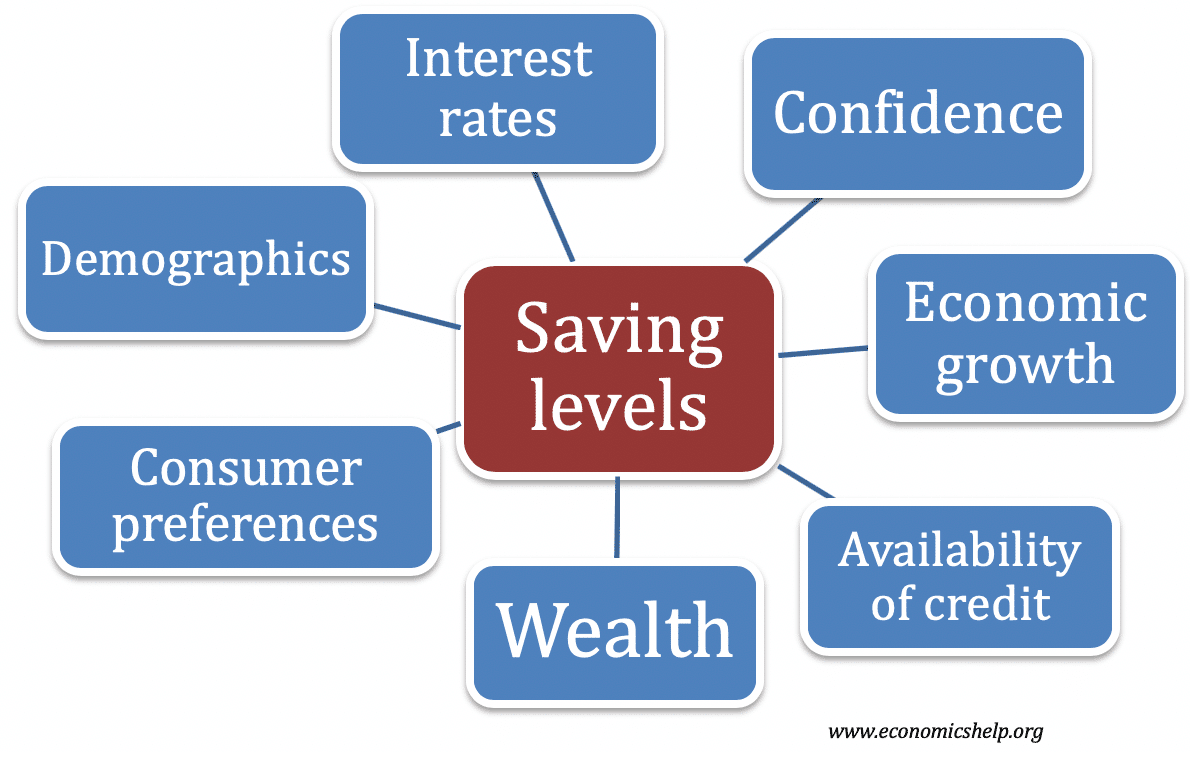
Factors that influence saving levels
Household saving is defined as income that is not consumed. Savings can be kept in cash form, saved in a bank account or saved in long-term assets, such as government bonds. Quick summary of factors that influence saving levels Interest rates – higher interest rates make saving more attractive. Rising income enables higher savings. People …