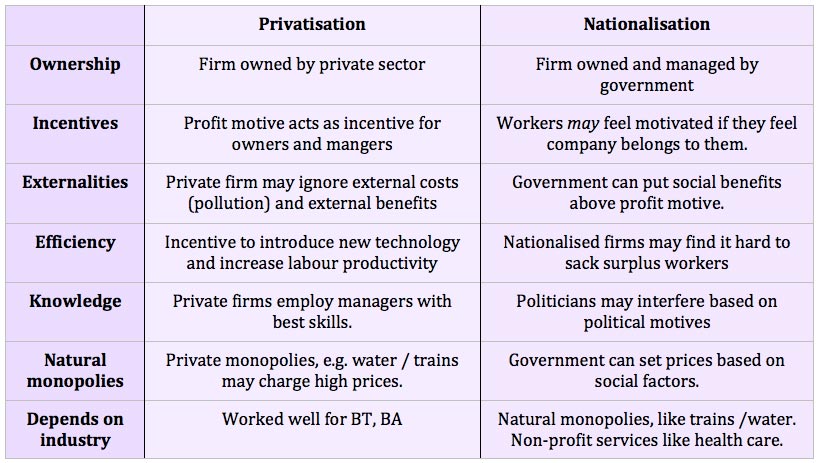
A look at the arguments for and against privatisation.
Privatisation involves selling state-owned assets to the private sector. It is argued the private sector tends to run a business more efficiently because of the profit motive. However, critics argue private firms can exploit their monopoly power and ignore wider social costs. Privatisation is often achieved through listing the new private company on the stock market. In the 1980s and 1990s, the UK privatised many previously state-owned industries such as BP, BT, British Airways, electricity companies, gas companies and rail network.
Arguments for and against privatisation
Potential benefits of privatisation
1. Improved efficiency
The main argument for privatisation is that private companies have a profit incentive to cut costs and be more efficient. If you work for a government run industry managers do not usually share in any profits. However, a private firm is interested in making a profit, and so it is more likely to cut costs and be efficient. Since privatisation, companies such as BT, and British Airways have shown degrees of improved efficiency and higher profitability.
2. Lack of political interference
It is argued governments make poor economic managers. They are motivated by political pressures rather than sound economic and business sense. For example, a state enterprise may employ surplus workers which is inefficient. The government may be reluctant to get rid of the workers because of the negative publicity involved in job losses. Therefore, state-owned enterprises often employ too many workers increasing inefficiency.
3. Short term view
A government many think only in terms of the next election. Therefore, they may be unwilling to invest in infrastructure improvements which will benefit the firm in the long term because they are more concerned about projects that give a benefit before the election. It is easier to cut public sector investment than frontline services like healthcare.