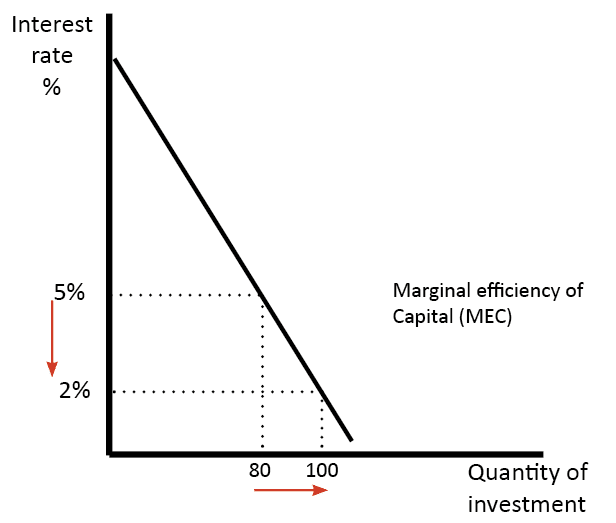
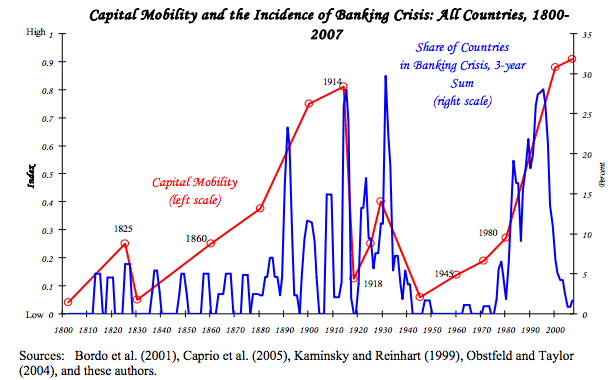
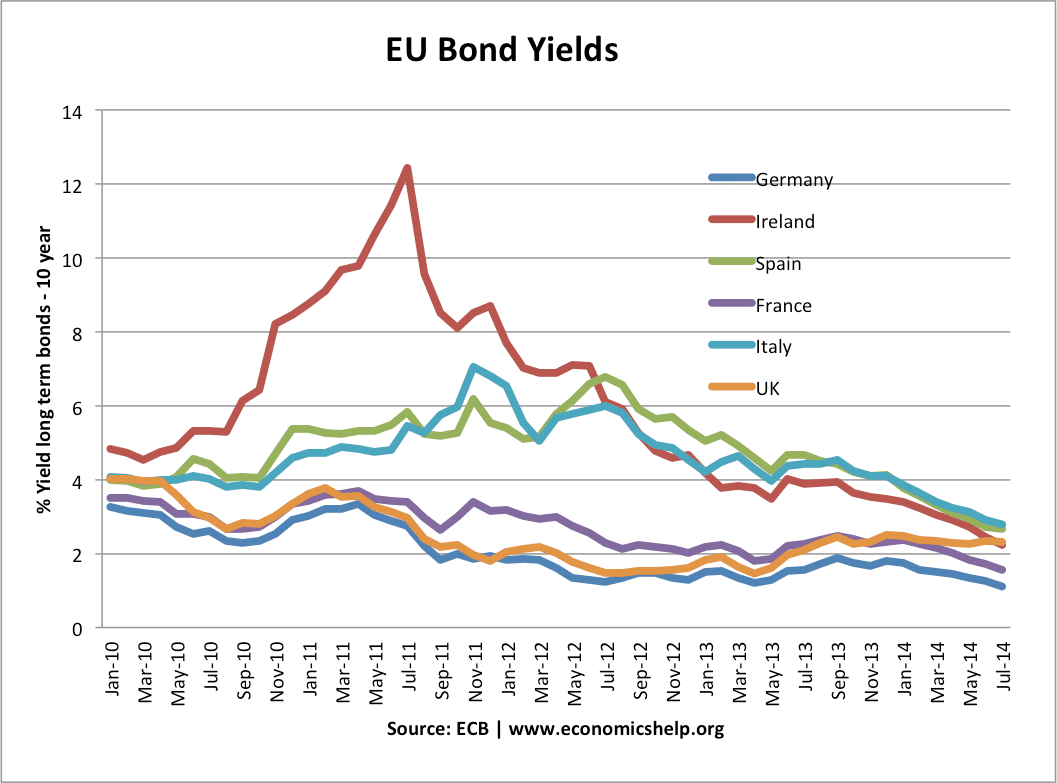
Gross Fixed Capital Formation
Definition: Gross fixed capital formation is essentially net investment. It is a component of the Expenditure method of calculating GDP. To be more precise Gross fixed capital formation measures the net increase in fixed capital. Gross fixed capital formation includes spending on land improvements, (fences, ditches, drains, and so on) plant, machinery, and equipment purchases; …