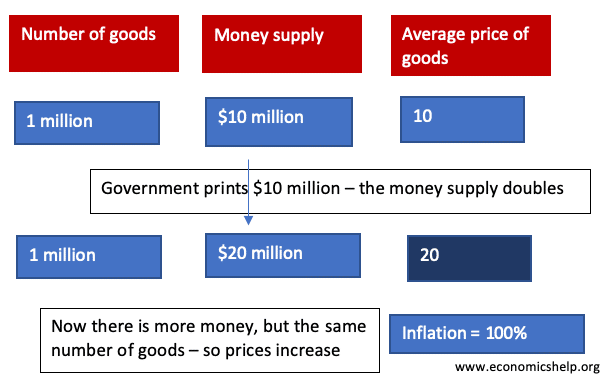
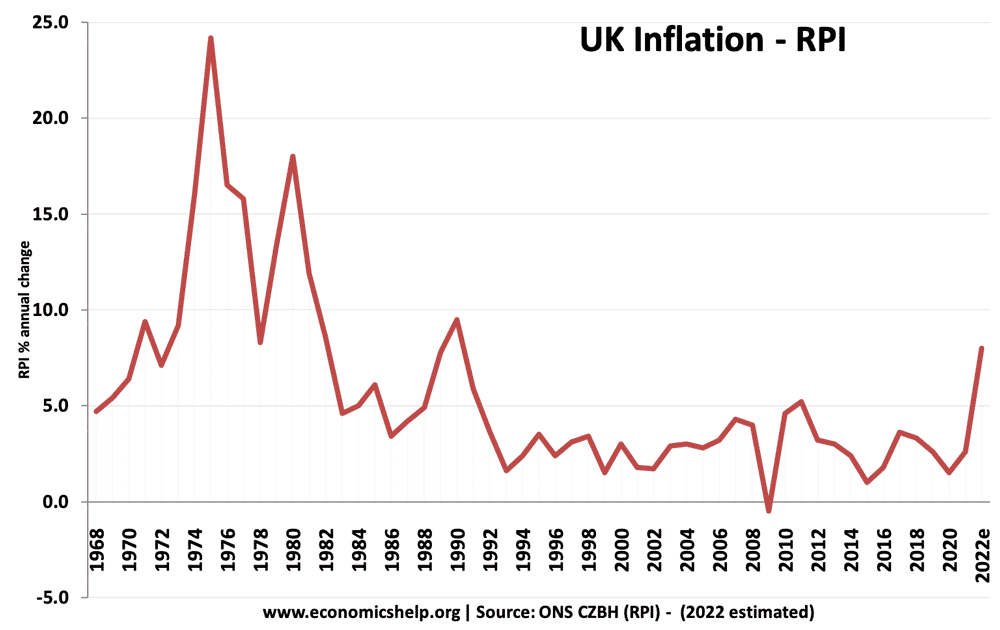
Inflation is a period of rising prices. The primary policy for reducing inflation is monetary policy – in particular, raising interest rates reduces demand and helps to bring inflation under control. Other policies to reduce inflation can include tight fiscal policy (higher tax), supply-side policies, wage control, appreciation in the exchange rate and control of the money supply. (a form of monetary policy).
Summary of policies to reduce inflation
- Monetary policy – Higher interest rates. This increases the cost of borrowing and discourages spending. This leads to lower economic growth and lower inflation.
- Tight fiscal policy – Higher income tax and/or lower government spending, will reduce aggregate demand, leading to lower growth and less demand-pull inflation
- Supply-side policies – These aim to increase long-term competitiveness, e.g. privatisation and deregulation may help reduce costs of business, leading to lower inflation.
