Paradox of Value – Definition, Explanation, Examples
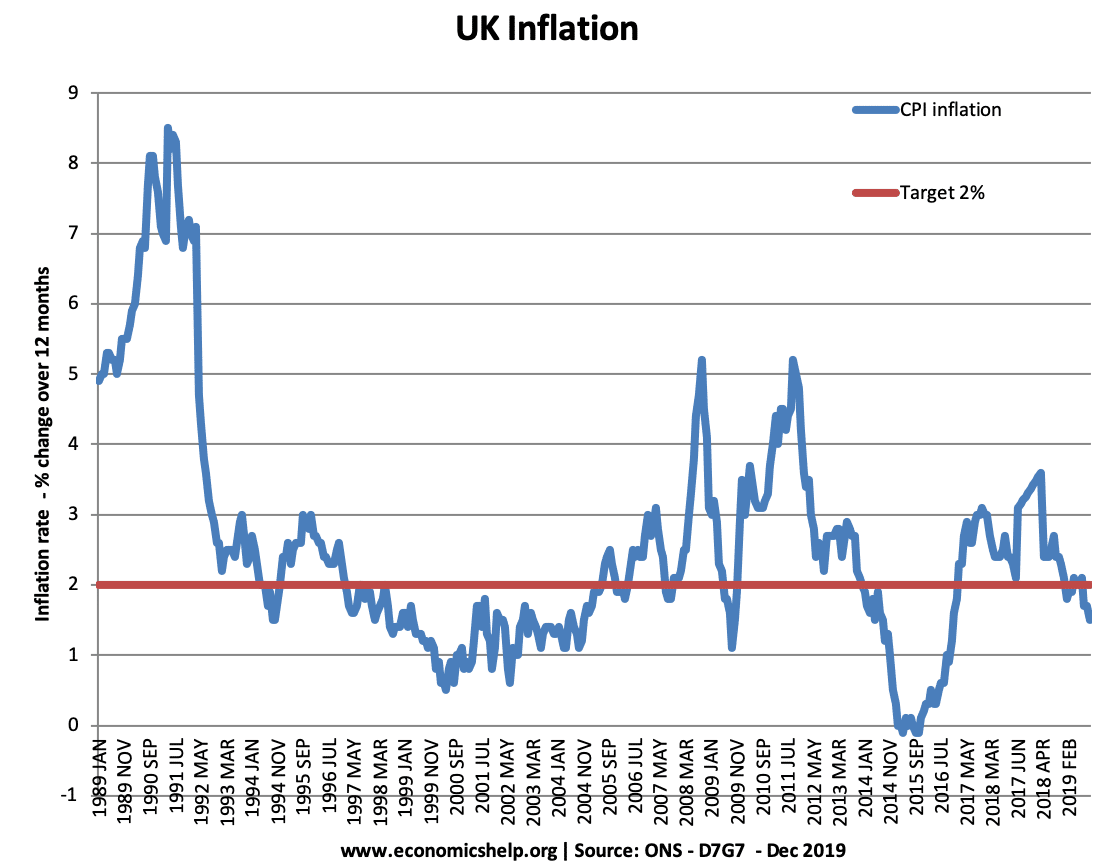
Definition The observation that some goods (e.g. water) which are more essential to human life can be cheaper than non-essential goods (e.g. diamonds) Paradox of value – Economics explainedWatch this video on YouTube Explanation The paradox of value examines why goods that are not essential to life can command a much higher price than goods …