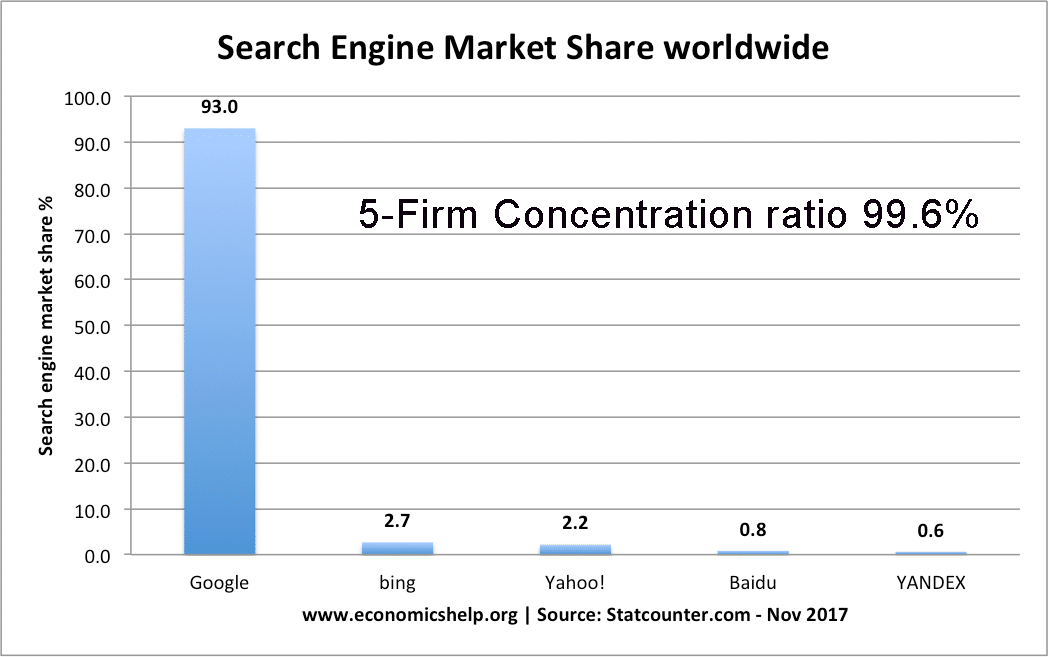
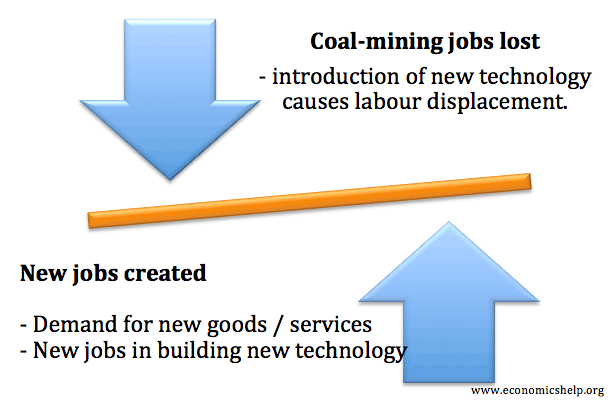
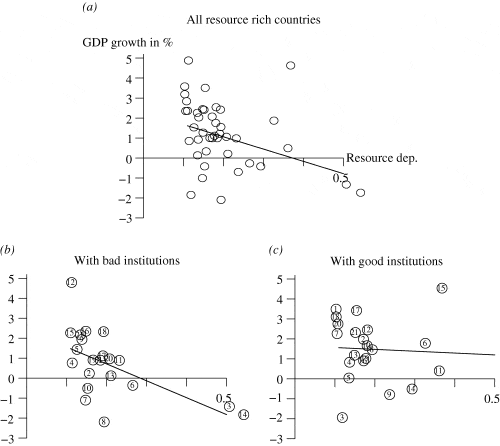
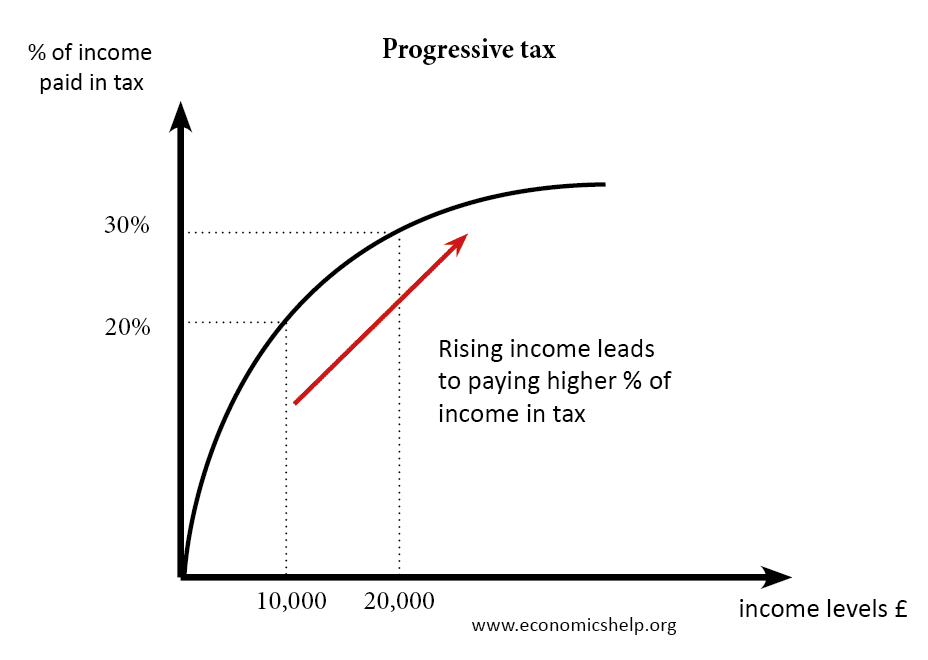
Keynesian economics
The essential element of Keynesian economics is the idea the macroeconomy can be in disequilibrium (recession) for a considerable time. To help recover from a recession, Keynesian economics advocates higher government spending (financed by government borrowing) to kickstart an economy in a slump. Keynesian economics includes Disequilibrium in macroeconomy (insufficient demand) Imperfect labour markets (e.g. …