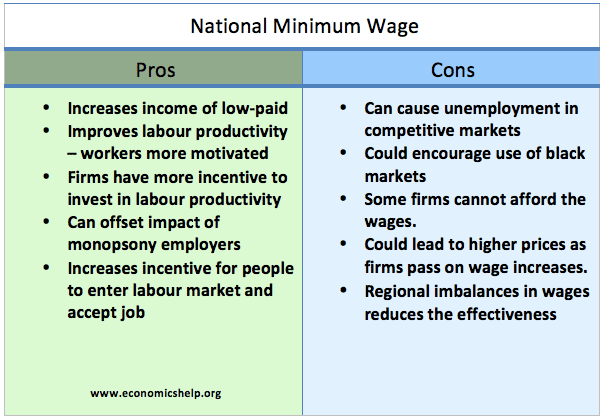
Adjusting to oil price shocks
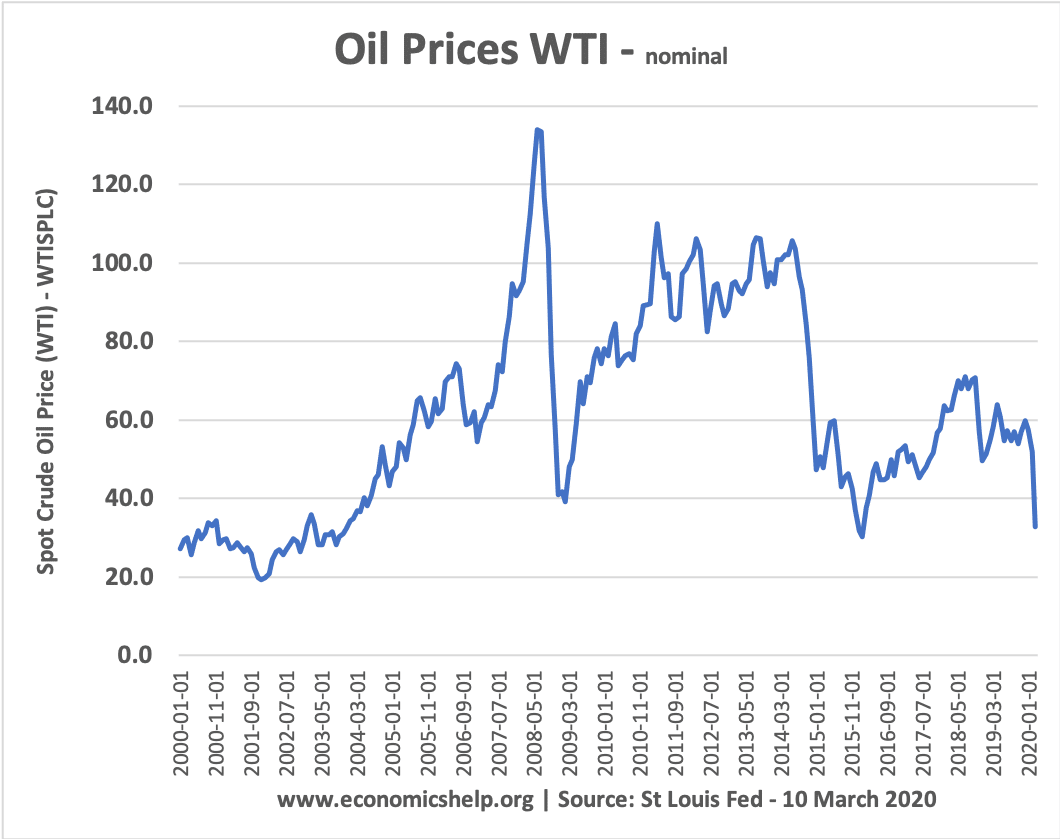
Oil prices tend to be volatile for a few reasons. Demand varies with the economic cycle. Changes in the price of oil can be magnified by speculators who buy forward contracts Supply is quite inelastic in the short-term. Therefore, a small change in demand can have a significant impact on the price. Firms and consumers …