The inflation rate measures the annual percentage rise in the cost of living. (CPI) A rise in the inflation rate – means prices are rising at a faster rate.
Summary of higher inflation
In the short-run, it is more likely the Central bank will increase interest rates to moderate the inflation rate. Savers who have fixed income may become relatively worse off. Borrowers, by contrast, are likely to find it easier to pay back their debts. A higher inflation rate could cause greater uncertainty amongst business leading to lower investment. Inflation may also cause a depreciation in the exchange rate.
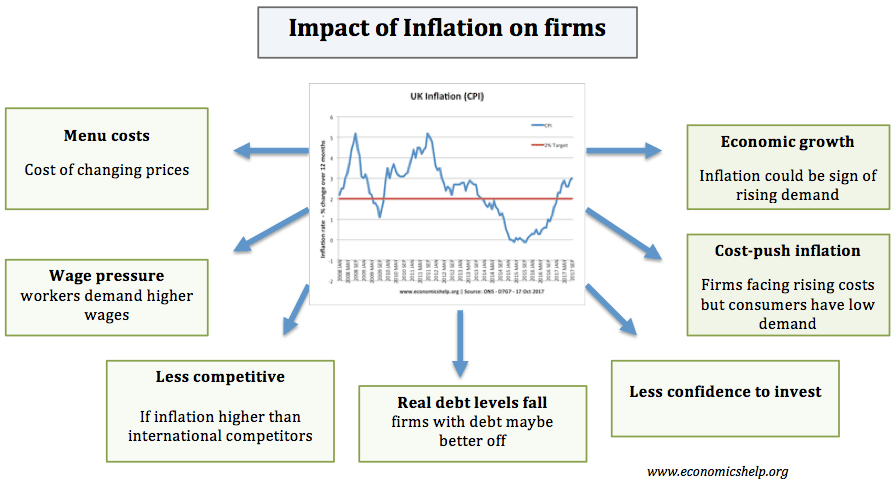
Effects on business
A rise in inflation is likely to mean a rise in the cost of raw materials. Also, workers are likely to demand higher wages to cope with the higher cost of living. This rise in prices can also cause greater volatility and uncertainty. With firms uncertain about future costs, they may hold back from making investment decisions. Firms generally prefer a low and stable inflation rate.
Also, with a inflation rate, firms may expect rising interest rates, which will increase cost of borrowing – another reason to hold back on investment.
With higher inflation, firms may face menu costs (the cost of changing and updating prices). However, with modern technology this cost has diminished in importance – as it is easier for firms to update prices automatically.
Effects on consumers
With rising prices, consumers may be more inclined to try and purchase more quickly before prices rise further. With rising prices, it can create more confusion over which prices are good value. It could lead to costs of consumers looking around different shops comparing prices (this is known as shoe leather costs). However, for moderate rises in inflation, this is unlikely to be too serious. Also, the internet and price comparison sites can make it easier to compare prices.
Effect on Central Bank and interest rates
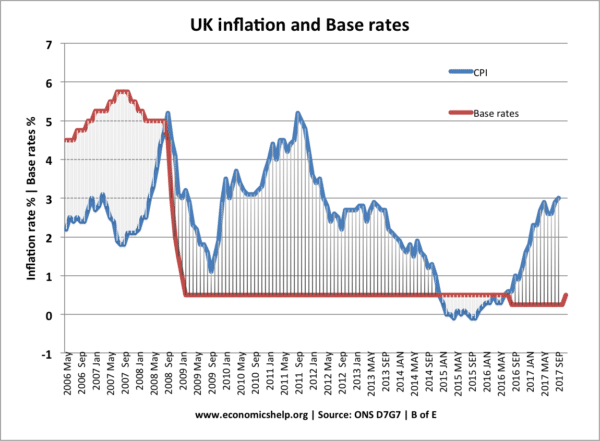
Most Central Banks have an inflation target of around 2%. (UK CPI target of 2% +/- 1.) Therefore, if inflation rises above the target, they may feel the need to increase interest rates. Higher interest rates will increase borrowing costs and slow down the rate of investment and economic growth. Lower economic growth will lead to lower demand-pull inflation (though there can be time-lags)
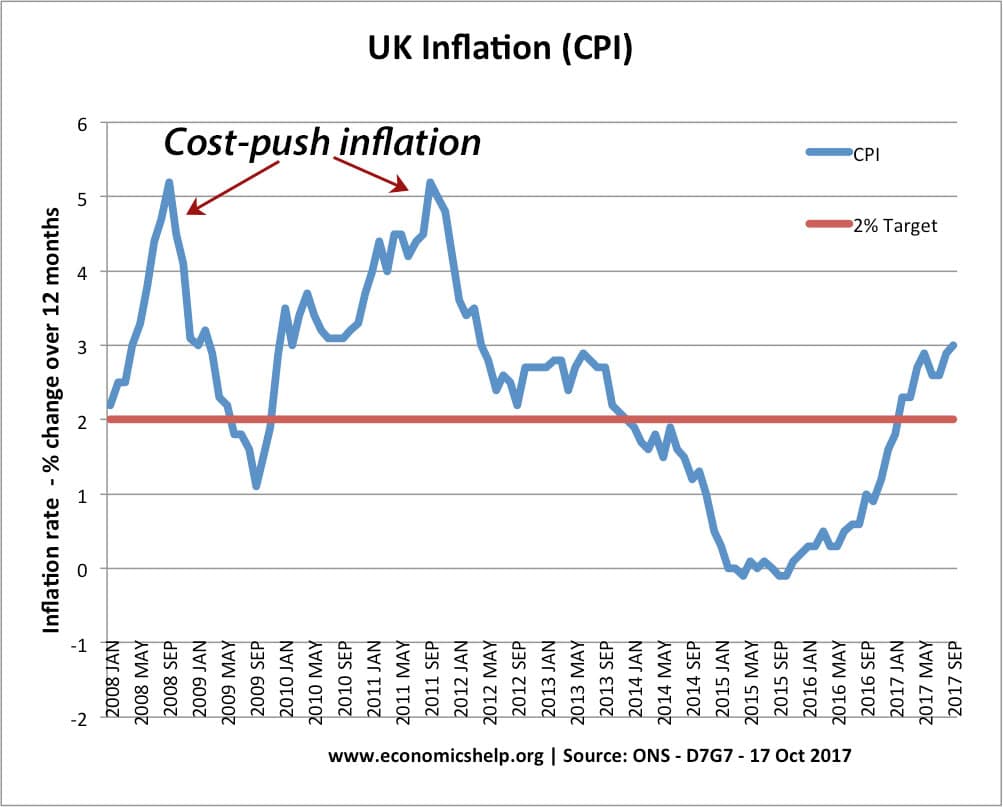
However, it is possible, that Central Banks respond to higher inflation by keeping interest rates the same. If inflation was due to cost-push factors and economic growth was low – the Bank may feel it would be inappropriate to raise interest rates.
For example, in 2008 and 2011, the UK saw periods of cost-push inflation – but low economic growth. The Bank felt this inflation would prove temporary and higher interest rates could push the economy into recession – therefore in 2011 they kept interest rates unchanged at 0.5%. However, in more normal circumstances – with inflation caused by strong economic growth – interest rates are likely to rise.
