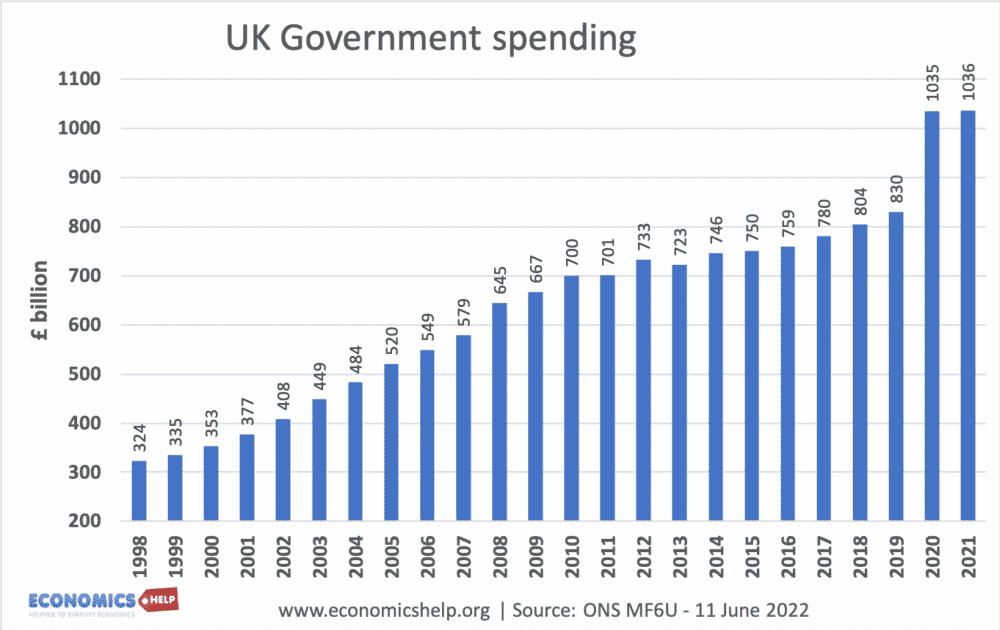
Source: ONS MF6U
UK government spending passed over £1 trillion in 2020 due to the extra spending measures of the Covid Pandemic.
Total spending compared to Nominal GDP
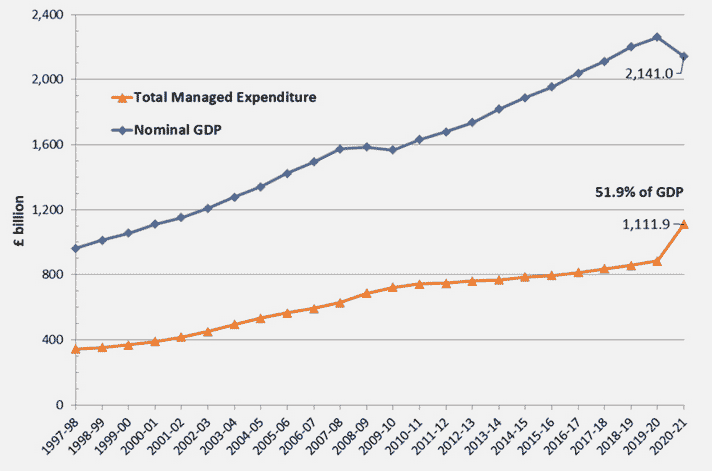
Source: HMT public spending statistics (May 2022)
The rise in spending 2020-21, also combined with a fall in GDP
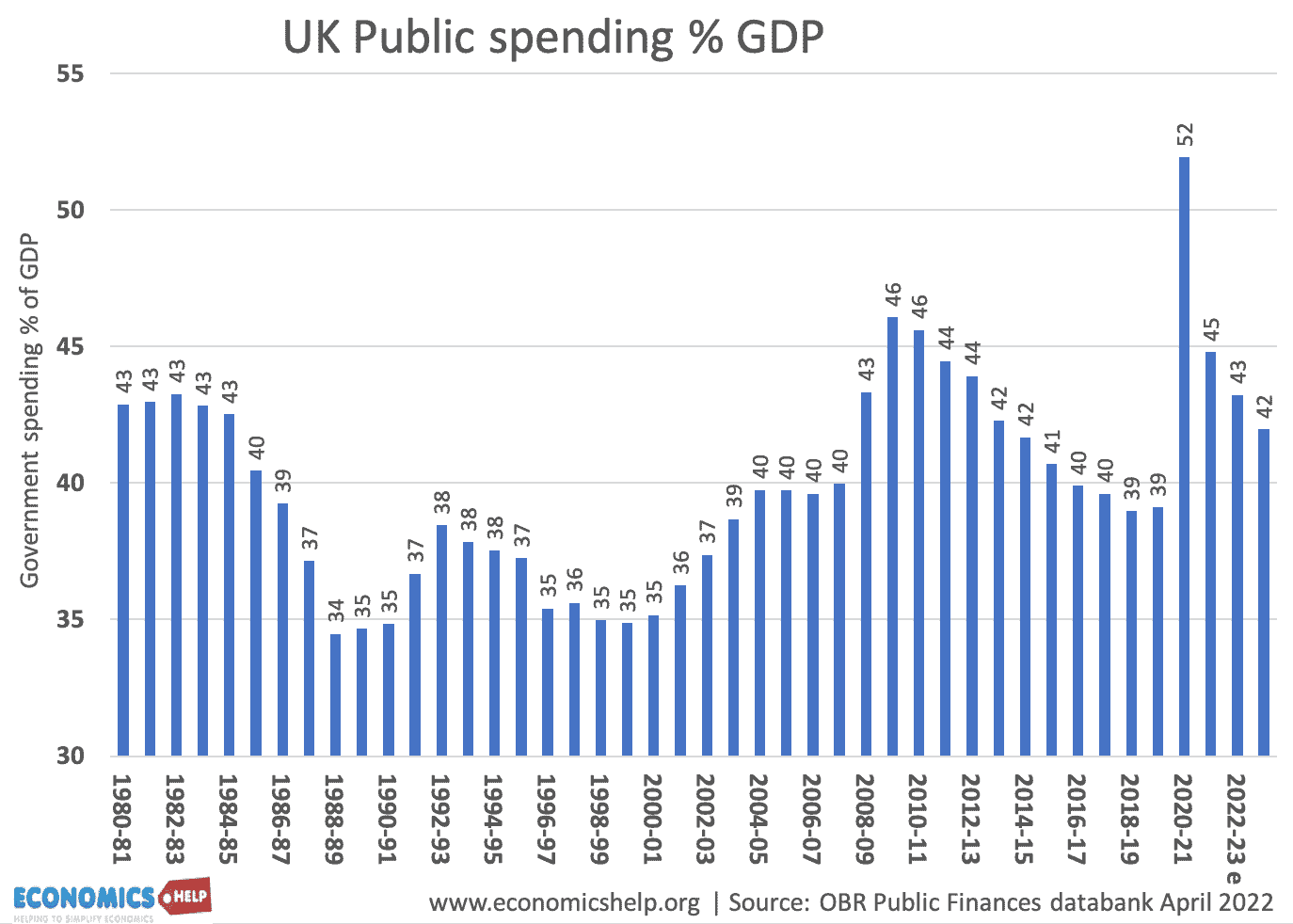
