This is a collection of diagrams for supply and demand. It is mainly for my benefit, so when creating a post, like the price of tea (or when I’m teaching online) I can easily find a suitable diagram to illustrate what is happening.
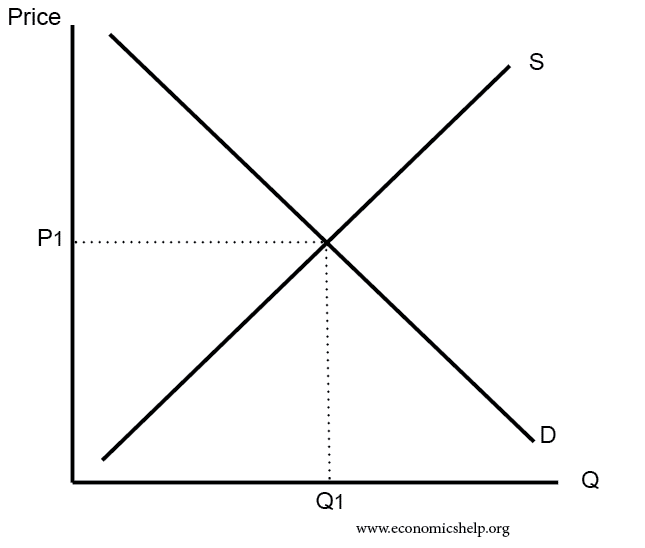
Demand curve
-
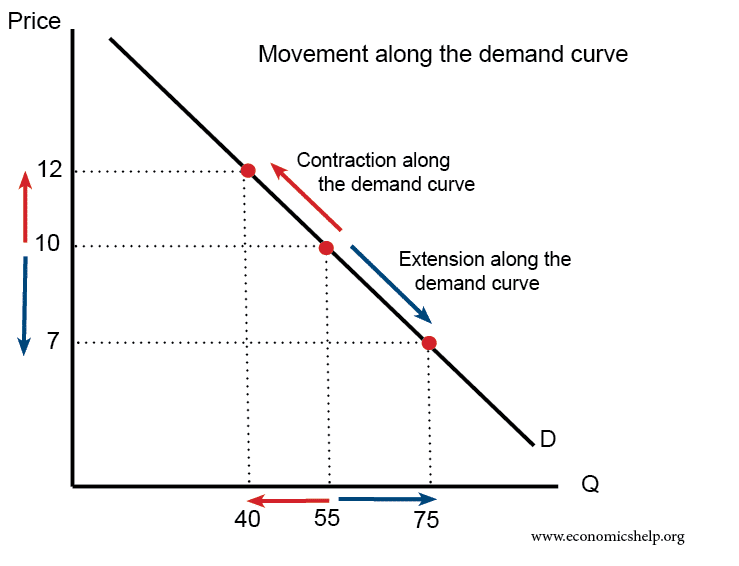
- An extension on the demand curve is due to lower price leading to higher demand.
