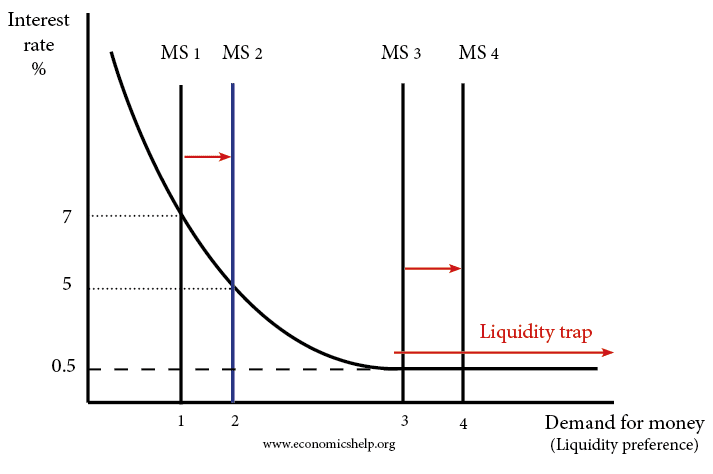
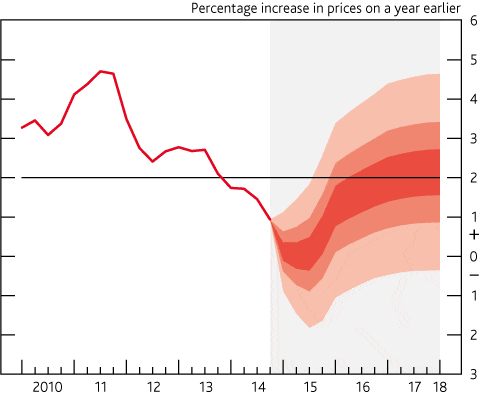
Primary Products: Advantages and Disadvantages
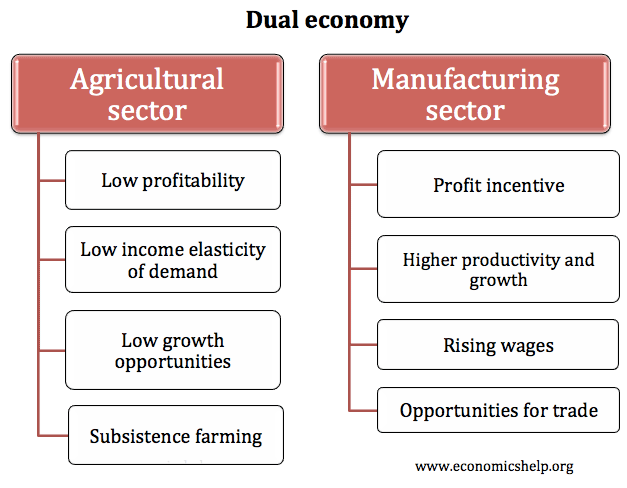
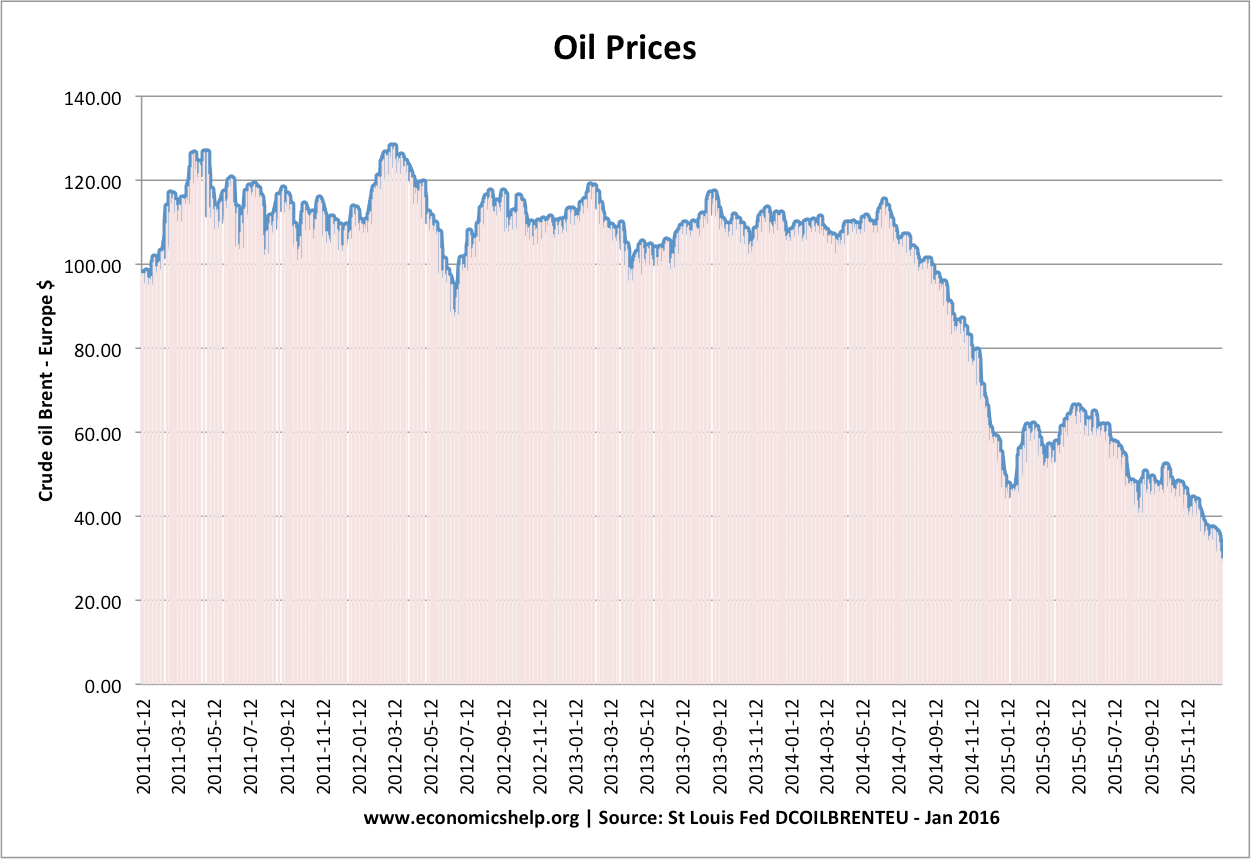
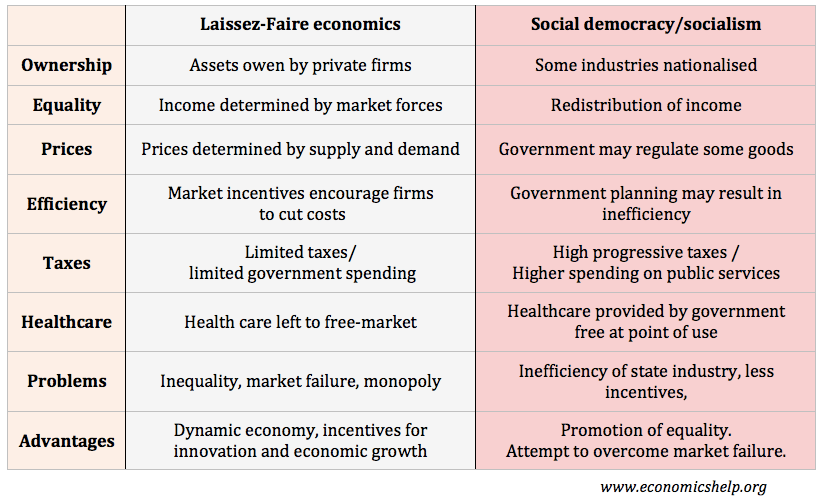
What are the advantages and disadvantages for a developing economy, such as Ghana if it is dependent on primary products? Definition of Primary products: Raw materials and resources used in the productive process. Examples include metals, agricultural products and minerals. Advantages of Producing Primary Products For many developing economies, their main comparative advantage will be …