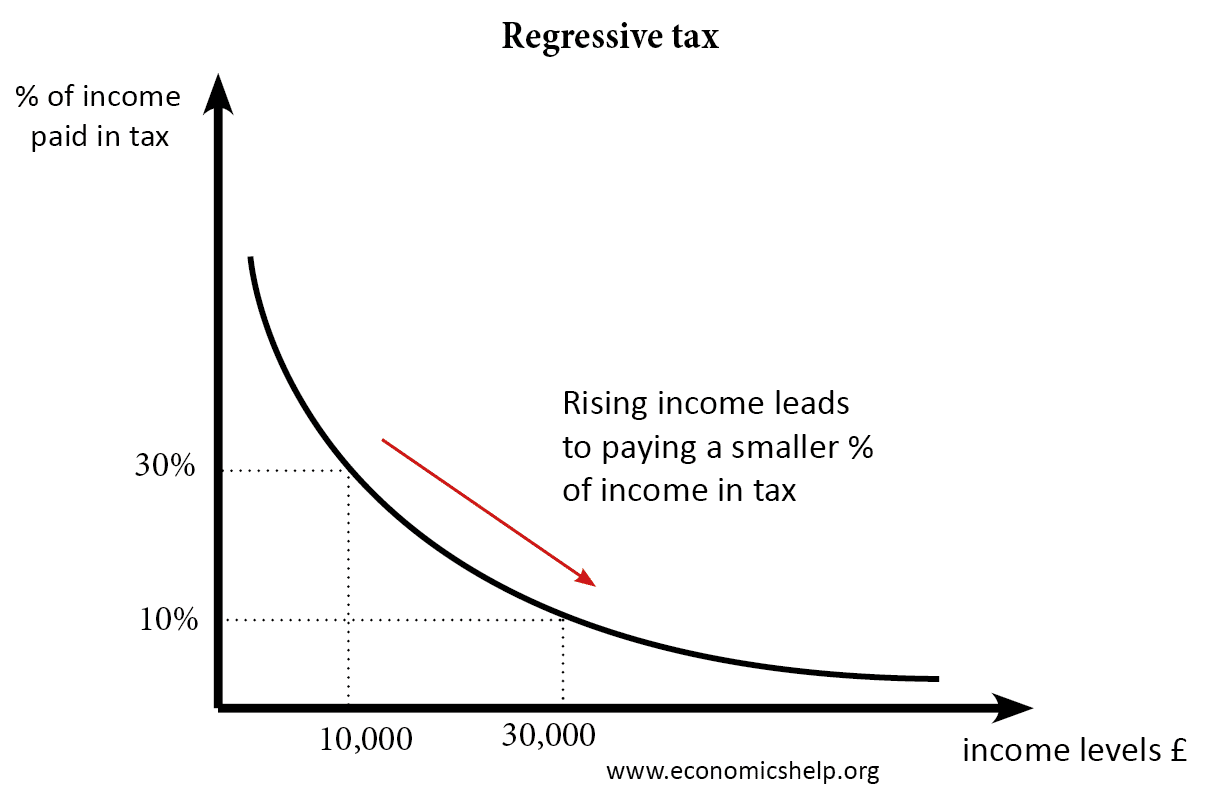
What is the difference between inflation and tax?
Readers question: What is the difference between tax and inflation? Tax is a way for the government to raise revenue. It includes charges placed by the government on goods/income. For example, VAT is a tax which means consumers have to pay an additional 20% of the price in the form of tax which goes to …