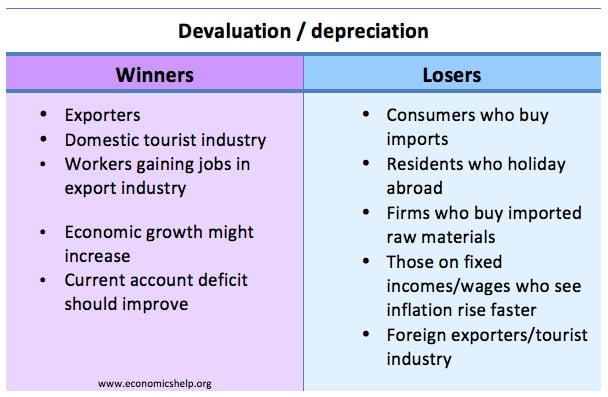
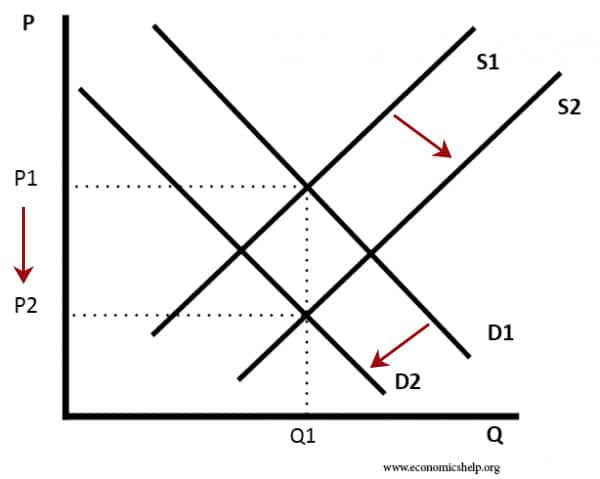
Short-run, long-run, very long-run
The short run, long run and very long run are different time periods in economics. Quick definition Very short run – where all factors of production are fixed. (e.g on one particular day, a firm cannot employ more workers or buy more products to sell) Short run – where one factor of production (e.g. capital) …