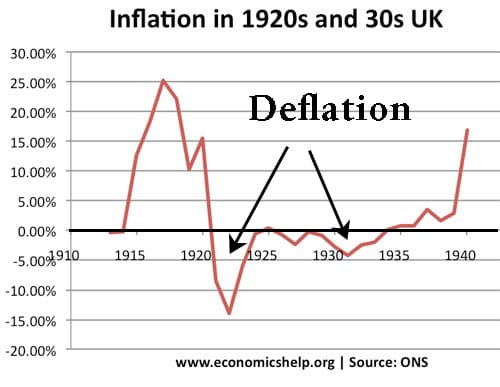
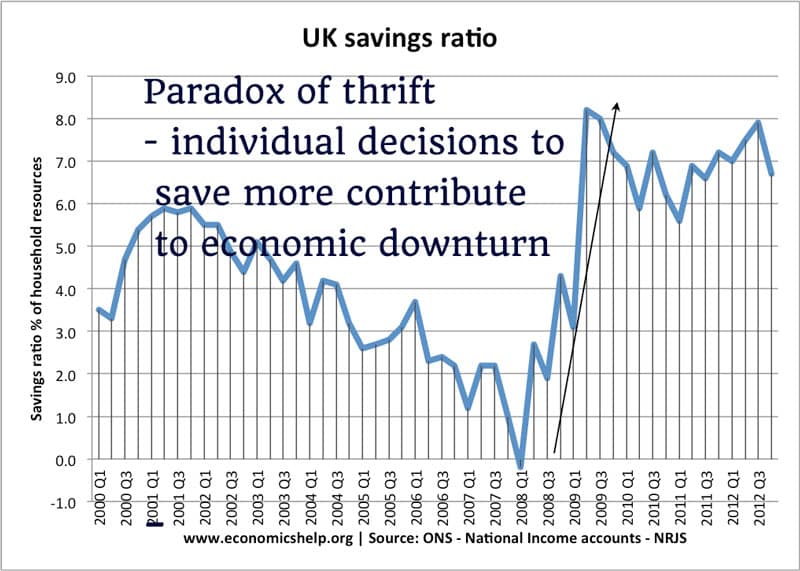
Will 2020 recession become another Great Depression?
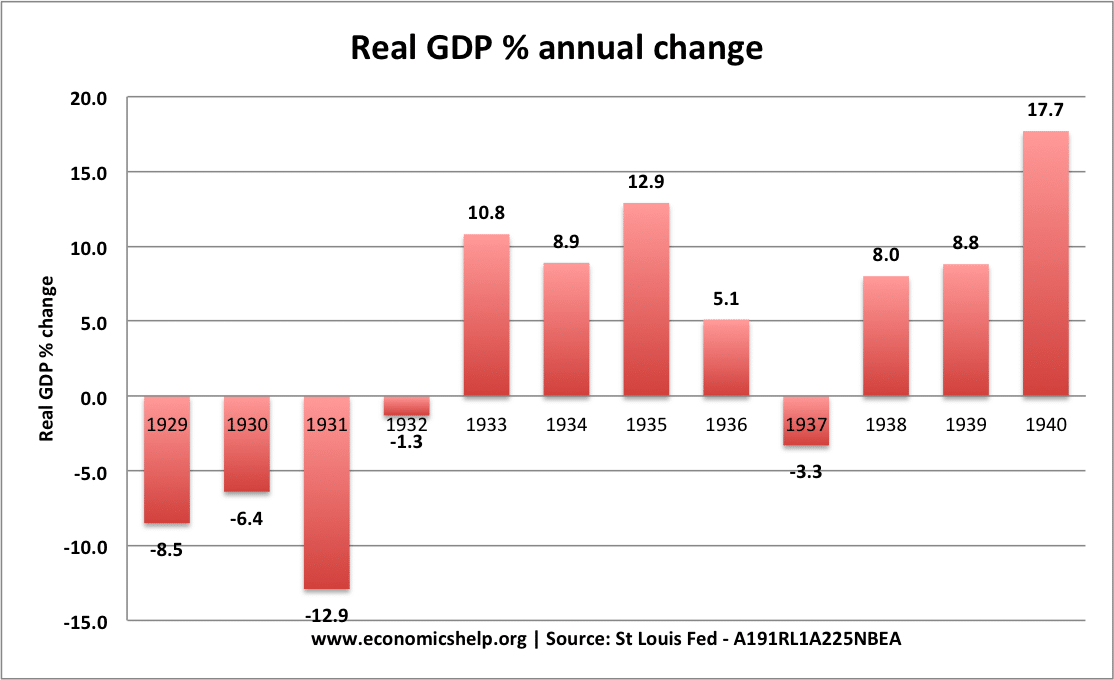
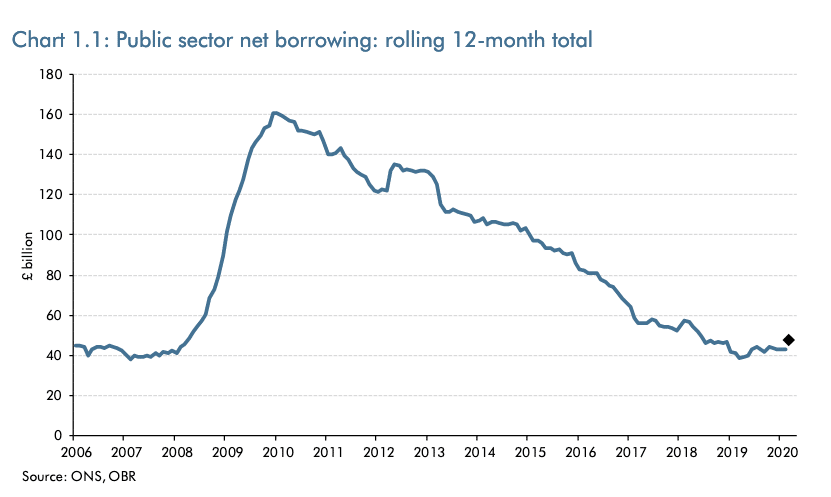
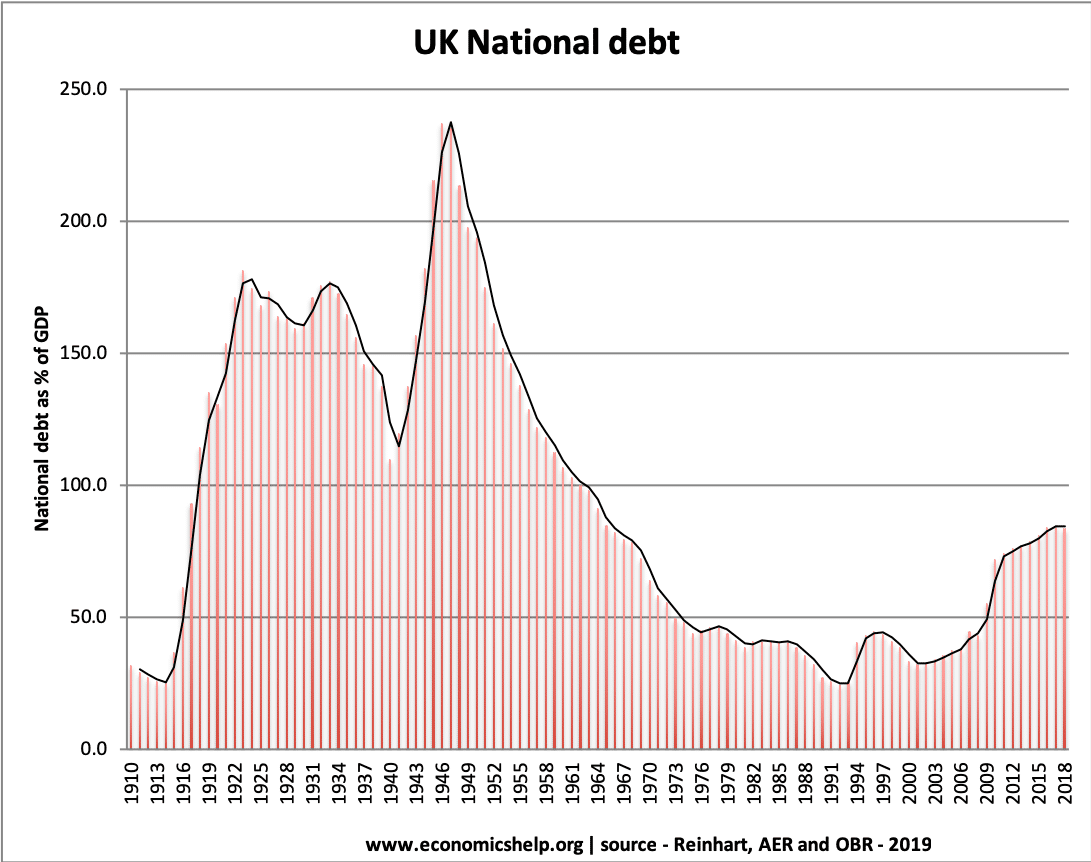
The world economy is already entering a very deep recession, with GDP falling by an estimated 20-25%. Unemployment will rise very fast as large parts of the economy close down. An optimistic assessment is that the economic shock will be short-term, policymakers are responding with as much monetary and fiscal help as they can, and …