Video on reducing inflation
Policies to reduce inflation in more details
1. Monetary Policy
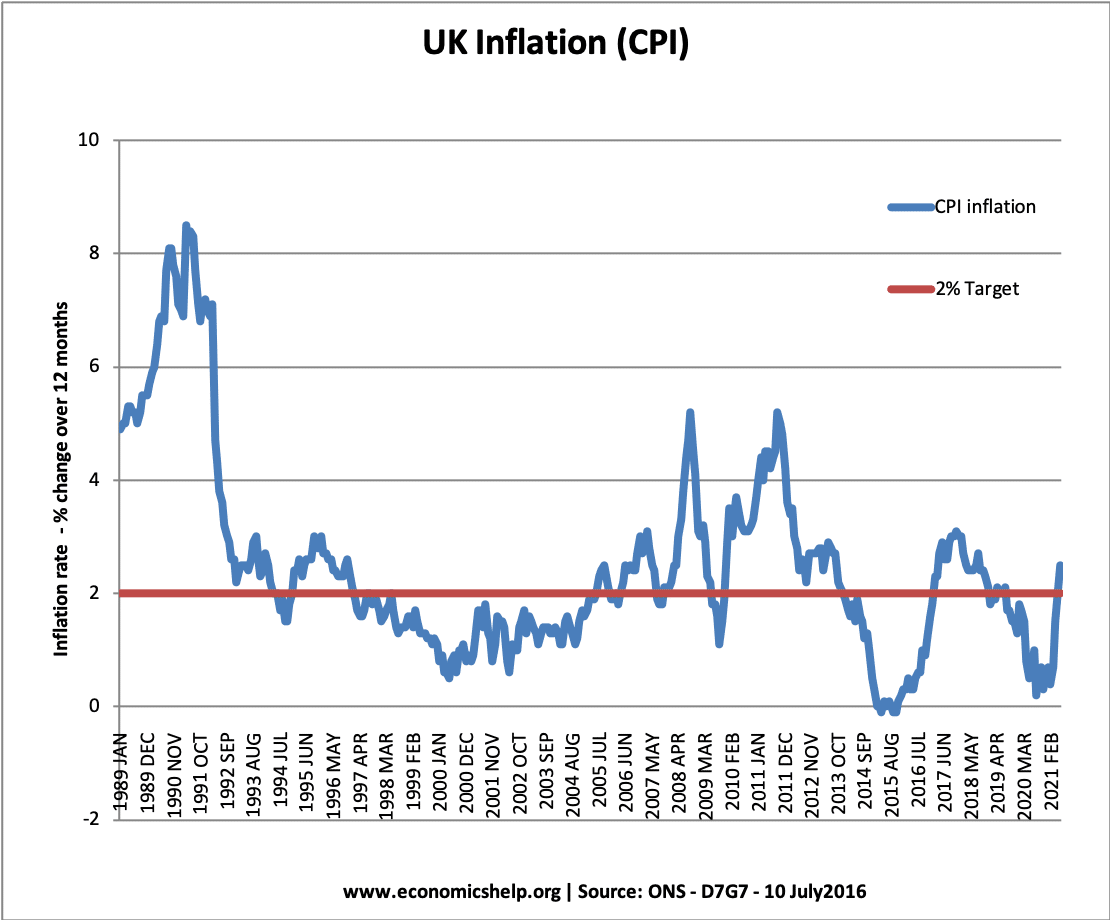
In the UK and US, monetary policy is the most important tool for maintaining low inflation. In the UK, monetary policy is set by the MPC of the Bank of England. They are given an inflation target by the government. This inflation target is 2%+/-1, and the MPC use interest rates to try and achieve this target.
The first step is for the MPC to try and predict future inflation. They look at various economic statistics and try to decide whether the economy is overheating. If inflation is forecast to increase above the target, the MPC are likely to increase interest rates.
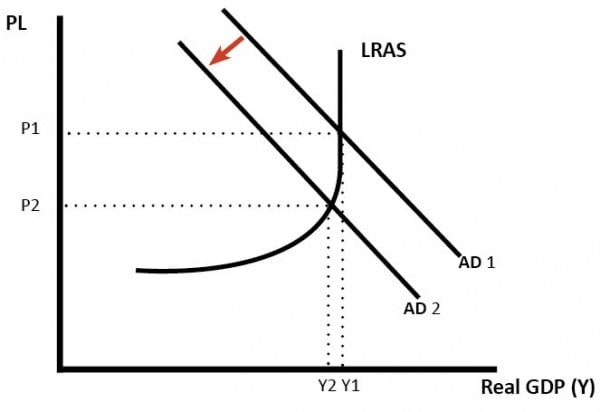
Increased interest rates will help reduce the growth of aggregate demand in the economy. The slower growth will then lead to lower inflation. Higher interest rates reduce consumer spending because:
- Increased interest rates increase the cost of borrowing, discouraging consumers from borrowing and spending.
- Increased interest rates make it more attractive to save money
- Increased interest rates reduce the disposable income of those with mortgages.
- Higher interest rates increased the value of the exchange rate leading to lower exports and more imports.