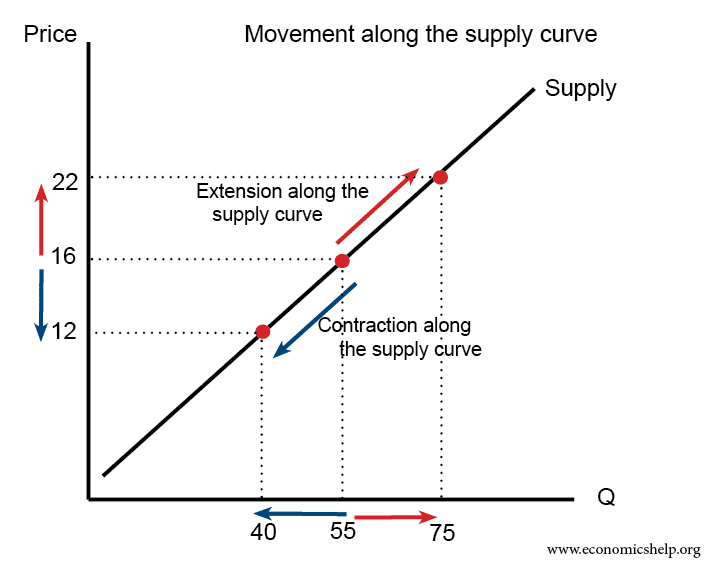
The supply curve
- A higher price causes an extension along the supply curve (more is supplied)
- A lower price causes a contraction along the supply curve (less is supplied)
Supply Shifts to the left
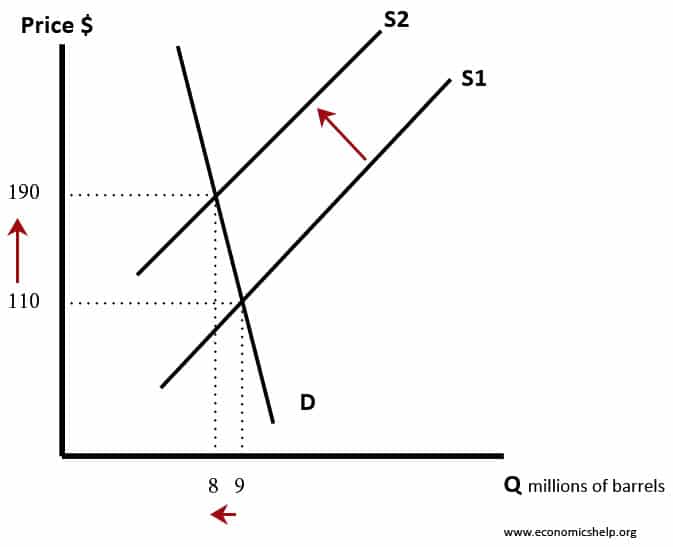
In this diagram the supply curve shifts to the left. It leads to a higher price and fall in quantity demand. The supply curve may shift to the left because of:
- Higher costs of production
- Higher taxes
- Fall in productivity
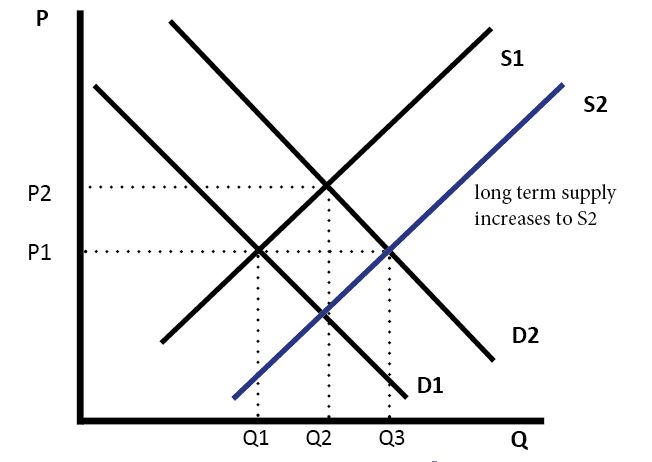
Supply and Demand Shift Right
In this diagram, supply and demand have shifted to the right. This has led an increase in quantity (Q1 to Q2) but price has stayed the same.
It is possible, that if there is an increase in demand (D1 to D2) this encourages firms to produce more and so supply increases as well.
