Historical Interest Rates in UK since 1800
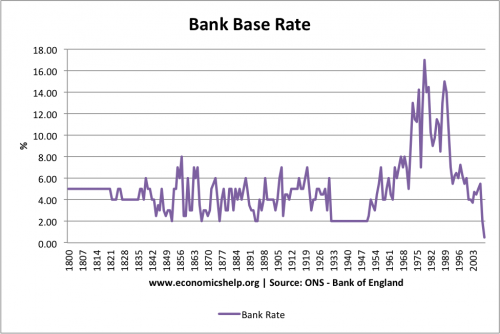 Interest rates in the UK since 1800.
Interest rates in the UK since 1800.
Bank Rate 1830–1972 and 2006–09, Minimum Lending Rate 1972–81, London clearing banks’ base rate 1981–97, repo rate 1997–2006. End year observation.
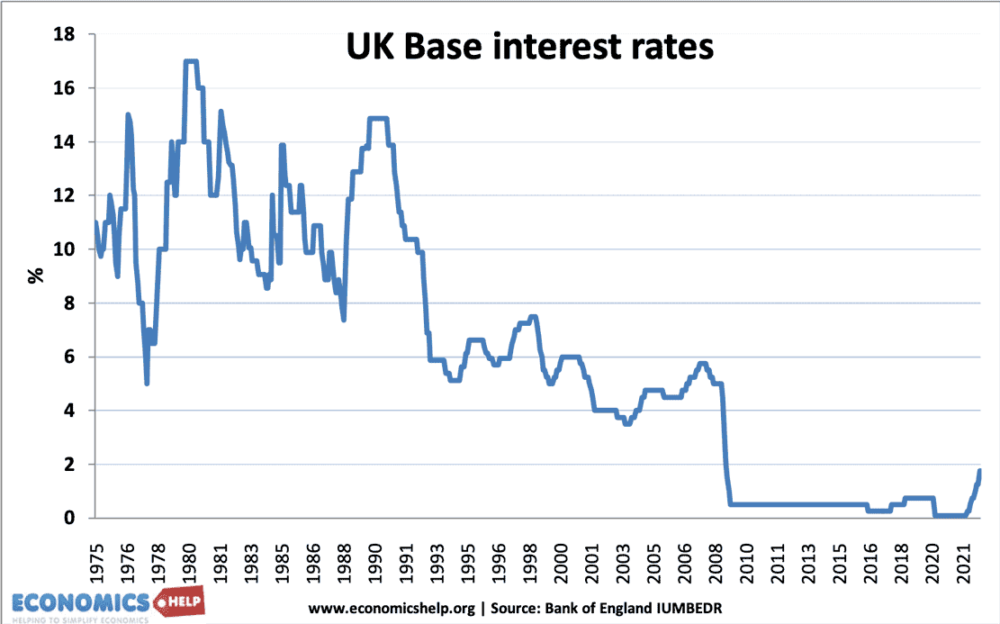
Interest Rates since 1975
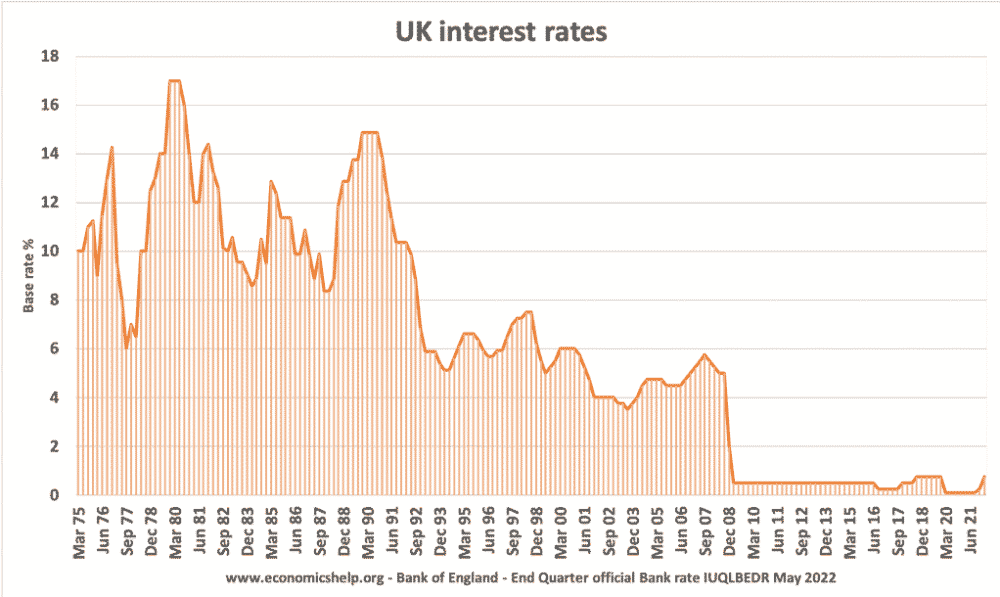
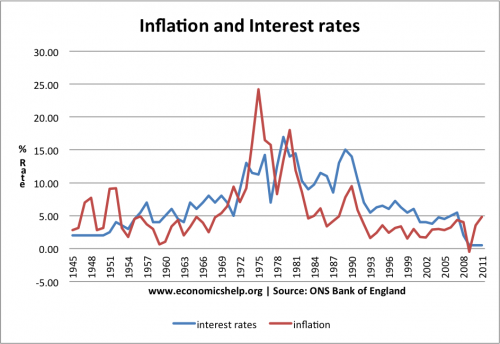
The highest period of interest rates was in the late 1970s, when the government were fighting high inflation caused by oil prices and rising wages.
