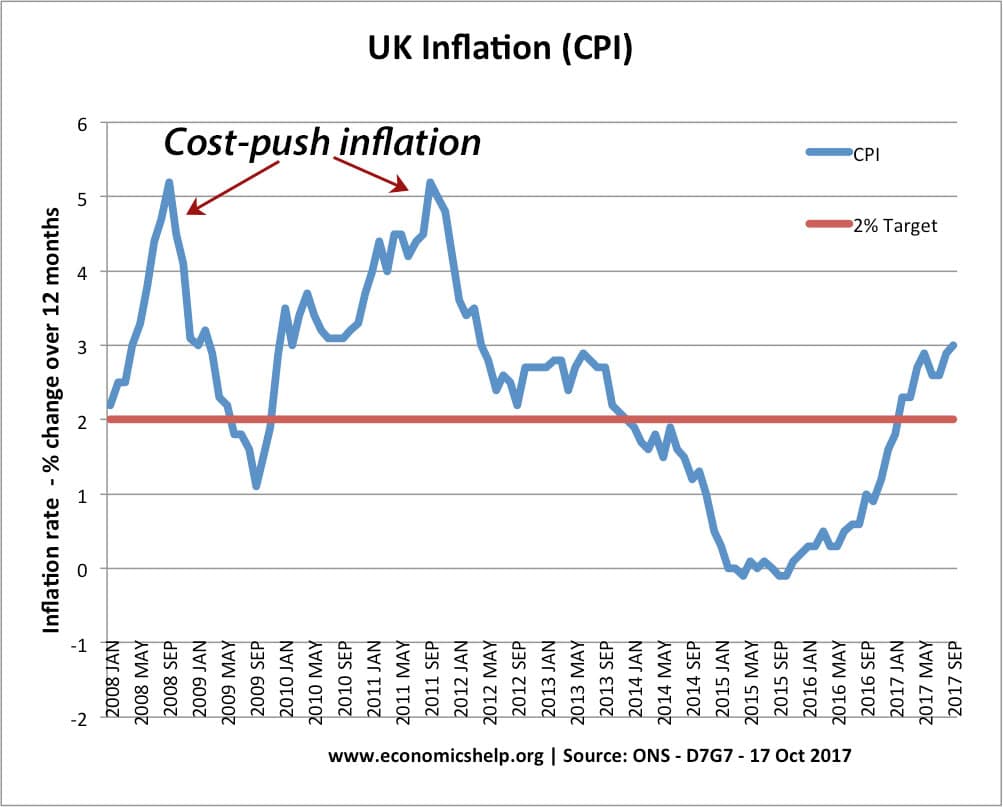
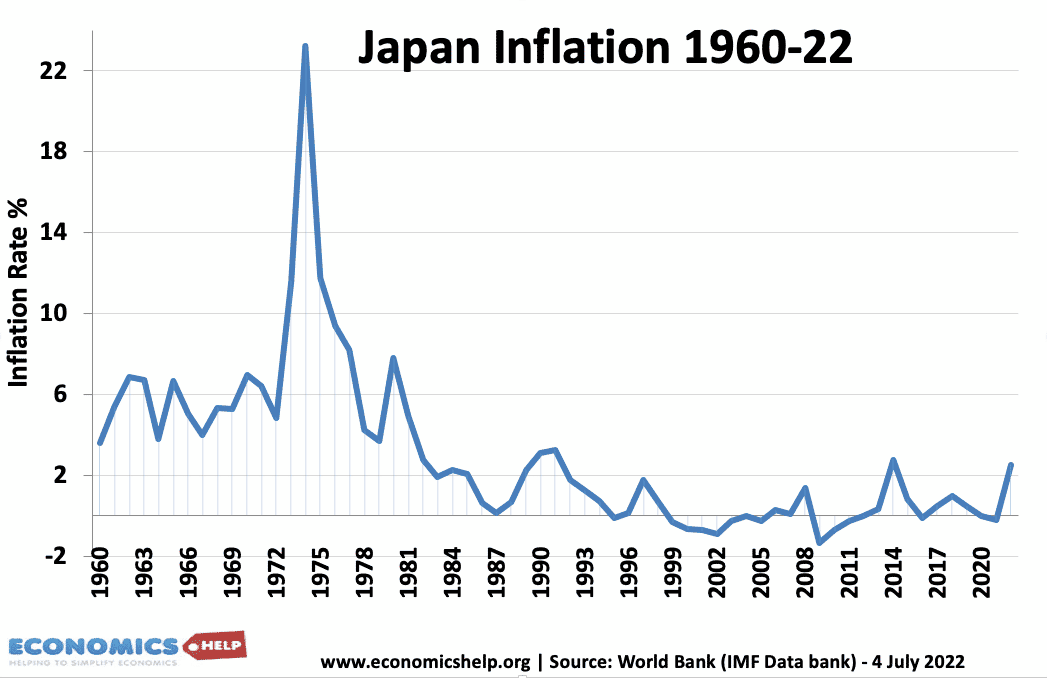
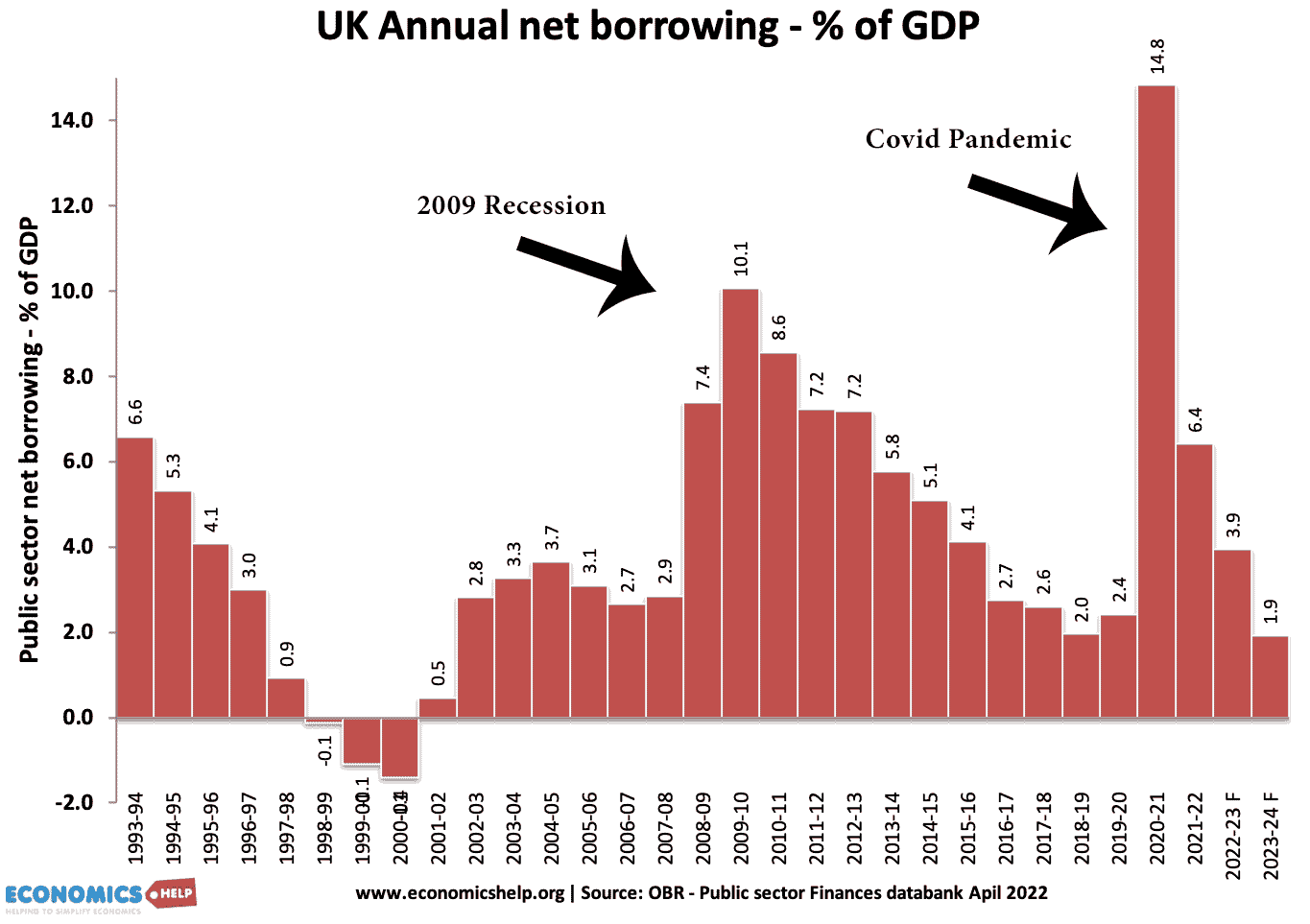
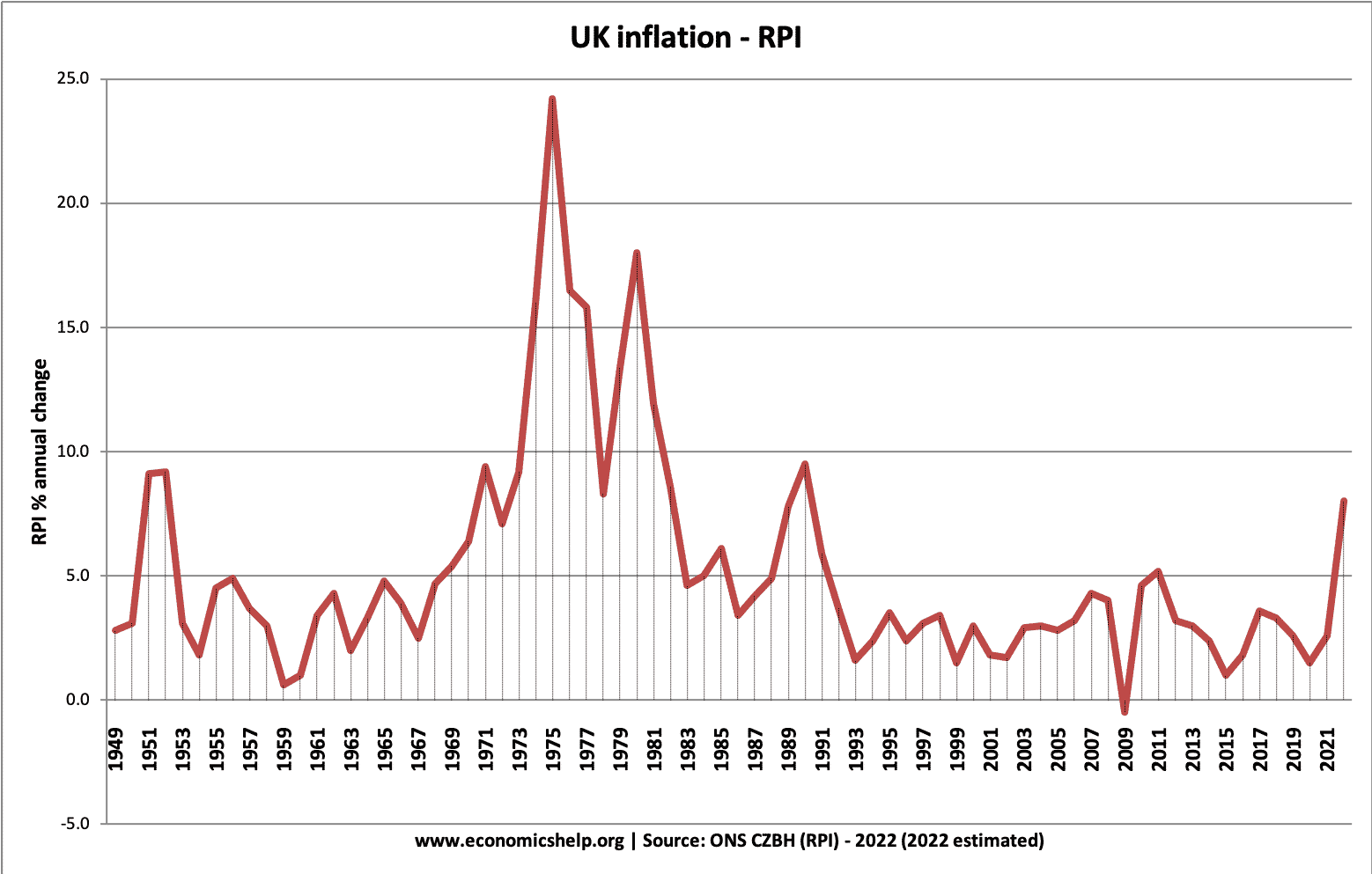
