Investment and Aggregate Demand
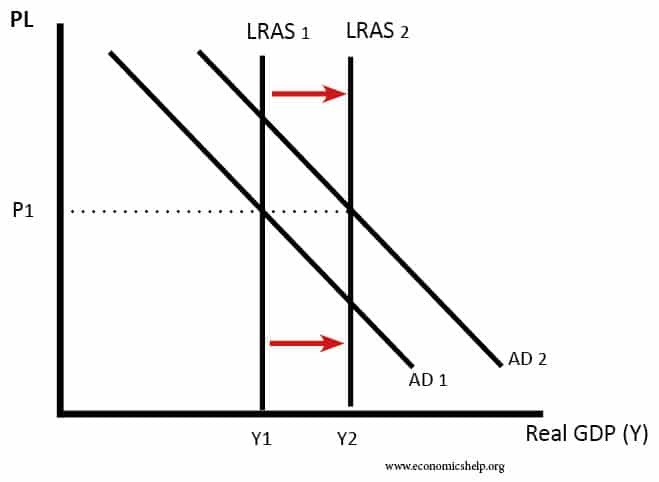
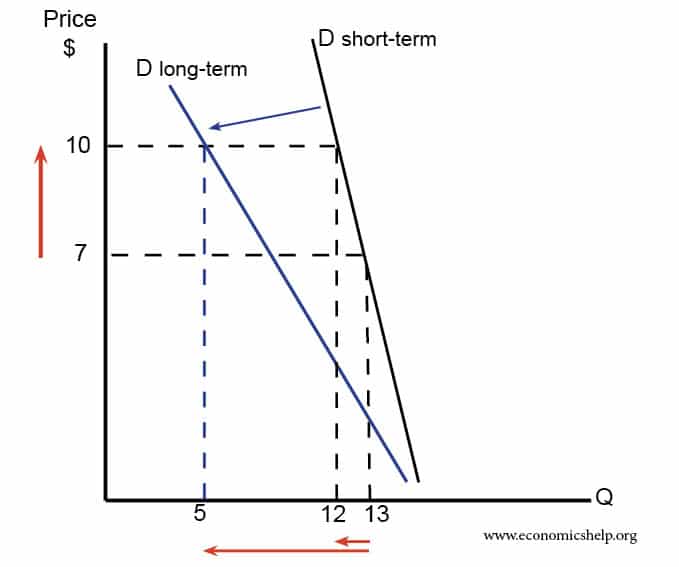
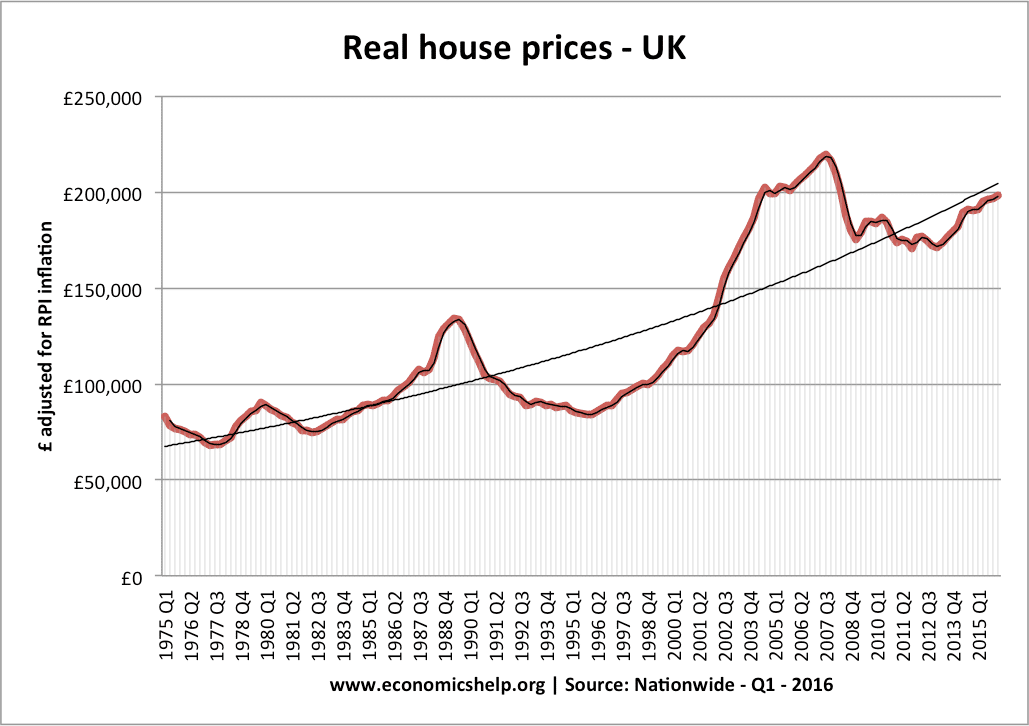
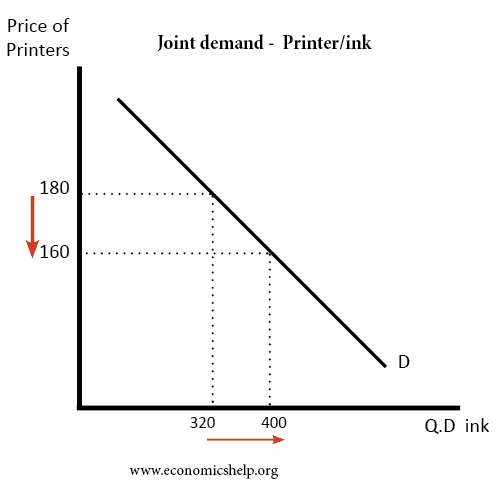
Readers Question: What are the effects of increased investment on aggregate demand in the short term and the long term. Investment means capital expenditure (e.g. purchasing machines or building bigger factory) Investment is a component of AD – AD+ C+I+G+X-M. Investment spending takes about 15% of AD; it is not as significant as consumer spending …