Interest rates were also increased to 15% at the beginning of the 1990s when the UK was trying to keep the value of Pound fixed in the ERM and reduce inflation from the Lawson boom.
Since the credit crunch of 2008, interest rates have been close to zero.
Bond yields on UK debt
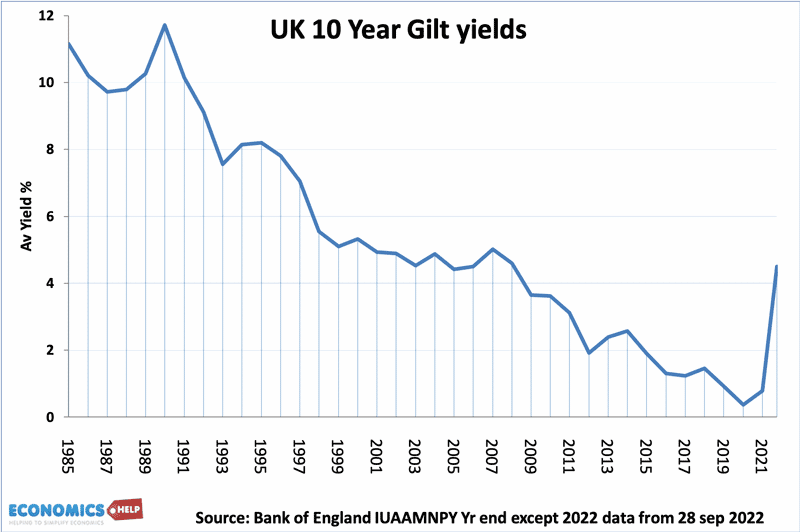
This is the average yield on 10 year government bonds. THere is steady decline from 1989 to 2021, then a surge in September 2022.
Historical Real Interest Rates
Inflation and Interest Rates 1945-2011
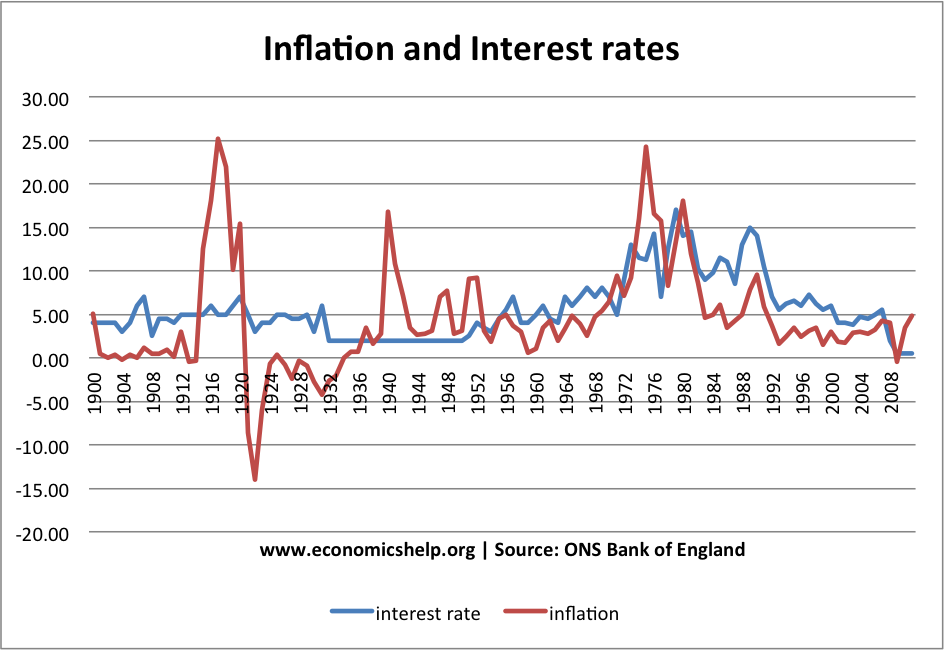
Inflation and Interest Rates since 1900
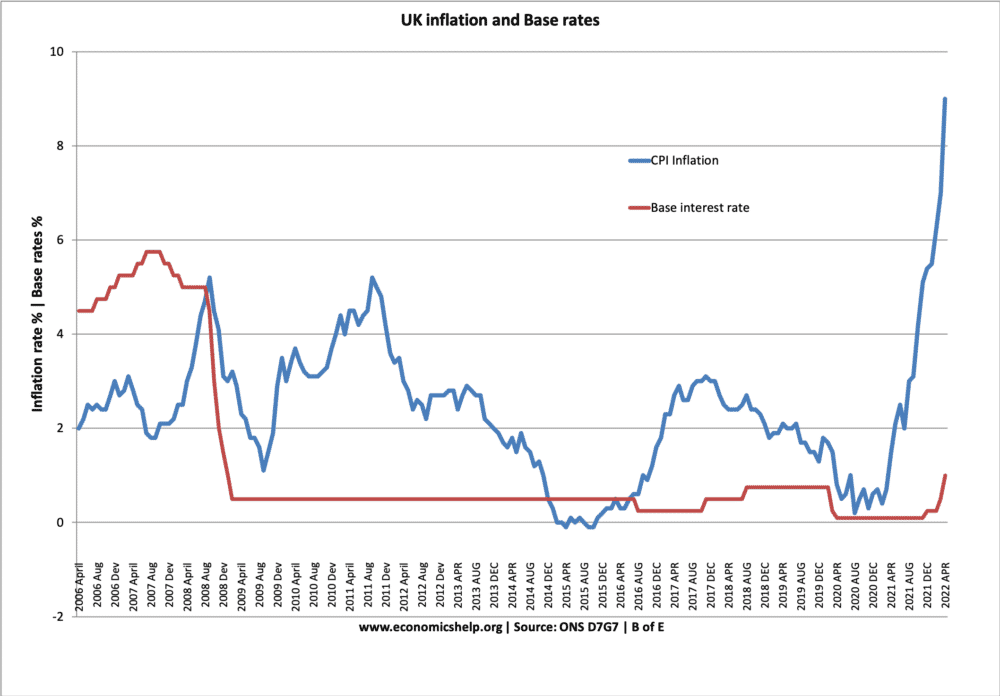
Interest rates and Inflation since 2006
Definition of Real interest Rate = Nominal interest rate – inflation.
The long period of 0.5% interest rates has led to an unprecedented period of negative real interest rates.
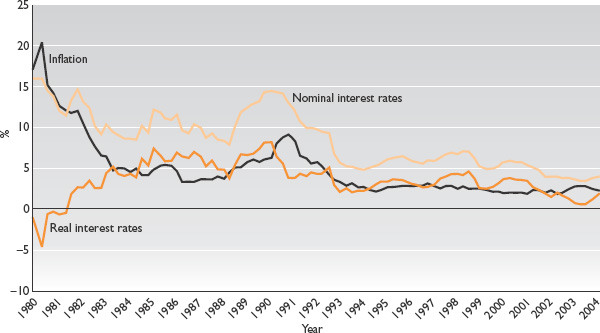
Real interest rates were generally positive in 1980s and 1990s – until financial crash of 2007.
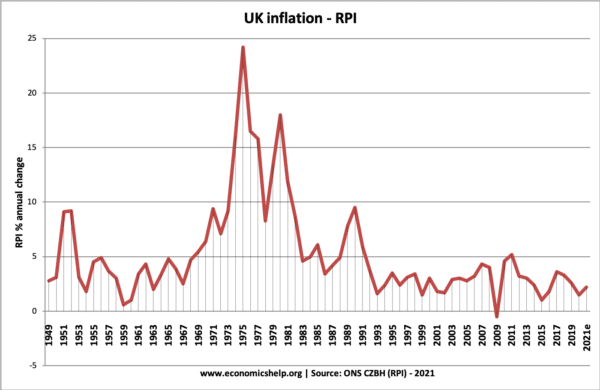
Inflation History
Related
- Definition of Interest Rates
- Interest rates and economy
- Interest rate cycle
- Effect of higher interest rates
External
Base rates at the Bank of England

In theory, banks should not buy bad investments… the caution generated by the economic crisis and uncertainty about job security etc… means that not many of the ‘ordinary men on the street’ will be throwing their money around quite as much as they have been used to doing… whatever the statistics say about real or imagined interest or inflation rates.
I believe that the real interest rate definition you are using is incorrect
“Real interest Rate= Nominal interest rate – inflation”
It is general agreed that it is instead Ri=[(1+Ni)/(1+P)]-1
As a result the graph should show that in a low inflationary environment Ri is far less volatile than Ni the opposite is true in high inflationary environment
I am trying to understand the rate of interest on a mortgage my parents took out in 1937 in England in 1937. It was for 591 £ with an interest rate of “one £ per centum per annum” over the current bank rate and calculated over a 12 month period, 31 December to December 31. I am trying to calculate how much would have been realized when the home was sold in 1948 prior to our move to Canada. Thanks