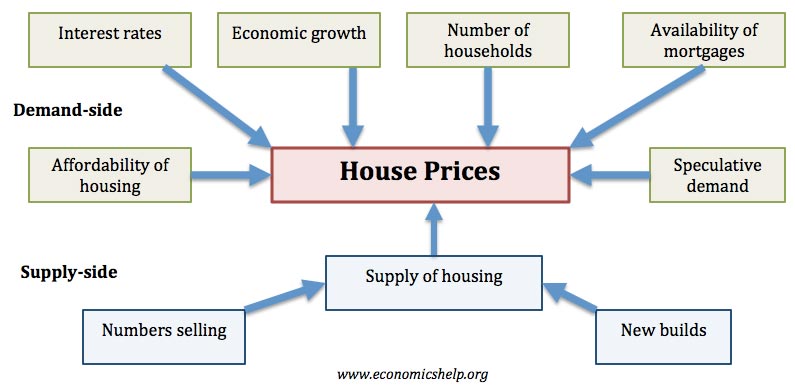
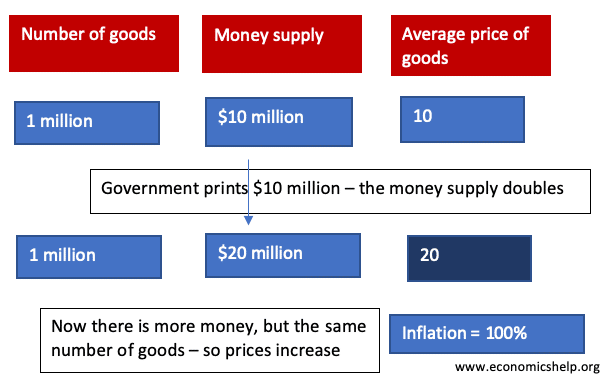
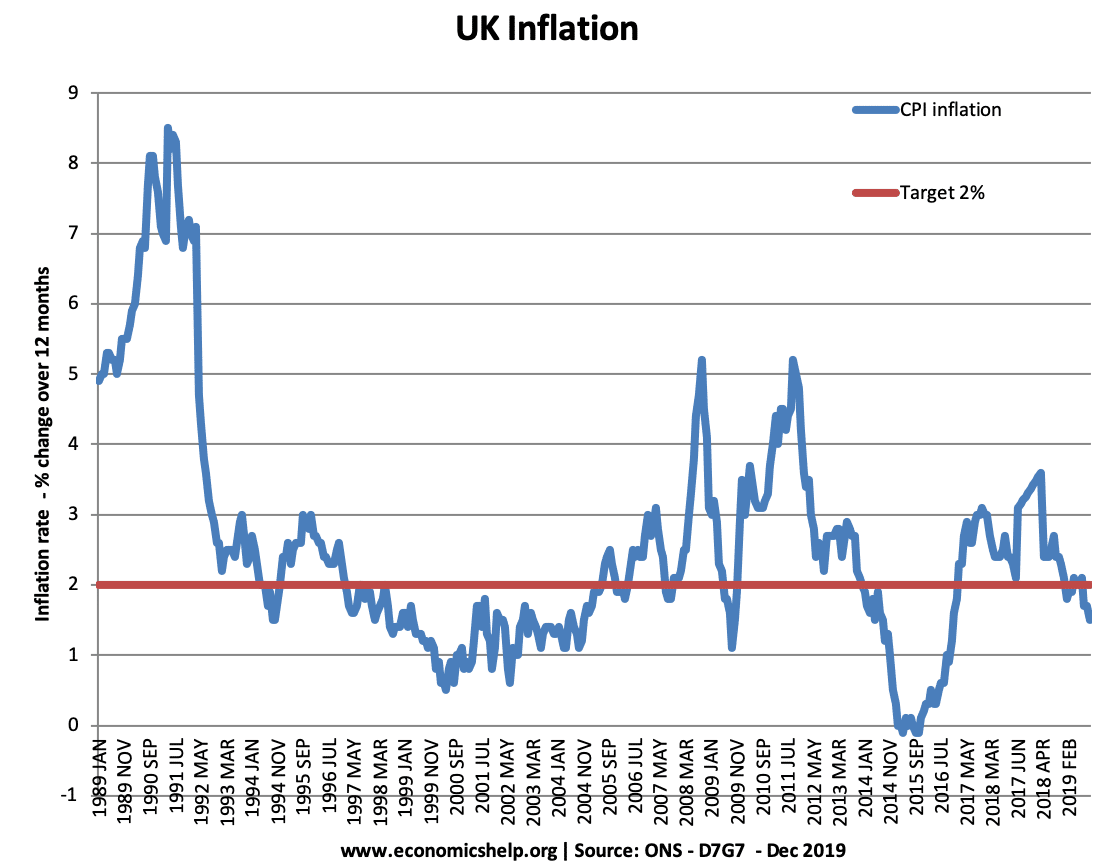
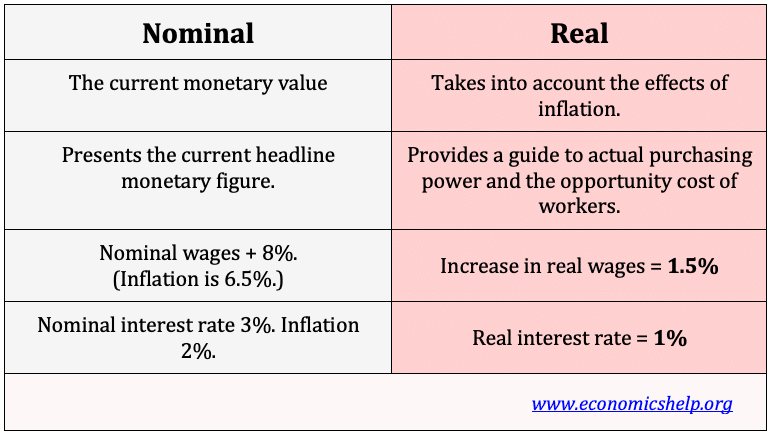
Privacy Policy
Who we are Economicshelp.org is managed by Tejvan Pettinger, Oxford, UK. We can be contacted here Comments When visitors leave comments on the site we collect the data shown in the comments form, and also the visitor’s IP address and browser user agent string to help spam detection. Managing Cookie Preferences [wt_cli_manage_consent] You can manage …