Effect on savers
For savers with cash under the bed or receiving fixed interest payments, then a higher inflation rate could reduce the real value of their savings. For example, if bond holders buy government bonds with interest rate of 3% and anticipated inflation of 2% – then they expect a real interest rate of 1%. However, if inflation rises to 7% and their interest rate stays at 3%, their effective real interest rate is 4% – in this case, their savings reduce in value.
However, if savers have index-linked savings they will be protected from the effects of inflation. Also, if the Central Bank respond to higher inflation by putting up interest rates, then they can protect their real savings.
Effect on workers
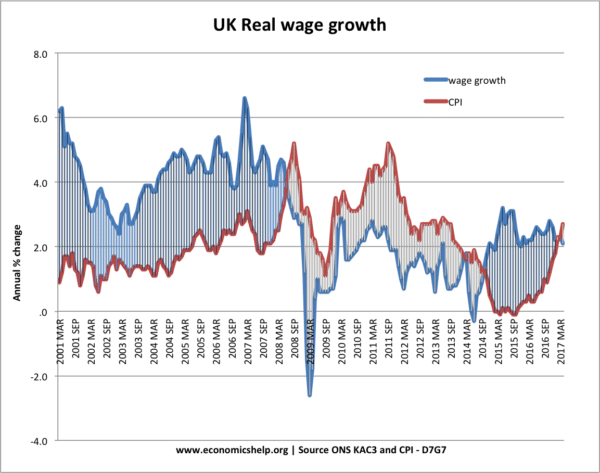
Higher inflation will raise the cost of living. The impact on workers depends on what happens to nominal wages. For example, if inflation is caused by rising demand and falling unemployment, firms are likely to raise wages to keep attracting workers. In this case, workers real wages will continue to rise.
However, in the period 2008-14, UK workers saw inflation erode the real value of their earnings because wages were not keeping up with the rise in inflation.
Effect on the exchange rate
If inflation in the UK rises faster than our international competitors, then UK goods will become relatively uncompetitive, leading to lower demand for UK goods and Sterling. This will cause a depreciation in the exchange rate.
A possible confusion is that if the UK experience higher inflation, in the very short-term, markets may respond to news of higher inflation by expecting higher interest rates. This expectation of higher interest rates might actually cause Sterling to rise in anticipation of higher interest rates and hot money flows. But, it will be a one-off adjustment. The long-term effect of higher inflation will invariably be a gradual depreciation in the value of the currency.
Effect on economic growth
The effect on economic growth is uncertain. Sometimes inflation is caused by a rapid rate of economic growth. However, if growth is above the long-run trend rate – this may not be sustainable – especially if interest rates rise. Therefore, higher inflation may be a sign the economic cycle is getting close to the end of the boom period and may be followed by a bust.
In 2016, the UK depreciation in Sterling caused inflation – but this tended to reduce economic growth because the imported inflation reduced real incomes and had a depressing effect on consumer spending. (despite making exports more competitive)
The cost-push inflation of 2008, was also a contributory factor in reducing economic growth. Some economists suggest that countries with higher long-term inflation rates tend to have poorer economic performance.
Related

This was really helpful in understanding inflation
Very good article help understand the inflation.