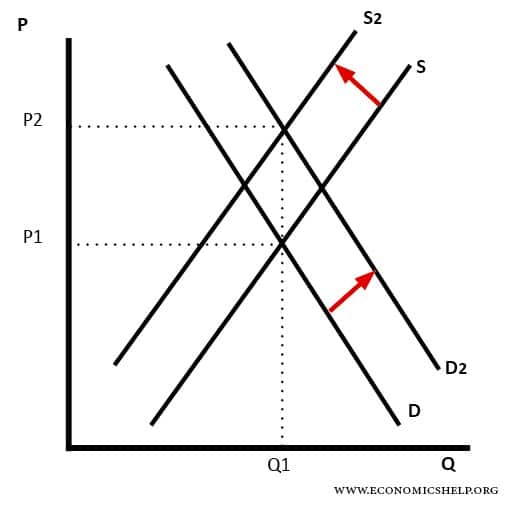
Diagram showing Increase in Price
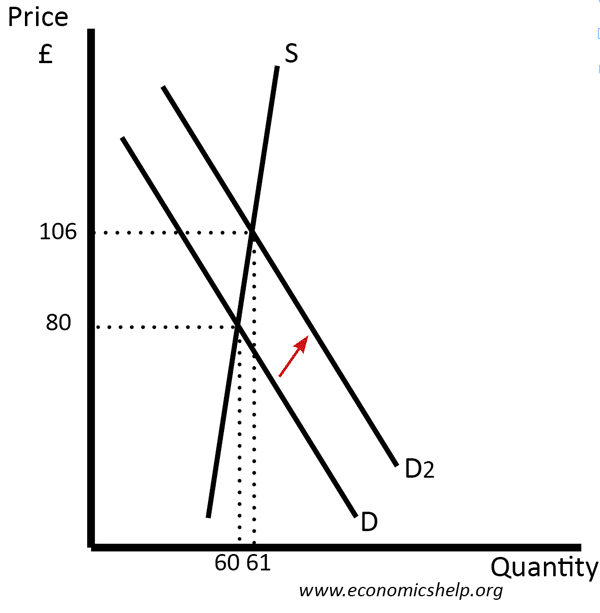
In this diagram, we have rising demand (D1 to D2) but also a fall in supply. The effect is to cause a large rise in price.
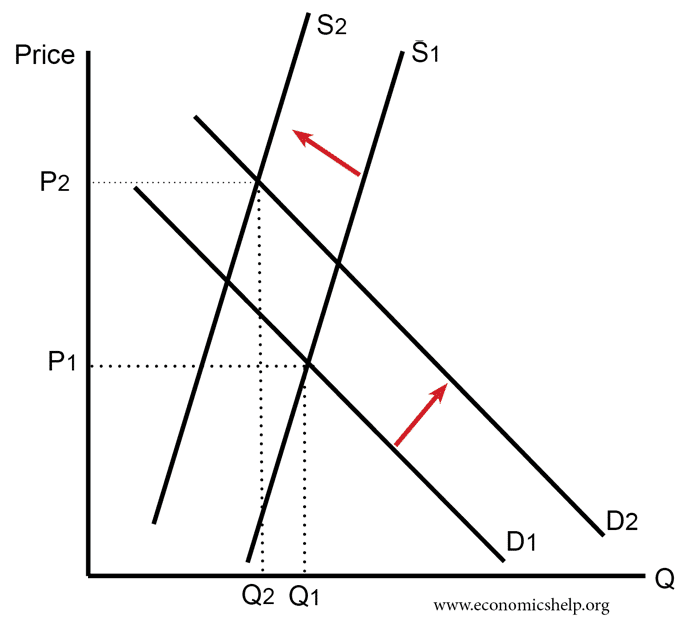
For example, if we run out of oil, supply will fall. However, economic growth means demand continues to rise.
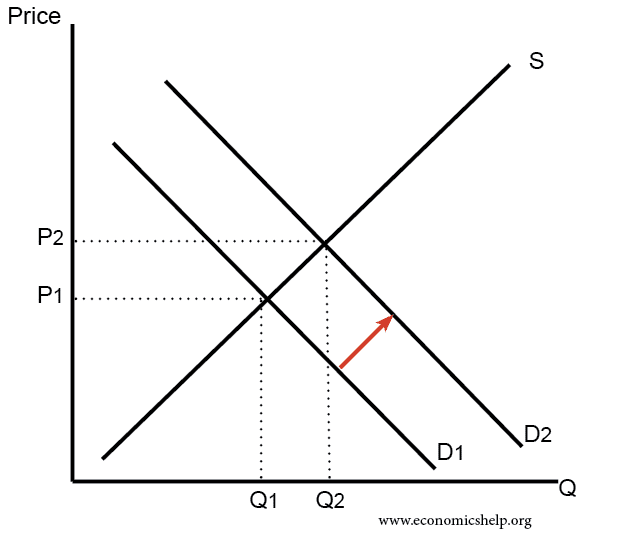
Increase in Demand
An increase in demand leads to higher price and higher quantity.
Increase in demand with inelastic supply