A tax is a charge levied by a government to raise revenue. The main types of taxes include
- Income tax – a percentage of income.
- Corporation tax – a percentage of a firm’s profit.
- Sales tax/VAT – an indirect tax on the sale of goods.
- Excise duties – taxes on alcohol, tobacco, petrol.
- Production taxes – taxes on particular goods/services, e.g. gambling tax, airlines, insurance.
- Environmental taxes – taxes on carbon, airports e.t.c.
- Stamp duty – tax on buying a house or shares.
- Tariff – this is a charge levied on the import of particular goods.
- Inheritance tax – a tax levied on the estate of a deceased person.
- Wealth tax – a tax levied on wealth, rather than income.
- Capital gains tax – a tax levied on an increase in the value of assets/wealth.
- Poll Tax – a tax on individuals. Introduced in UK as the “Community Charge”
- Windfall taxes – These are a type of corporation tax levied on companies making ‘excess’ profit. The UK introduced windfall tax on privatised industries. Also levelled on particular industries like north sea oil
- Council taxes – taxes collected by local government, could be a tax on property or local sales/income tax
Direct and indirect taxes
- A direct tax is a tax that a person or company pays directly. For example, income tax is taken out of your salary.
- An indirect tax is paid by a third party. For example, when you buy a TV, there is a VAT charge which is included in the price, the consumer does not pay, but the firm who sells the good is responsible for paying the tax to the government on your behalf.
Progressive, proportional and regressive taxes
- A progressive tax takes a higher percentage of tax from people with higher incomes.
- A proportional tax means different income levels pay the same % of income in tax.
- A regressive tax takes a higher percentage of tax from people with low income.
Advalorem vs specific tax
- An ad valorem tax is a certain percentage of the price of the good. VAT is levied at 20% so the more expensive the good is the more VAT that is paid.
- A specific tax is a fixed levy whatever the price of the good. For example, a £20 passenger levy on long-haul flights. This
Pigovian tax (or sin tax)
This is a tax that attempts to place a charge equal to the external cost of the tax. A Pigovian tax aims to make consumers pay the full social cost of the good. It was named after the economist Arthur Pigou, who contributed to the theory of externalities and social efficiency.
Diagram of Pigovian tax
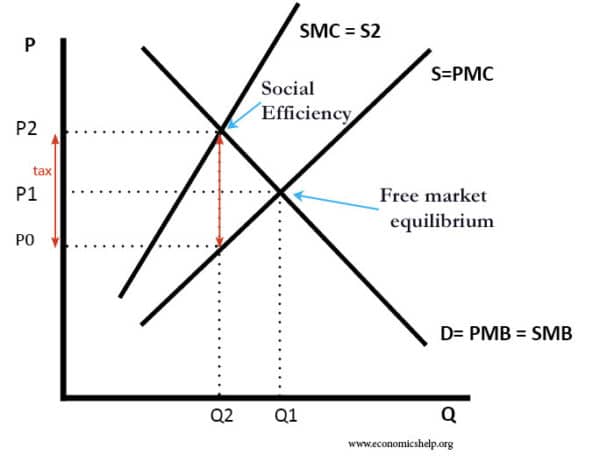
- For example, if a flight costs £200, but the external cost of flying is estimated at £150, then the tax will also be £150. So the final price will be £350.
- Examples of Pigovian taxes include alcohol tax, tobacco tax and tax on sugar. For this reason, in popular terminology, they are often referred to as a ‘sin’ tax because they refer to goods that we often feel guilty for consuming. Though the principle of Pigovian taxes is not morality but social efficiency.
Income tax
Income tax is a common form of tax which takes a percentage of income. Income tax makes use of the concept of marginal tax rates
For example, if the income tax threshold is £5,000 – this means you don’t pay any income tax on the first £5,000. If the basic rate of income tax is 20%. It means someone earning £6,000 only pays tax on the £1,000 above the threshold. They will pay £200 or 3.3% of their income in tax
- Income tax rates explained.
Different Types of Tax
- Carbon Tax – taxing the emission of carbon
- Cigarette Tax – tax on tobacco
- Death Tax – tax on the deceased.
- Fat Tax – tax on unhealthy food
- Petrol tax – tax on petrol
- Plastic bag – tax on plastic bags
- Poll Tax – tax on individuals
- Rubbish tax – tax on rubbish
- Tobin Tax – a specific tax placed on currency transactions.
