Source ONS | NTV
A possible unit 4 A Level question this summer could be:
Discuss the impact of a fall in public sector investment on the UK economy?
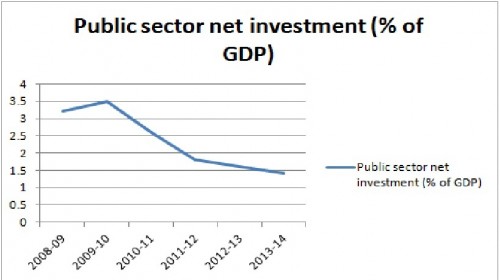
The graph shows a fall in public sector investment from 3.5% of GDP in 2008 to 1.5% in 2011. This means cuts of approximately £30bn a year.
It means the government is spending less on capital investment projects such as new schools, new roads and other infrastructure investment.
That is quite a significant fall. With a fall in government investment, the first impact will be to reduce aggregate demand, lower economic growth and lead to higher unemployment.
Investment spending in the construction sector also tends to have a high multiplier effect (1.7 – 2.0). This study by RICS claims a multiplier of 2.84. If there are fewer investment projects, construction workers will be more likely to be unemployed, and therefore, they will spend less causing a further fall in demand in the economy. Therefore, a fall in investment spending could cause a bigger fall in AD, than the initial cut in government spending.
Furthermore, given the weakness of other areas of the economy, this fall in government spending will lead to a significant fall in AD. If the economy was in robust shape with growing private sector demand and a strong export sector, this fall in public sector spending would not be so serious. But, the UK economy remains in a double dip recession with the uncertainty of the Euro crisis discouraging private sector investment.
One benefit of cutting public sector investment is that it will help reduce government borrowing. In the UK borrowing is forecast to be £123bn in 2011-12. Therefore, without a plan to reduce government spending and deficit, we may see a rise in bond yields as markets are concerned about the rise in government debt. An increase in interest rates would be very damaging for the UK economy given the levels of household debt and fragile nature of spending.
Another argument is that cutting government spending should enable ‘more efficient’ private sector spending and investment. It is argued, government spending can ‘crowd out’ the private sector spending. Reducing government spending helps reduce government borrowing, keeps interest rates low and encourages the private sector to spend and invest.
However, it is debatable whether interest rates would actually rise if the government invested an extra £30bn. Interest rates have fallen since 2008 because there has been a rise in private sector saving and demand for buying secure bonds. The interest rate on long term index-linked yields is low at 0.5%. This suggests public sector investment could be financed for a very low annual interest payment.