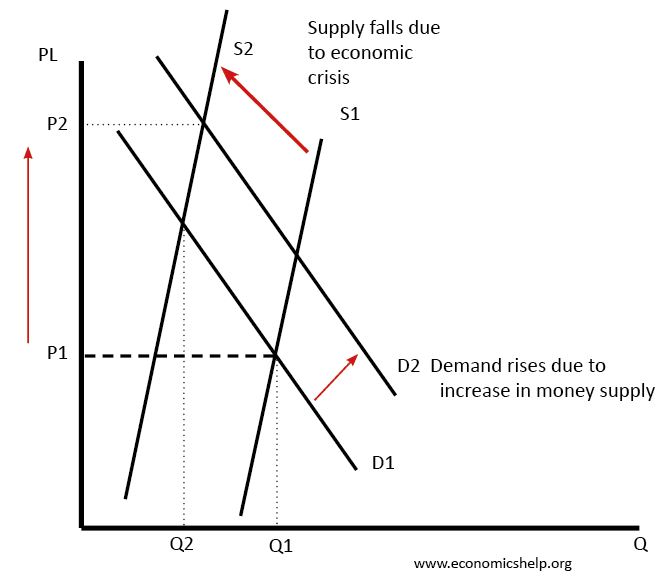
- Due to the decline in output, there were shortages of goods, which pushes prices up. Nominal demand was rising because people had more paper money. This combination of more money chasing fewer goods caused very rapid rises in price. When there is a shortage – prices rise. Combined with printing more money and this shortage of actual goods, prices rose rapidly.
Price control
Ironically, this shortage of supply was made worse by the imposition of price controls. Price controls set the price for basic goods (the idea was to keep prices affordable and stop inflation). But, because the cost of production increased faster than prices, suppliers had little incentive to supply the goods (at least through the official channels). This made the shortage worse and the actual inflation worse.
Expectations
Zimbabwe had high inflation since the mid-1960s. People became accustomed to expecting more inflation. This then becomes self-fulfilling. If people expect hyperinflation, they demand higher wages and push up prices in anticipation of higher inflation in future.
Inflation Rates in Zimbabwe
| 1996 | 16% |
| 1997 | 20% |
| 1998 | 48% |
| 1999 | 56.90% |
| 2000 | 55.22% |
| 2001 | 112.10% |
| 2002 | 198.93% |
| 2003 | 598.75% |
| 2004 | 132.75% |
| 2005 | 585.84% |
| 2006 | 1,281.11% |
| 2007 | 66,212.30% |
| 2008 Jul. | 231,150,888.87% |
| 2008 Nov | 79,600,000,000% |