Diagram showing fall in AD to reduce inflation
Base Rates and Inflation
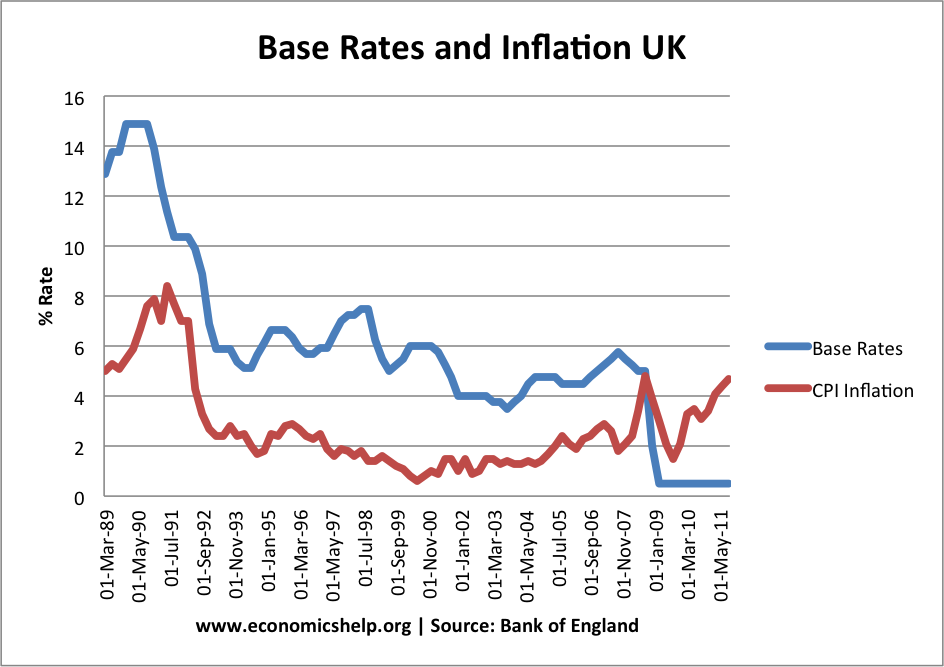
Base interest rates were increased in the late 1980s / 1990 to try and control the rise in inflation.
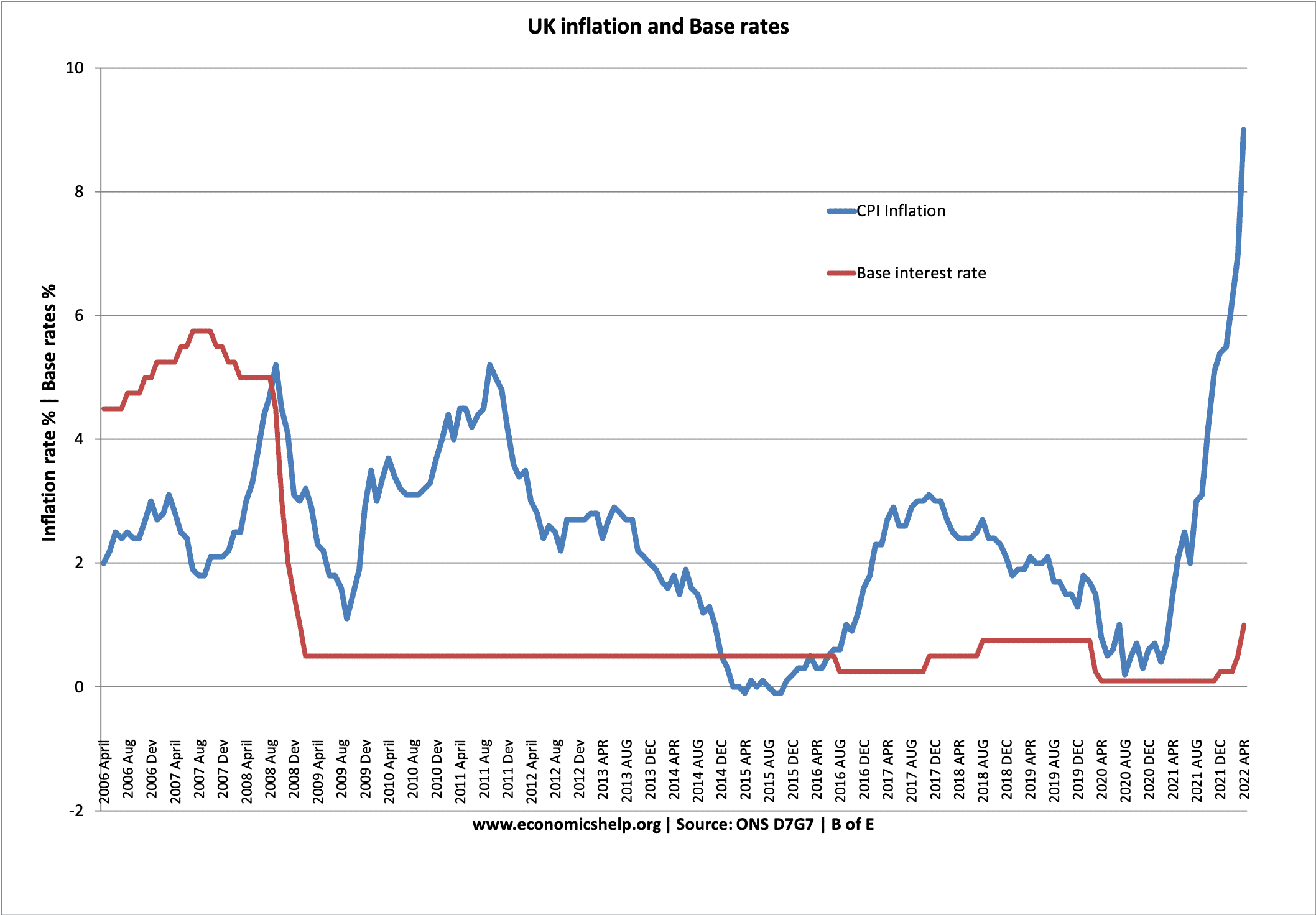
In 2022, there was a small increase in interest rates in response to the rapid rise in inflation.
Monetary policy can have some limitations
