AQA GCSE Revision Guide (Network license)
- An AQA GCSE Economics Revision Guide produced by economicshelp.org
- It includes all the topics for AQA GCSE Economics
- GCSE Revision Guide 113 pages.
- Network license £85.00
- Comes in pdf format (e-book)
- Last updated July 2022
Table of contents
- 1.1.1 Economic activity
- 1.1.2 Factors of Production
- 1.1.3 Making choices/opportunity cost
- 1.3.1 Demand
- 1.3.2 Supply
- 1.3.3 Equilibrium
- 1.3.4 Intermarket relationships
- 1.3.5 Elasticity of demand
- 1.3.6 Price Elasticity of Supply
- 1.4 Production, costs, revenue and profit
- 1.4.2 Production and productivity
- 1.4.3 Economies of Scale
- 1.5 Competition
- 1.5.2 Competitive Markets
- 1.5.3 Monopoly/non-competitive markets
- 1.5.4 The Labour Market
- 1.6 Market failure
- 1.6.2 Externalities
- 2.1 The national economy
- 2.1.2 Government income and expenditure
- 2.2.1 Economic Objectives of the government
- 2.2.2. Economic growth
- 2.2.3 Employment and Unemployment
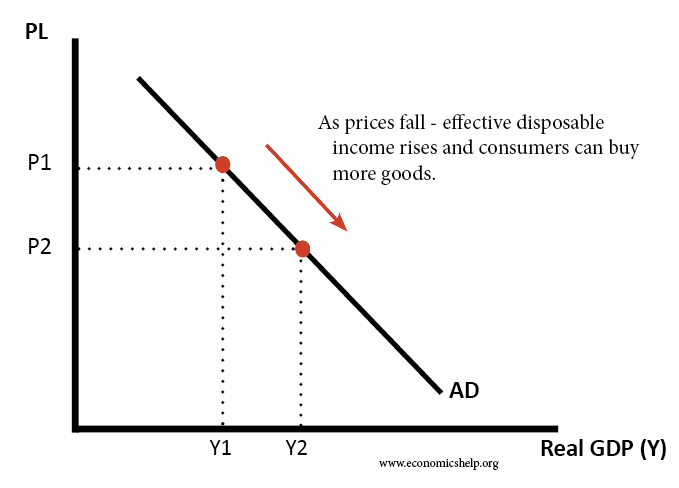
- 2.2.4 Inflation and Price stability
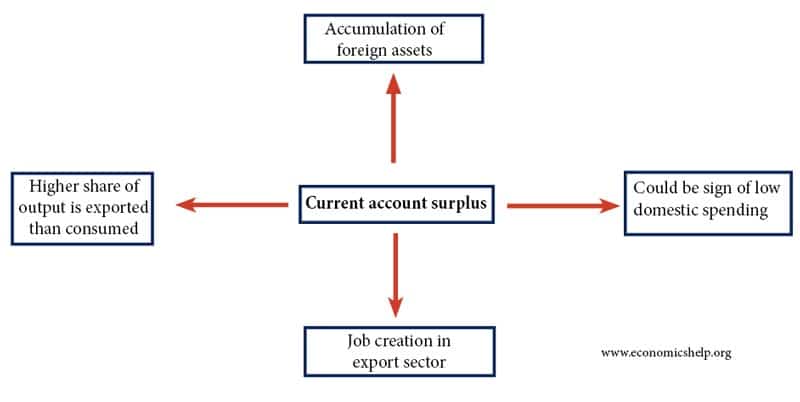
- 2.2.5 Balance of payments
- 2.2.6 Distribution of income
- 2.3.1 Fiscal Policy
- 2.3.2 Monetary Policy
- 2.3.3 Supply-Side Policies
- 2.4 International trade and the Global Economy
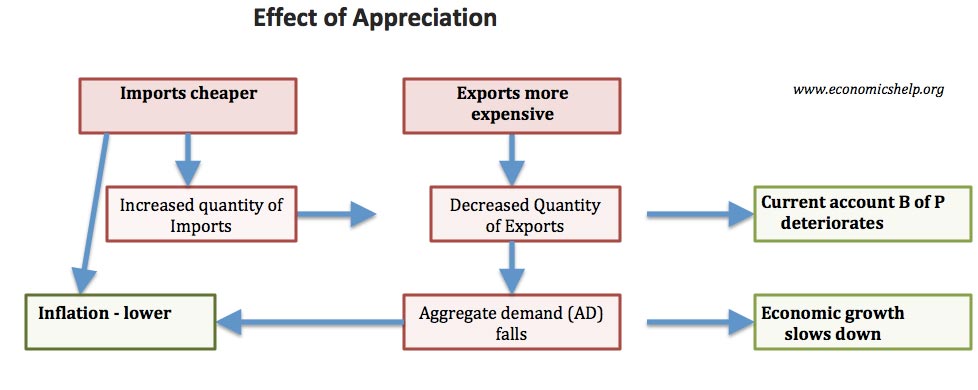
- 2.4.2 Exchange Rates
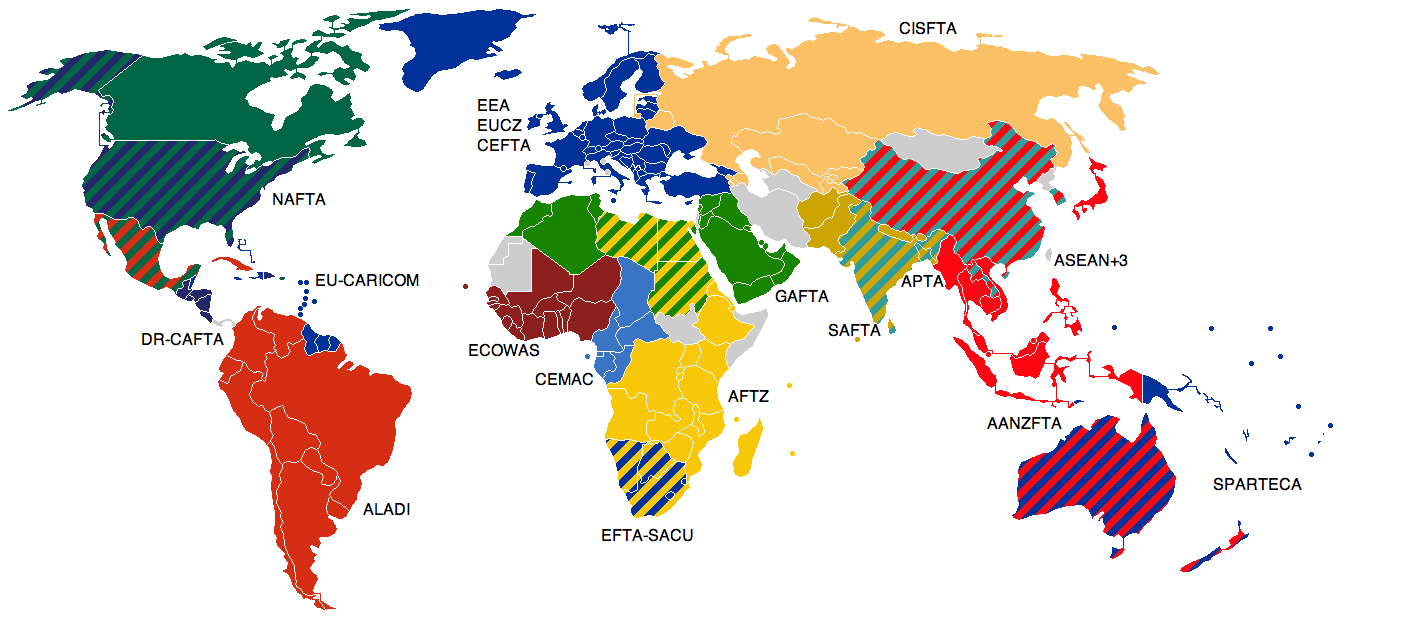
- 2.4.3 Free-trade agreements
- 2.4.4 Globalisation
- 2.5.1 The role of Money
- 2.5.2. The financial sector