How does the multiplier effect influence fiscal policy?
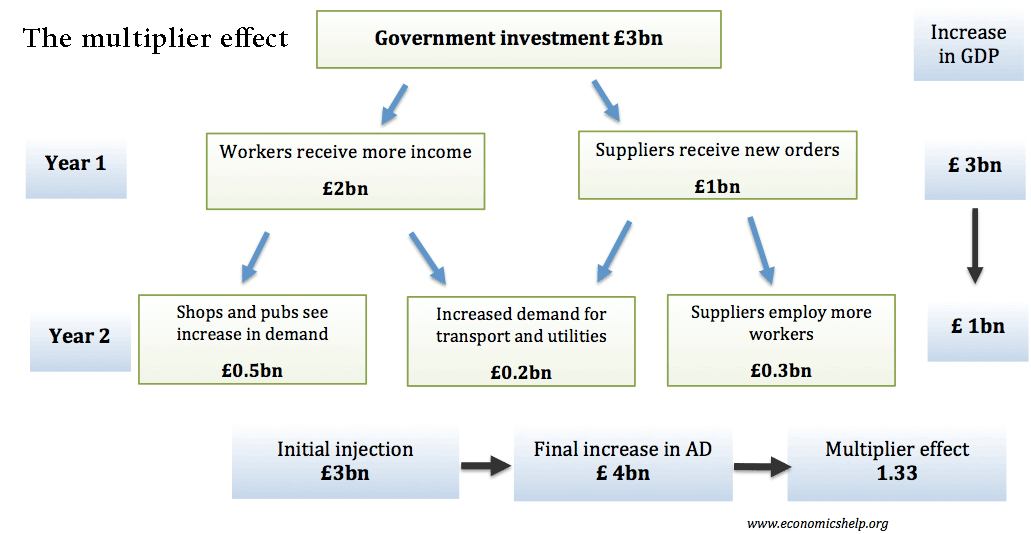
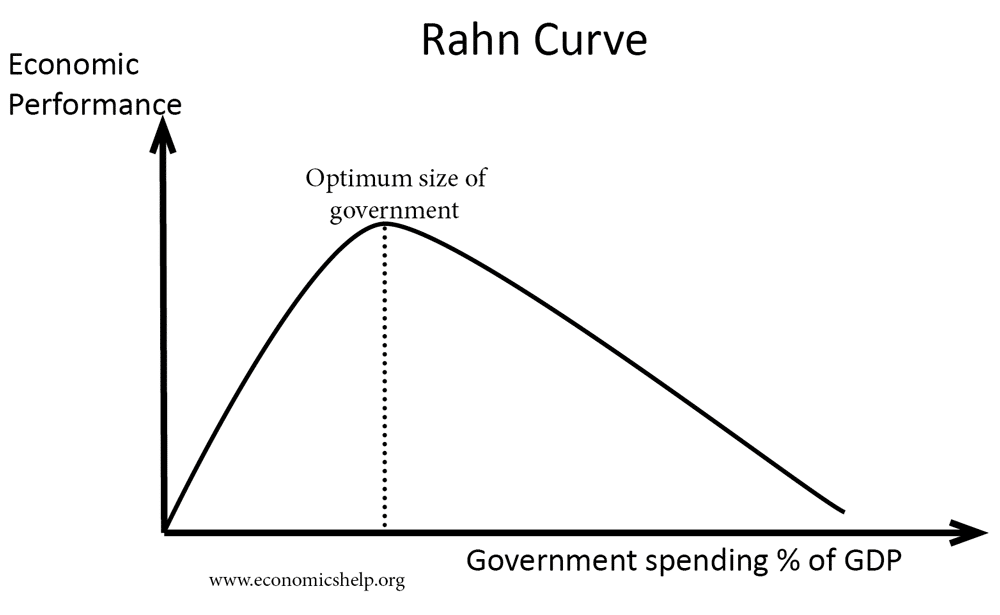
The fiscal multiplier effect occurs when an initial injection into the economy causes a bigger final increase in national income. Suppose the government pursued expansionary fiscal policy. The aim of expansionary fiscal policy is to increase aggregate demand (AD) and boost the rate of economic growth. This could involve the government increasing public sector investment …