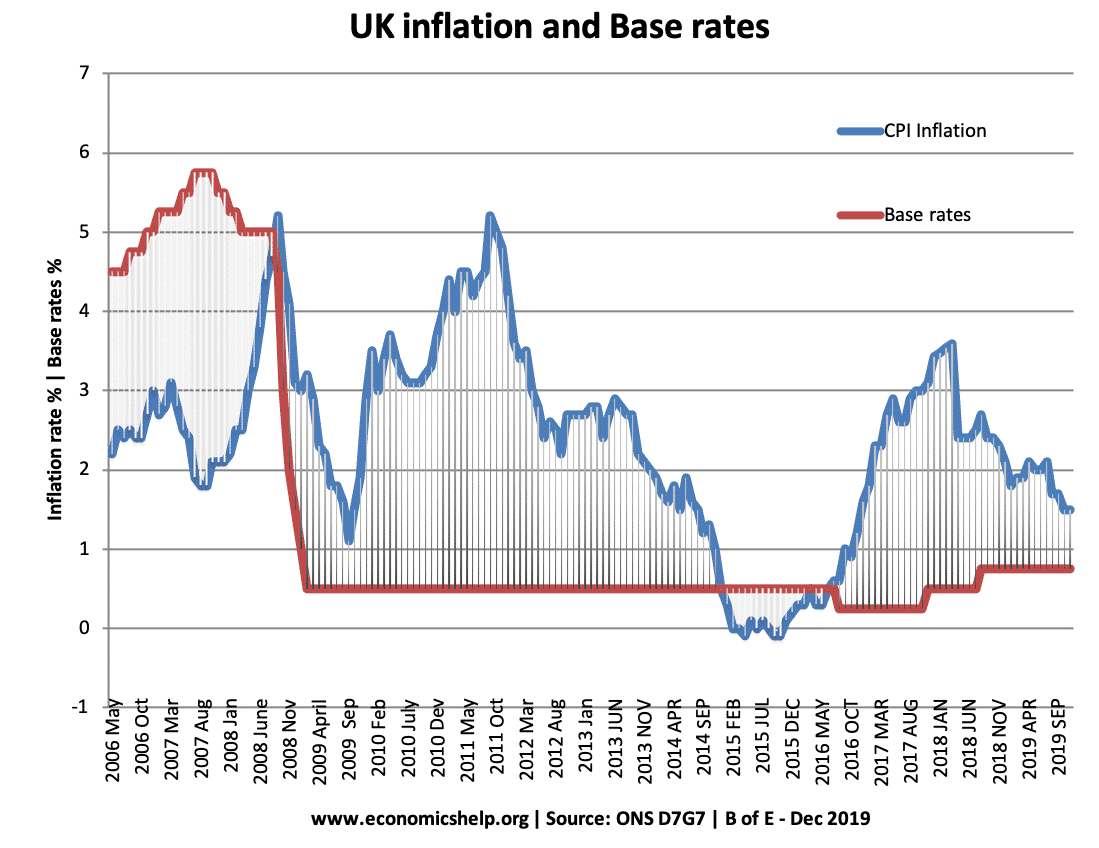
Unemployment during the great depression
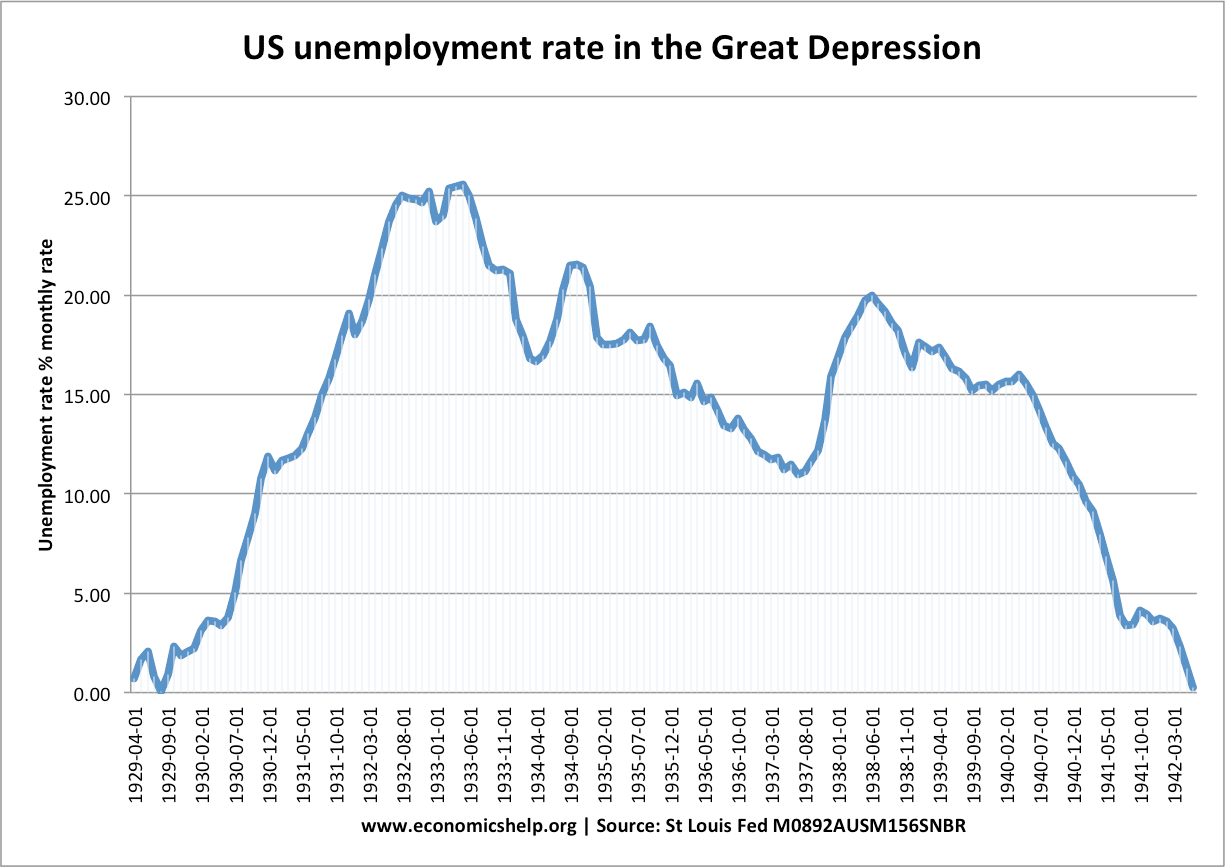
During the Great Depression, US unemployment rate rose from virtually 0% in 1929 to a peak of 25.6% in May 1933. This was the equivalent of 15 million people unemployed. Though this unemployment rate also excluded those on reduced hours or migrants/women not eligible to officially sign on for benefits. The unemployment caused serious economic …