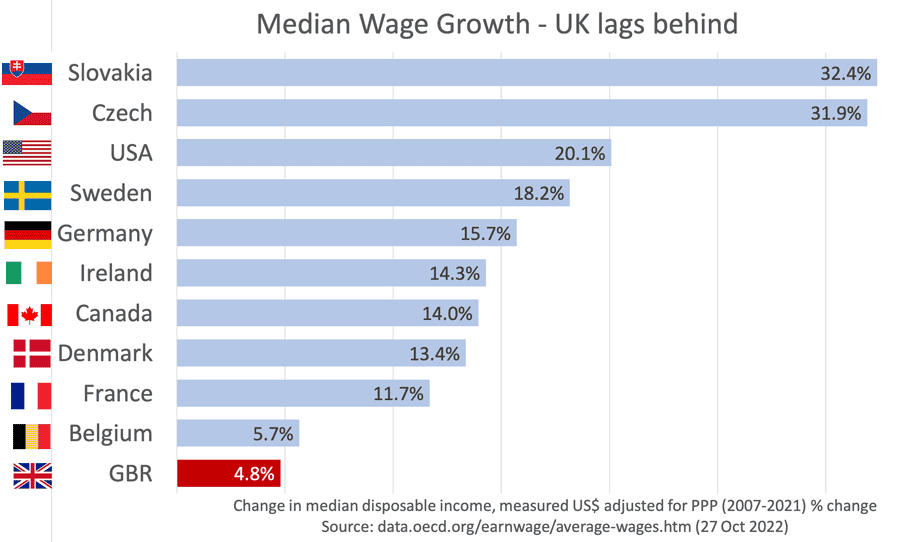
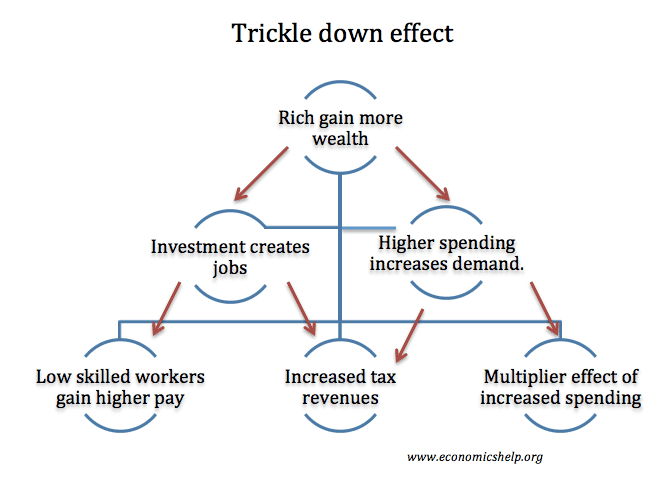
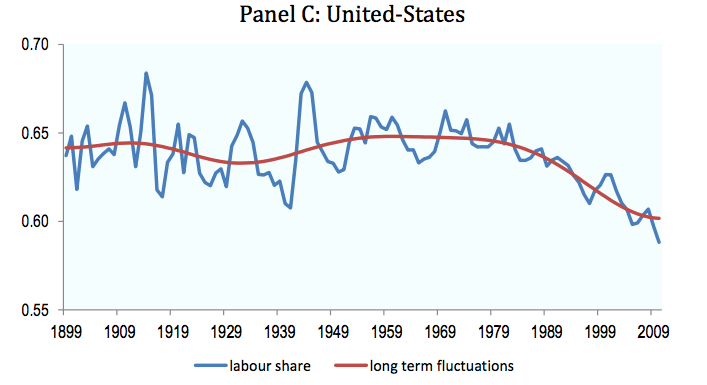
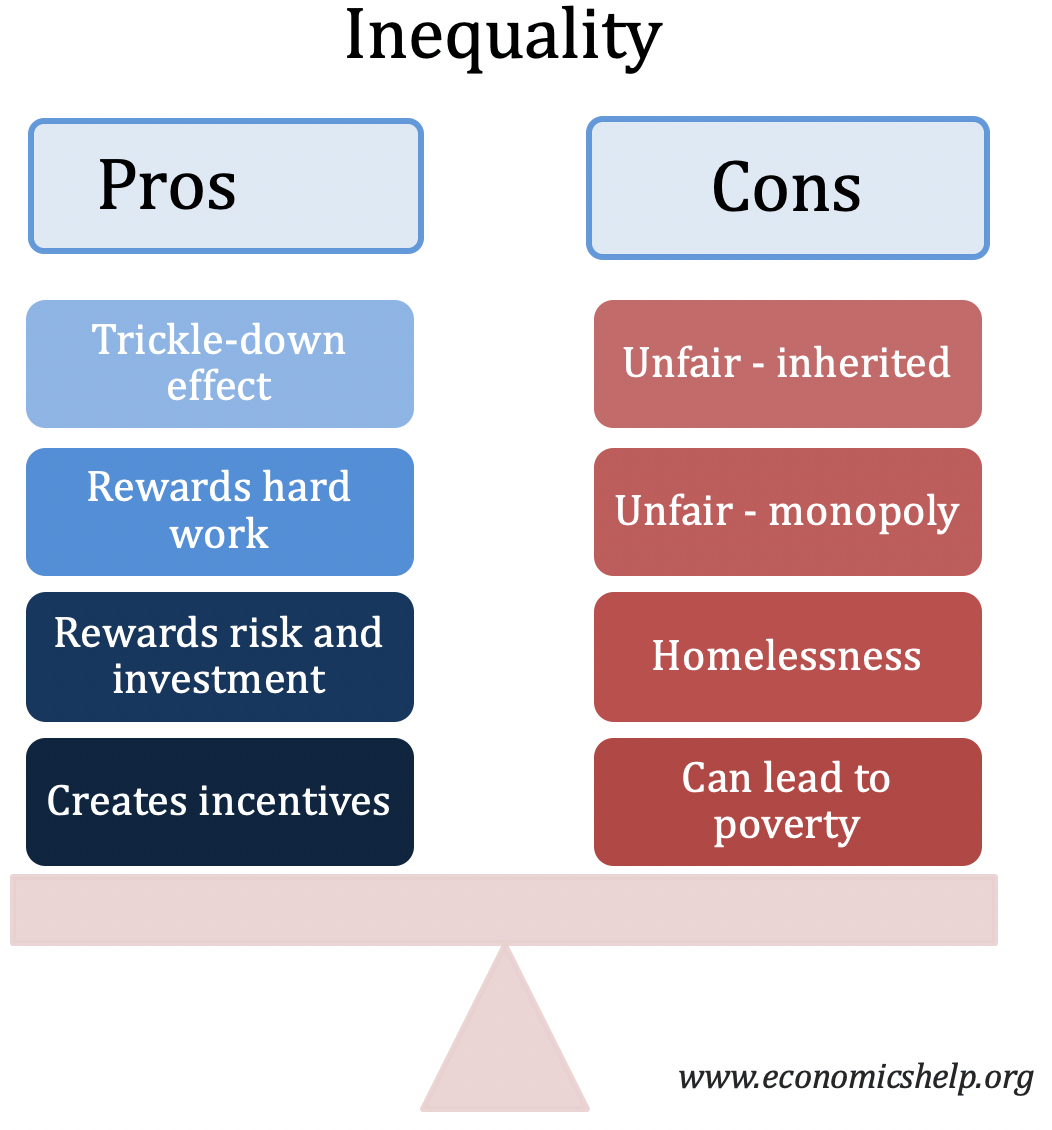
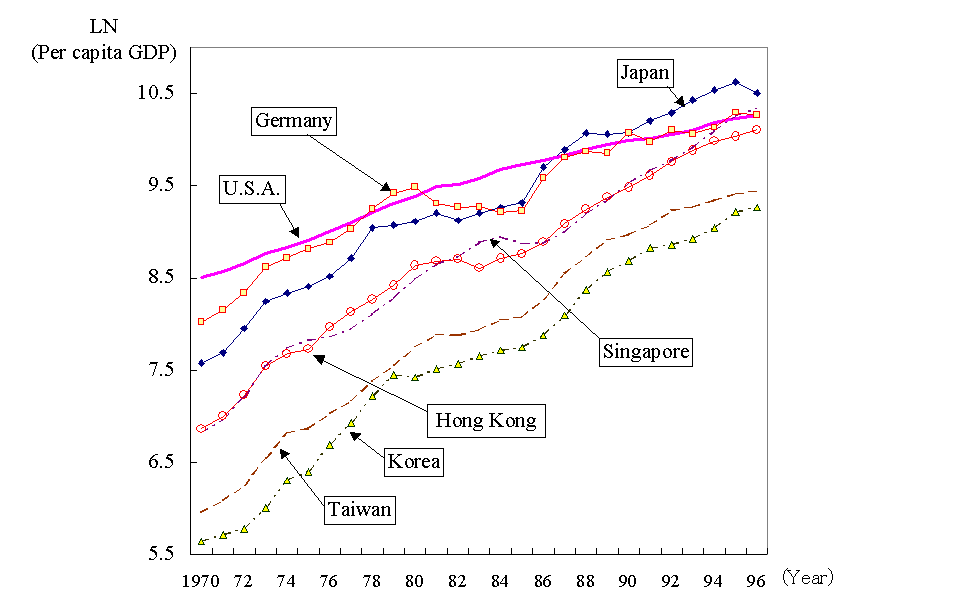
UK Economy’s long-term decline
Since the great financial crash of 2007, the UK economy has struggled. Although the past 15 years have been challenging from a global perspective, compared to many international competitors, the UK has slipped behind. Economic growth before global financial crisis of 2007-09 was 2.7%, the new normal is now closer to just 1.5% and with …