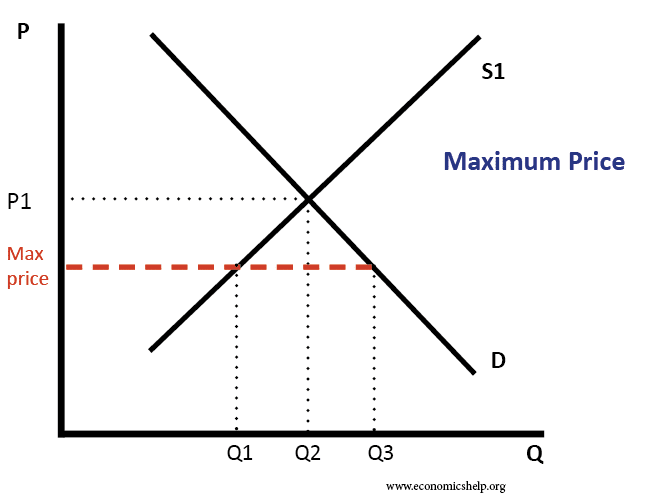
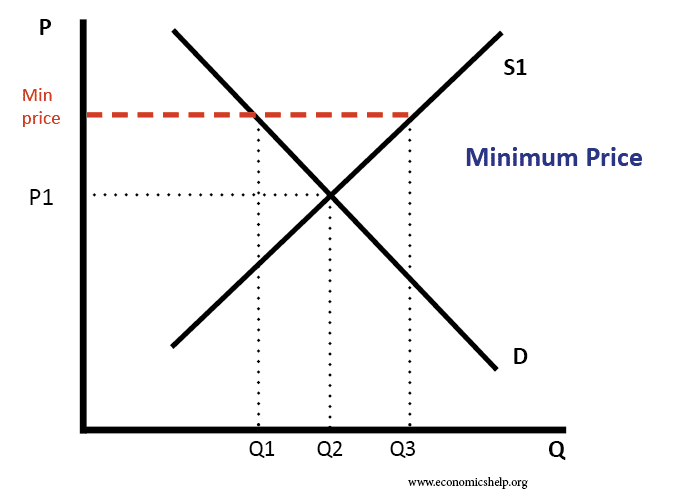
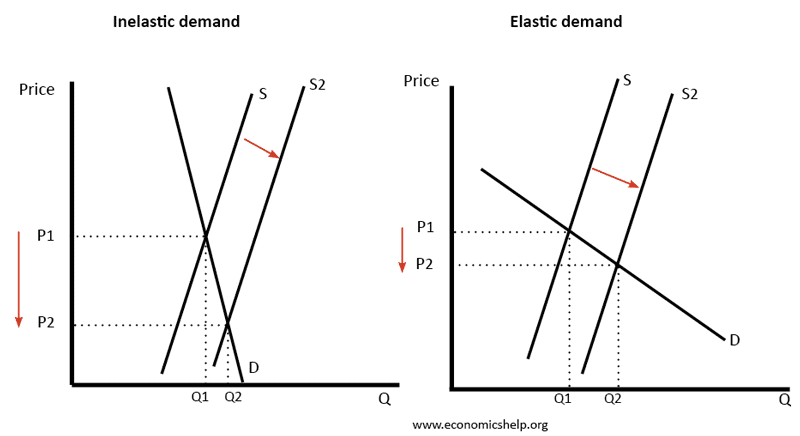
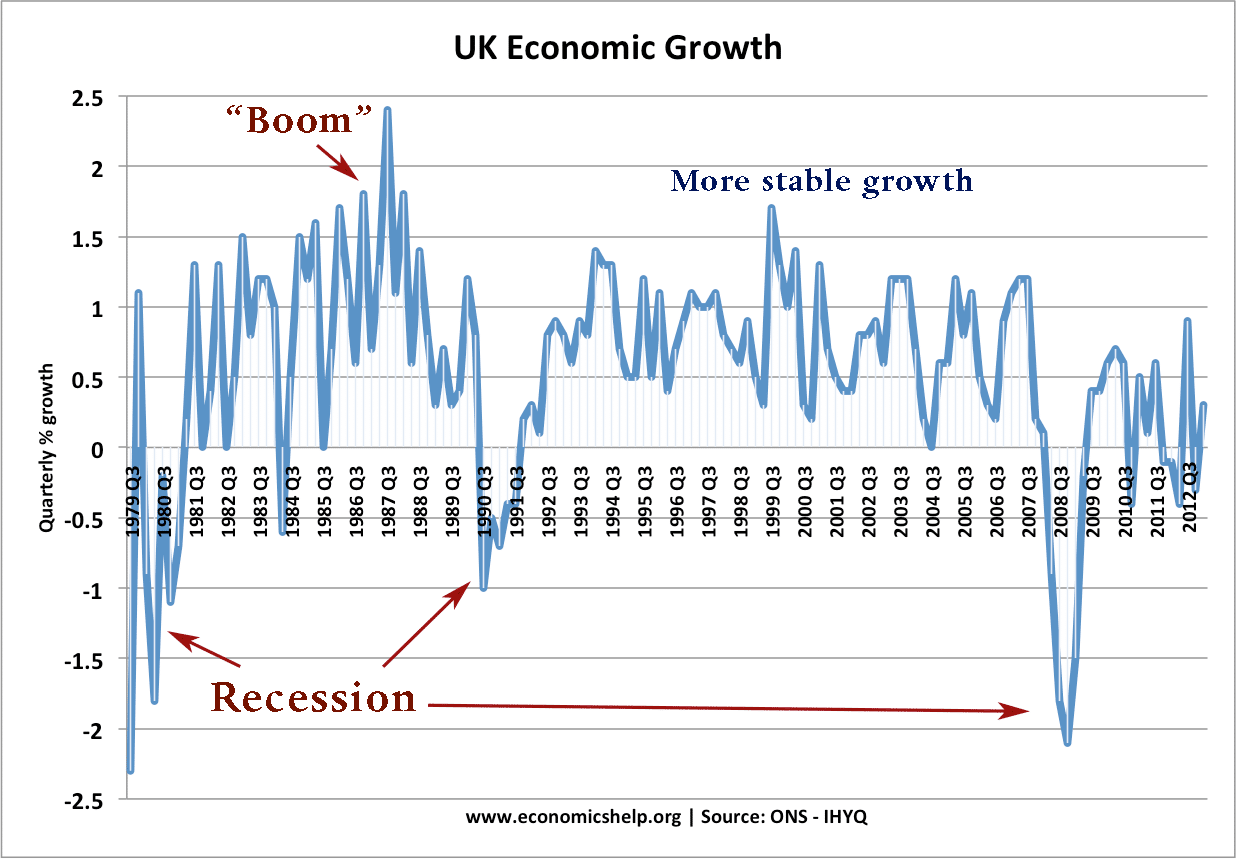
The invisible hand
The invisible hand is a concept that – even without any observable intervention – free markets will determine an equilibrium in the supply and demand for goods. The invisible hand means that by following their self-interest – consumers and firms can create an efficient allocation of resources for the whole of society. How does the …