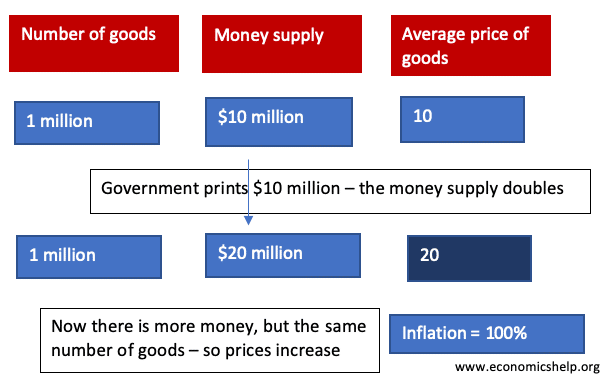
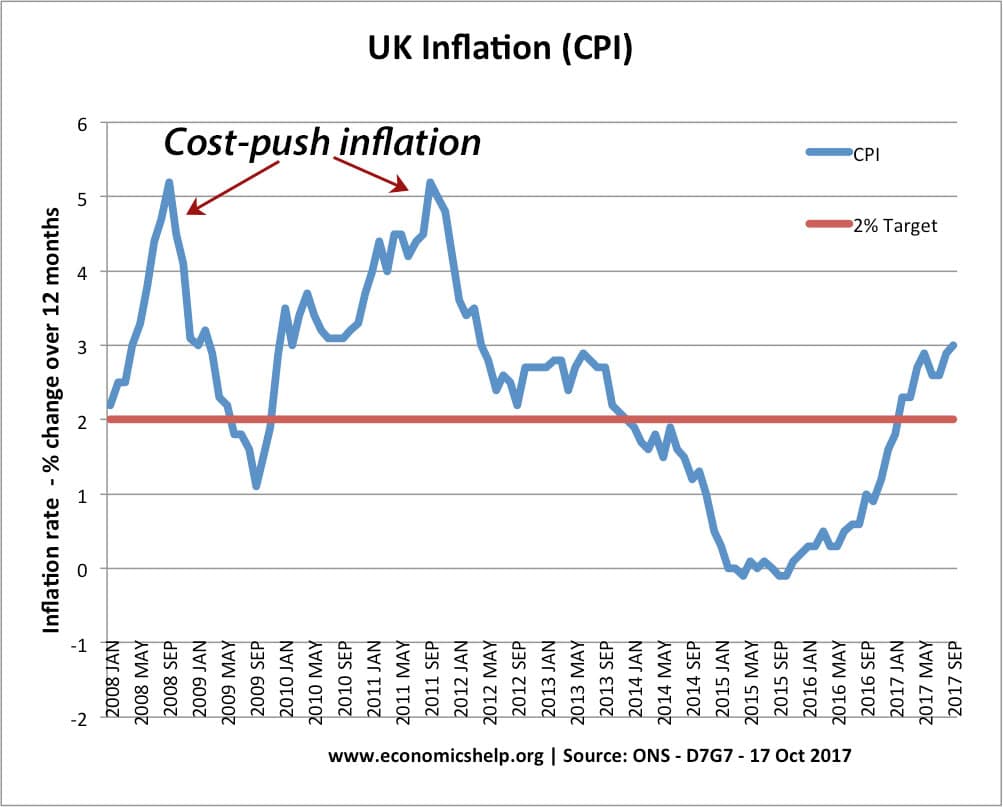
What causes a government to default on its debt
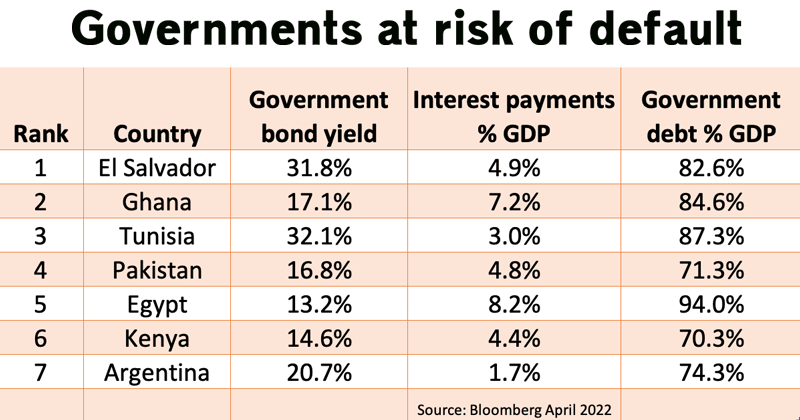
Earlier this year, the World Bank warned up to 40 nations are at risk of defaulting on their sovereign debt. Already Sri Lanka, once hailed as an economic jewel, has badly defaulted as the country slides into economic turmoil. But, the bank warns many others, such as El Salvador, Ghana, Tunisia, Egypt, Kenya and Argentina …