UK Public spending as % of GDP
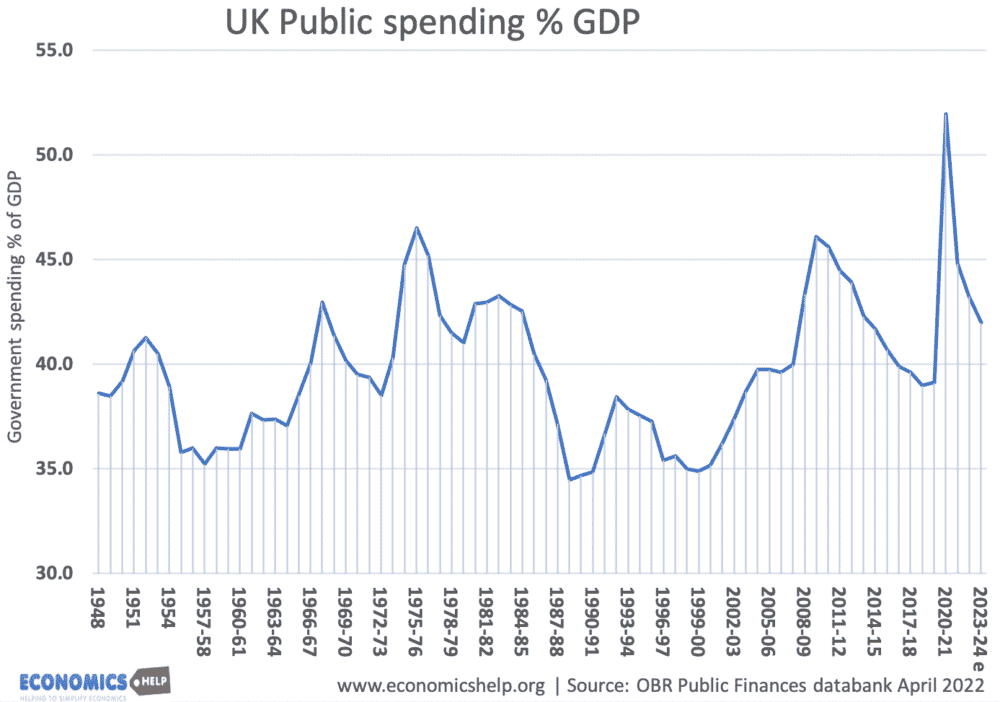
Source: OBR (April 2022)
In 2000-01, several years of government spending restraint combined with rising economic growth, saw government spending shrink to under 35% of GDP. Between 2001 and 2007-08, spending rose to over 40% of GDP due to sustained increases in spending on health, education and welfare spending.