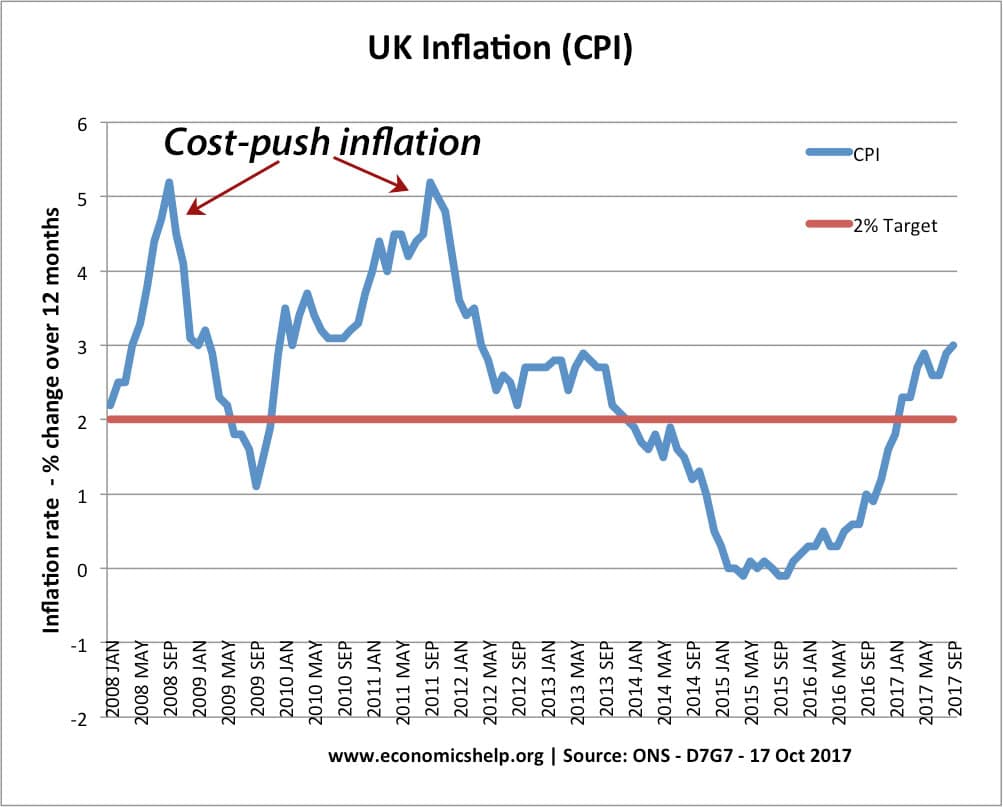
- It is difficult to deal with cost-push inflation (inflation and low growth at the same time)
- There are time lags. It can take up to 18 months for higher interest rates to have an effect on reducing demand. (e.g. people with fixed-rate mortgage)
- It depends on confidence. If confidence is high, business and consumers may continue to spend – despite higher interest rates.