A look behind the causes and consequences of the economic crisis, and why it has been difficult to solve.
Background to Economic Crisis
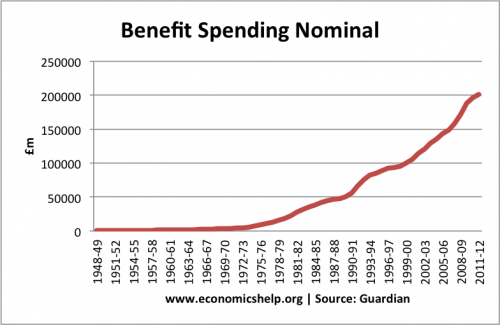
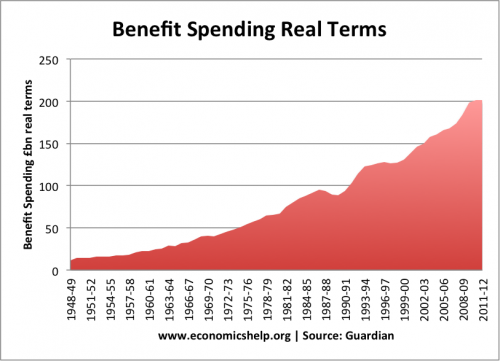
The 1990s and early 2000s was a period of economic prosperity – Low inflation and high economic growth gave an impression of economic stability, but in other areas of the economy there were signs of boom and bust.
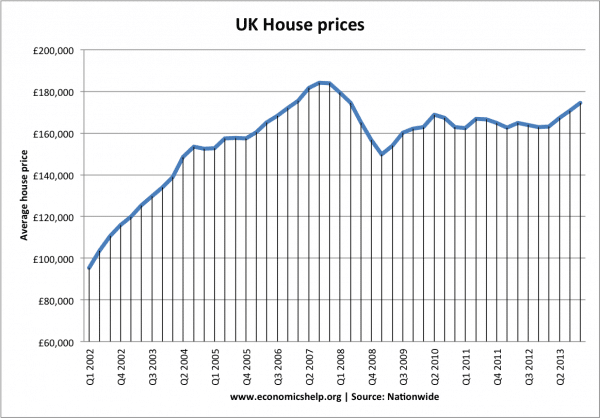
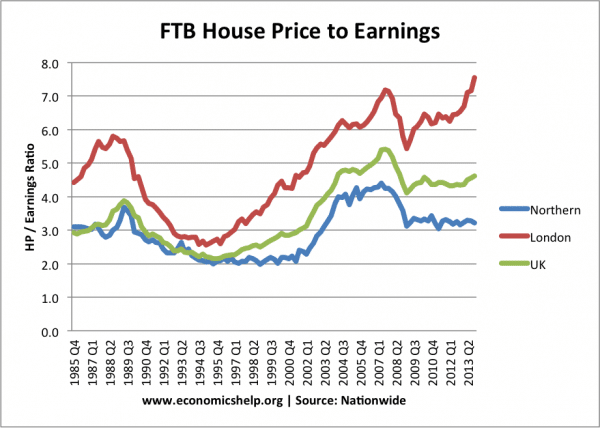
- Housing Bubble. In US and European countries, there was a rapid rise in house prices, which caused a boom in house building and bank lending. In the US, the housing bubble was helped by a boom in mortgage lending. Banks began lending mortgages to people with little regard for their ability to pay back. (housing boom and bust)
- Bank Lending Bubble. In the bubble years, banks became more aggressive in lending. They would borrow money on money markets to be able to lend more profitable mortgages. Banks became highly leveraged – high amount of debt to assets (deposits) This left them vulnerable to a downturn in the economy.
- Growth Financial derivatives. The financial boom was helped by a new range of financial derivatives, such as credit default swaps and CDOs. These enabled mortgage companies to sell on their mortgage debt to other banks around the world. This enabled mortgage companies to finance a larger range of new loans.
- See also: Understanding financial crisis
- See also: What went wrong with US economy
Credit Crisis
- From around 2006, US homeowners started to default on their mortgage because of a modest rise in interest rates. House prices started falling. Therefore, banks and mortgage companies started to lose money on their mortgage debt.
- Because of mortgage defaults in the US, banks around the world started losing money and stopped lending to each other.
- Full explanation of understanding credit crunch in 22 steps.
Economic Recession
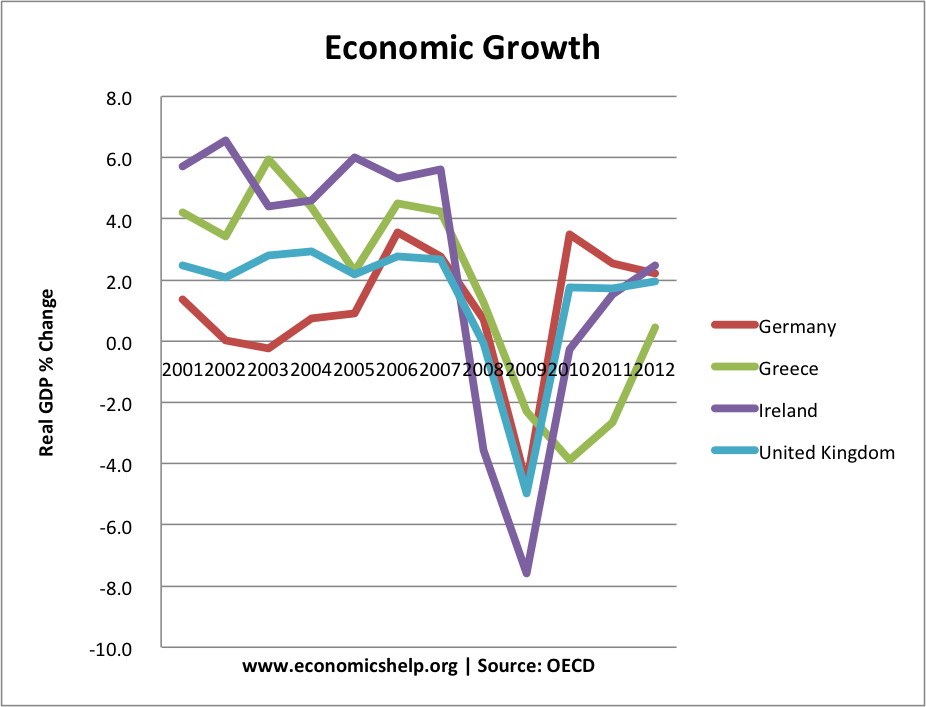
- The credit crunch led to a fall in bank lending. This led to a decline in investment and lower consumer spending.
- Also confidence was badly affected by news of bank failures. Consumers became more risk averse and sought to pay off debts rather than spend.
- Falling house prices also led to a negative wealth effect and lower spending.
- In 2008, rising oil prices also led to falling living standards, though this was quite minor.
- The scale of bank losses were very high so there was a substantial fall in lending.
- Despite cuts in interest rates, and expansionary fiscal policy, consumers were reluctant to spend because they were highly indebted. Also, despite low-interest rates, banks didn’t or couldn’t lend because they were short of cash.
- This could be caused a ‘balance sheet recession’ which tends to be longer lasting.
- See: causes of recession, with video on 2008/09 recession