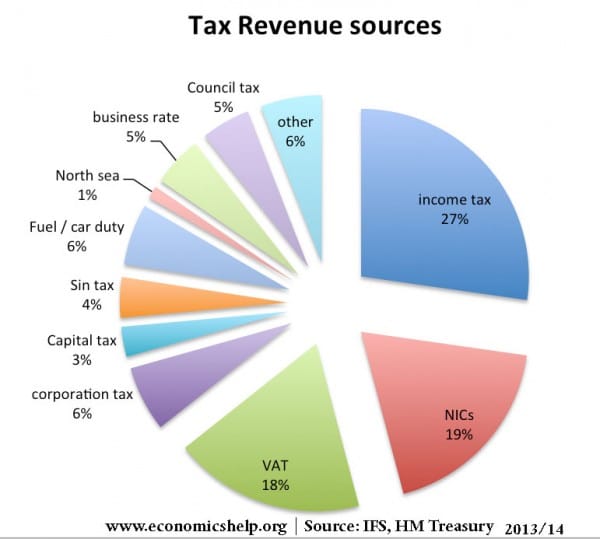
Examples of taxes in the UK
NICs is national insurance contributions. This is effectively a form of income tax.
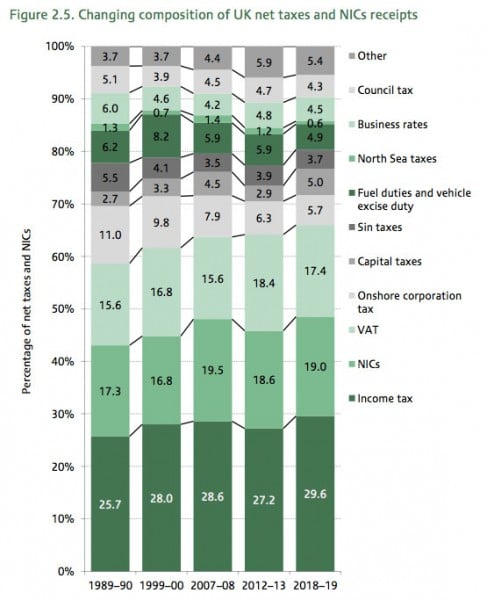
How tax revenue can change
Tax on production in UK
The UK publishes data on particular production taxes. Some of the tax revenue raised is very small.
- Aggregates levy
- Air passenger duty
- Apprenticeship Levy
- Air Travel Organisers Licence (ATOL)
- Betting, gaming & lottery
- British Transport Police
- Climate change levy
- Camelot payments to National Lottery Distribution Fund (NLDF)
- Driver and Vehicle Licensing Agency (DVLA) new car registration fees
- Environmental levies
- EU Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS) auction receipts
- Immigration skills charge
- Insurance premium tax
- Landfill tax
- Levy funded bodies receipts
- Lighthouse dues (tax on ships in UK waters to pay for lighthouses)
- Rail franchise premia
- Companies House – Registration Tax
- Land Registry – Registration of Title tax
- Pension Protection Fund Levy
- Soft drinks industry levy
- From: UK Public sector accounts Dec 2019
(I never knew there was a tax on ships to pay for lighthouses)
Proposed taxes
- Progressive consumption taxes – making VAT more progressive by setting higher rates on big, expensive luxury items
- Tobin tax is the name given to a specific tax placed on currency transactions.
- Turnover tax – tax on multinational companies who have high turnover but profit is kept in tax havens.
Obscure taxes through history
- Beard tax In 1705, Russian Emperor Peter the Great placed a tax on beards. He hoped Russian men to become clean-shaven like western Europe.
- Scutage – a tax that allowed English knights to avoid fighting – just pay a tax to the king.
- Playing card tax – In the UK there was specific tax on playing cards from 1710 until 1960.
- Window tax. In the UK, a tax was imposed in 1696 on the number of windows in a house. It led to houses being built without windows – which led to health problems.
- Tax on the aromatic powders put on wigs. In 1795 this tax was imposed and it led to a decline in use of wigs. They fell out of fashion.
Concepts related to tax
- Tax avoidance and tax evasion
- Tax cuts – essay on pros and cons of tax cuts
- Deadweight weflare loss of tax
- Tax in UK
- Tax tolerance
- Tax rates by country
- Tax and wealth
- Fiscal drag
- Hidden taxes

helpful
Superb