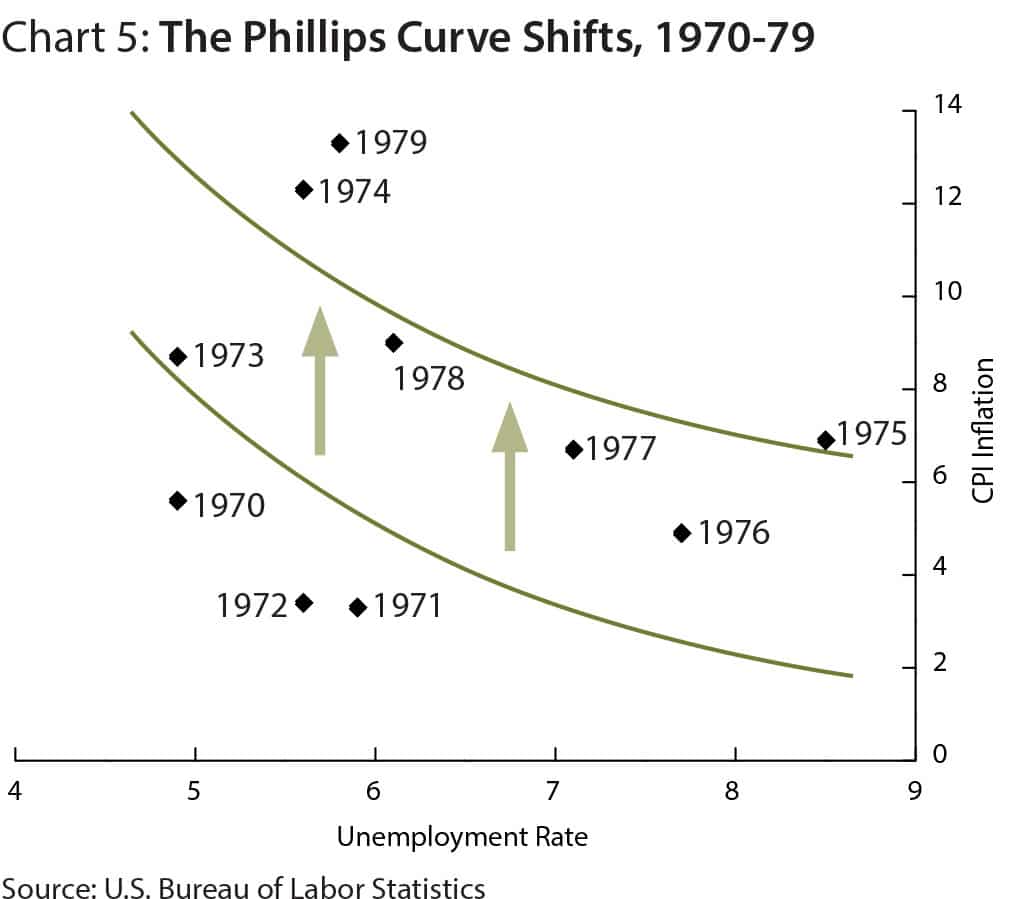
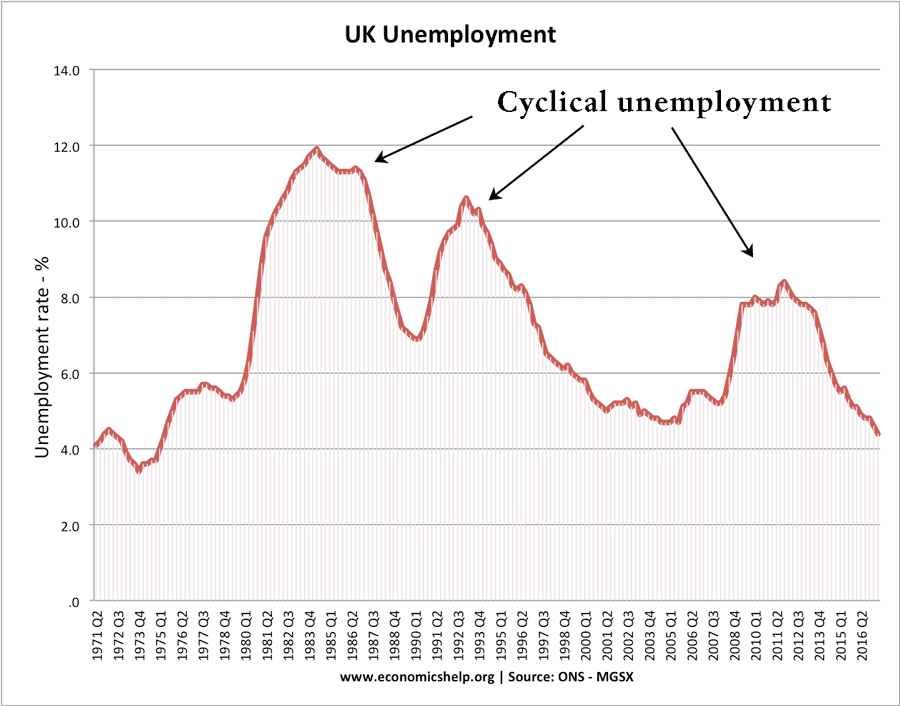
Cost-Push Inflation
Definition: Cost-push inflation occurs when we experience rising prices due to higher costs of production and higher costs of raw materials. Cost-push inflation is determined by supply-side factors, such as higher wages and higher oil prices. Cost-push inflation is different to demand-pull inflation which occurs when aggregate demand grows faster than aggregate supply. Cost-push inflation …