In 2007/08 the financial crisis and subsequent recession led to higher spending as ratio of GDP – even though the new Conservative government pursued austerity and sought to cut government spending or limit spending in many areas.
Real term trends in public spending
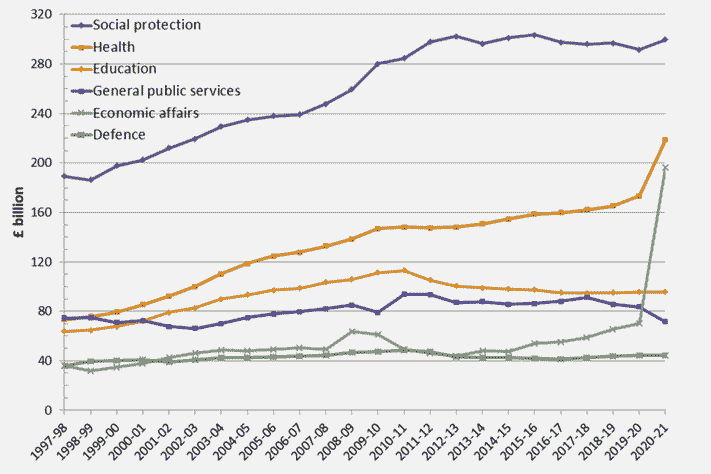
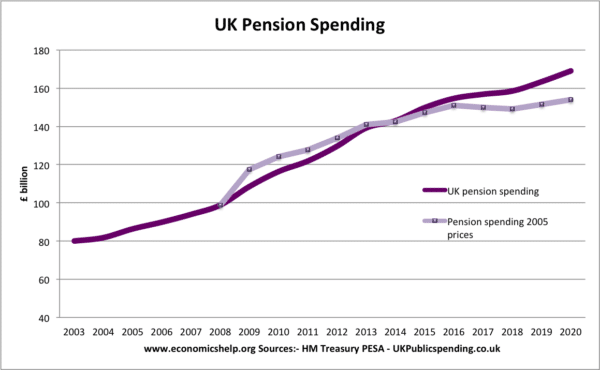
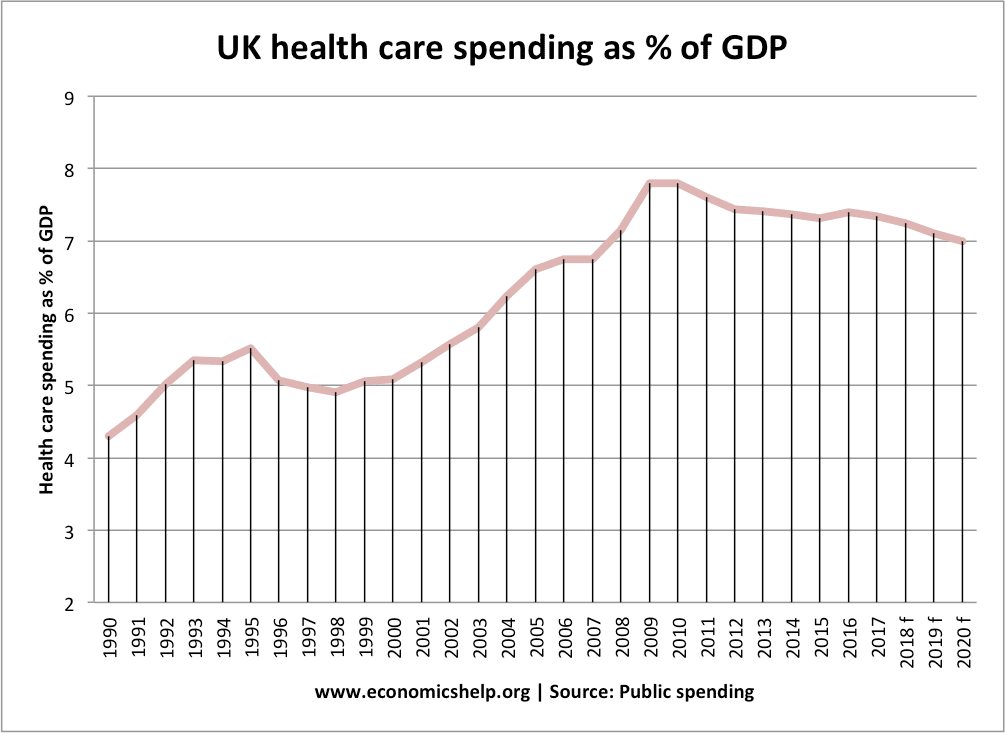
Health care has been the biggest source of growth since 2010. Social protection, which includes pensions has been flatter since 2010 because of low real income increases in welfare benefits.
Source HMT Public spending statistics (May 2022) UK Pension spending
More details on pension spending.
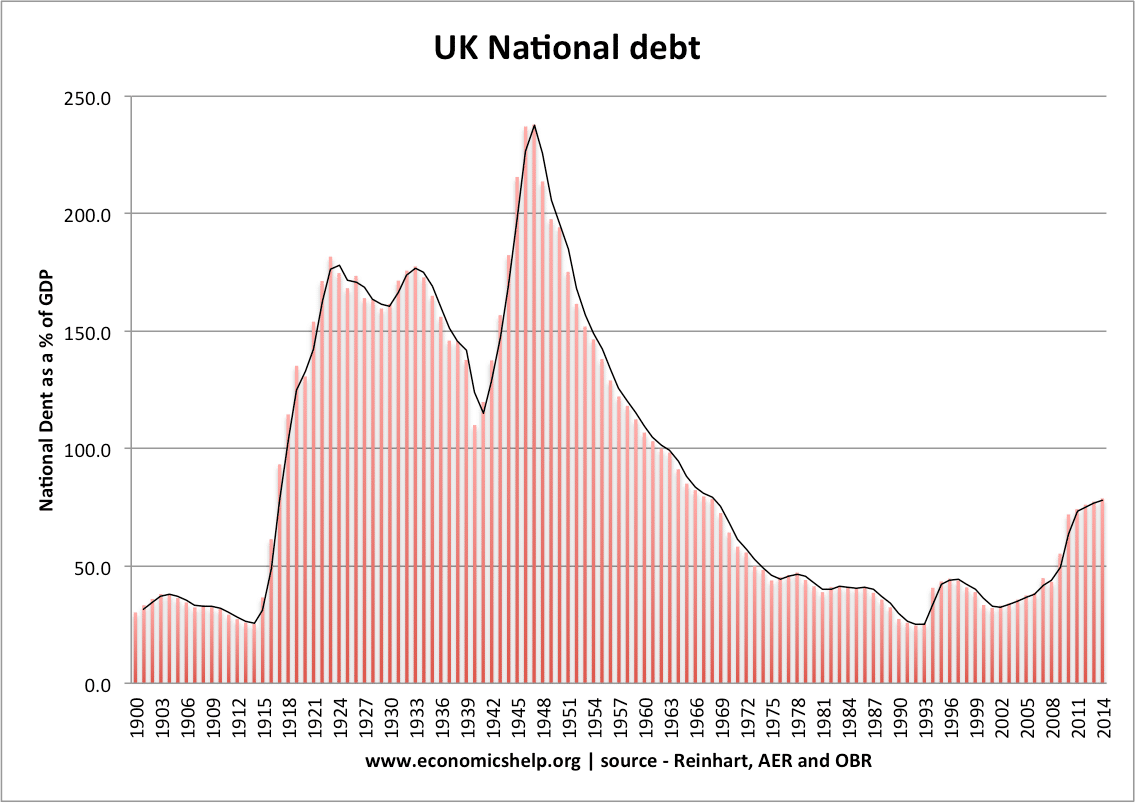
Government borrowing
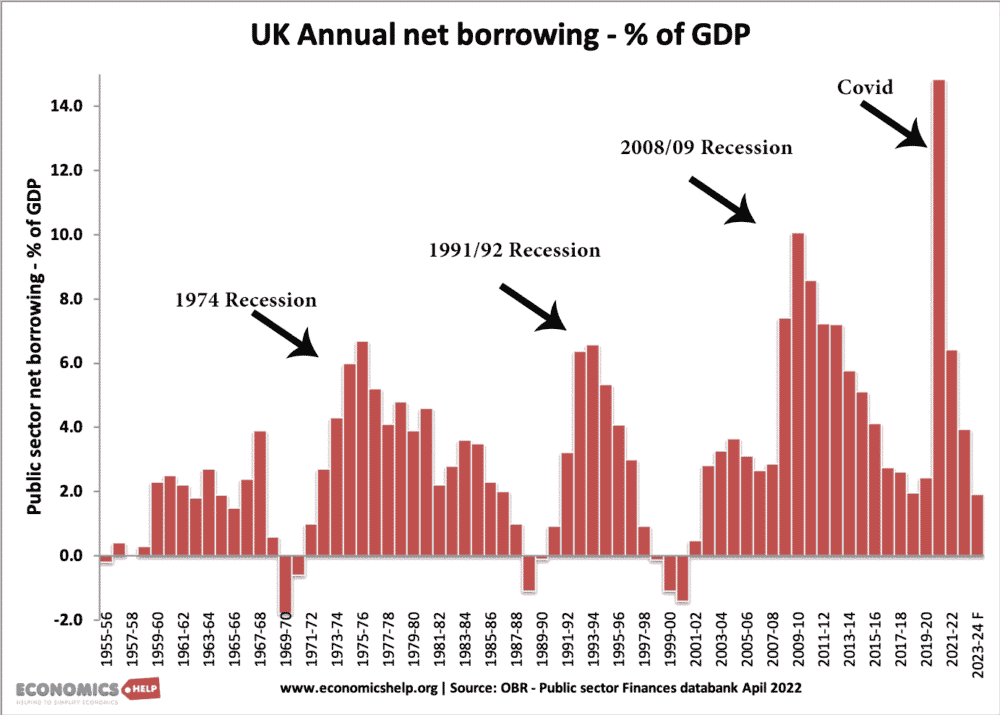
This shows recent government borrowing. As expected in a recession, borrowing peaks.
- More on Government net borrowing here
Background to government spending
- Between 2008-09 and 2009-10, the UK saw a large drop in real GDP of 6%, but due to automatic stabilisers government spending increased (e.g. higher unemployment benefits). This caused government spending as % of GDP to rise to 47%.
- Government spending as % of GDP is forecast to fall closer to 40% of GDP by 2016-17 (if growth targets are met)